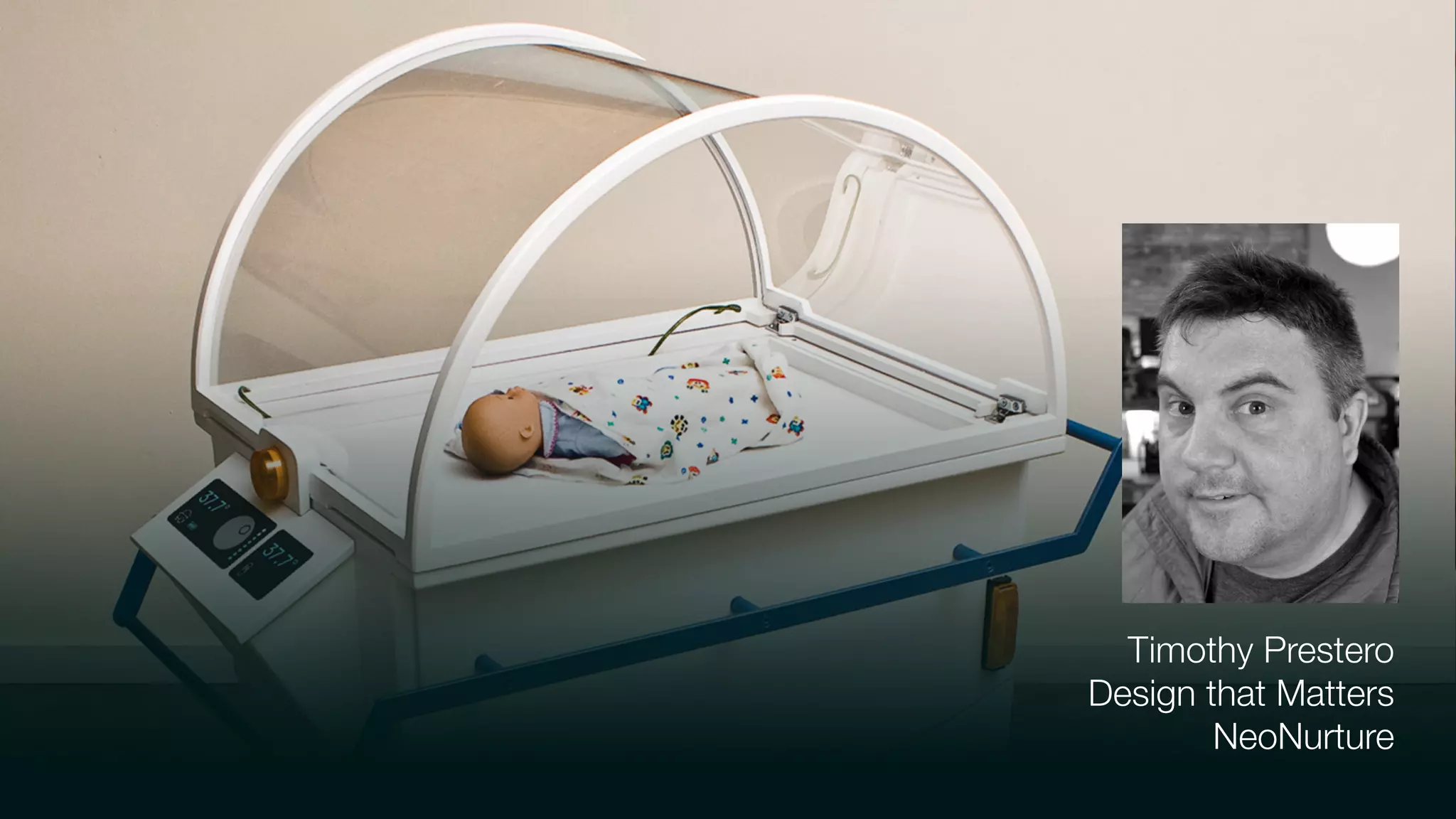
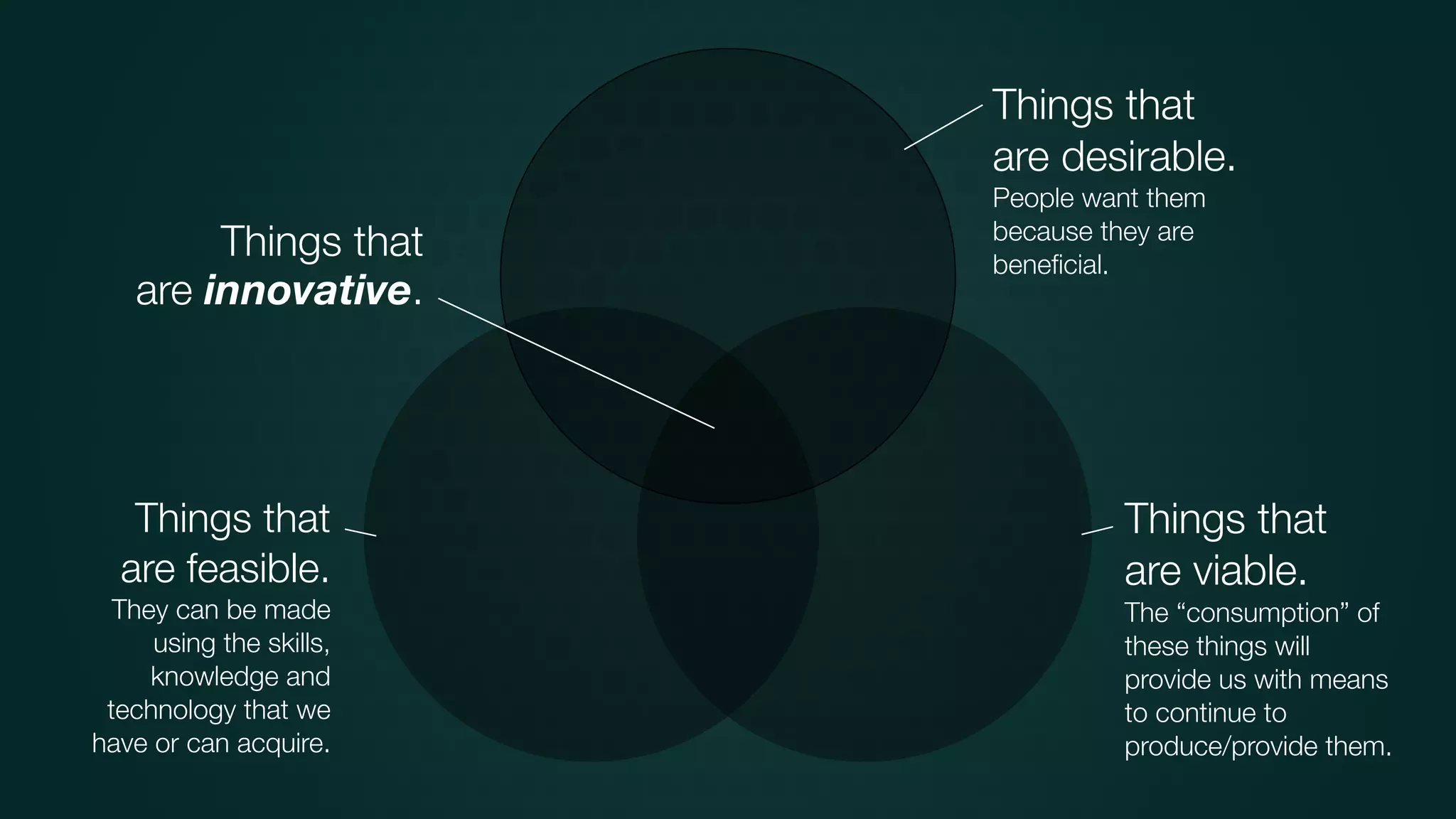
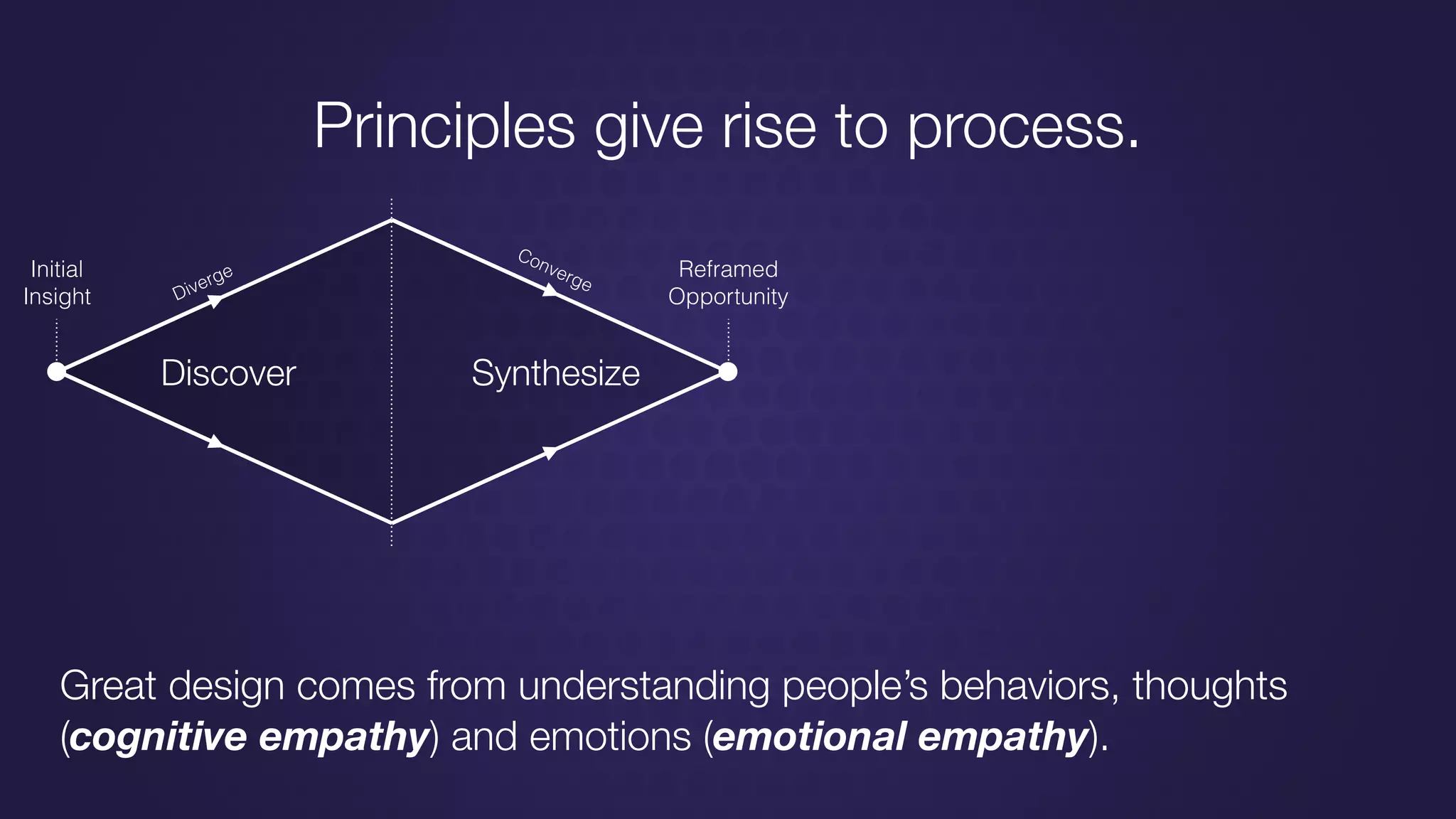
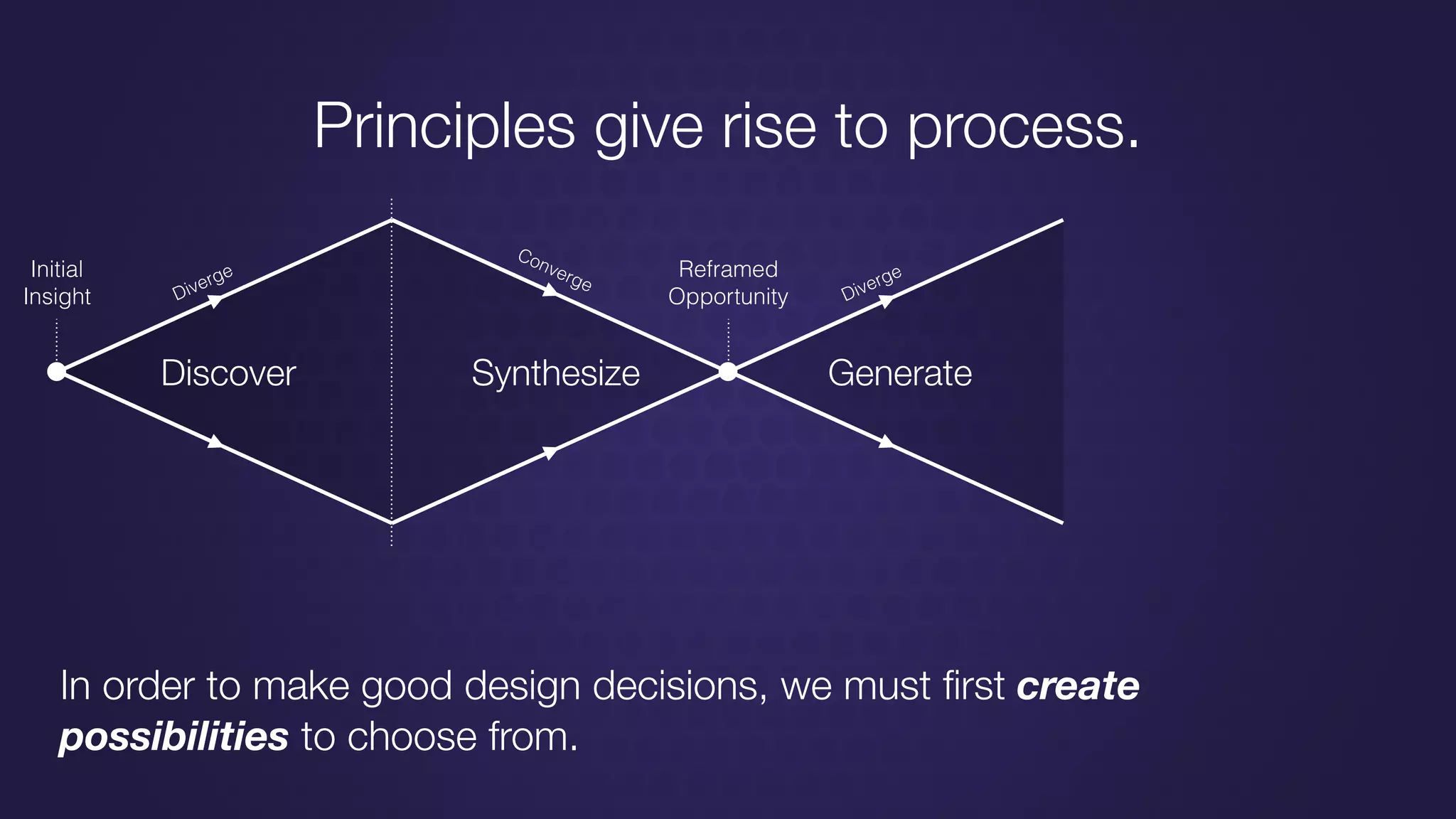
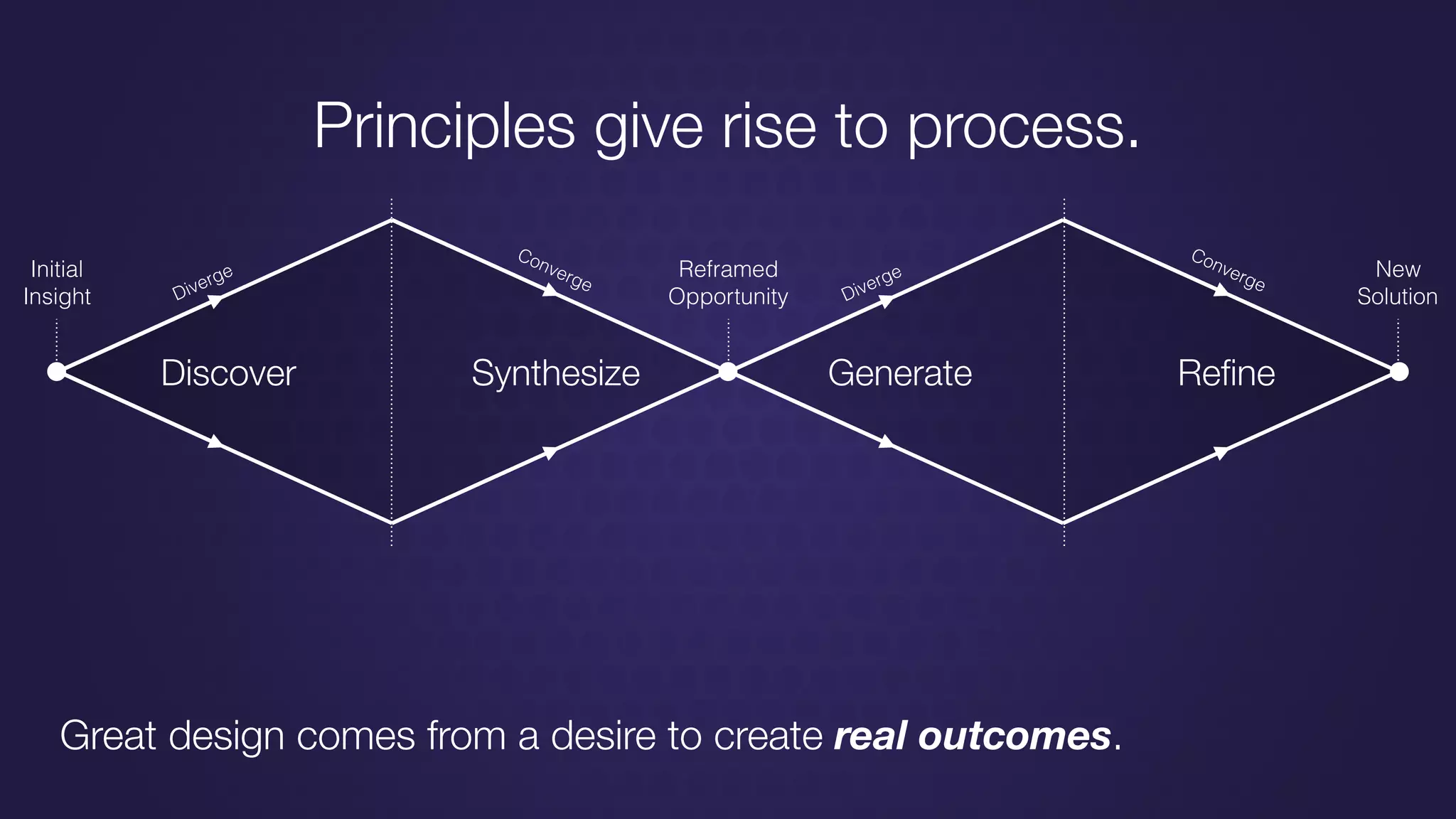
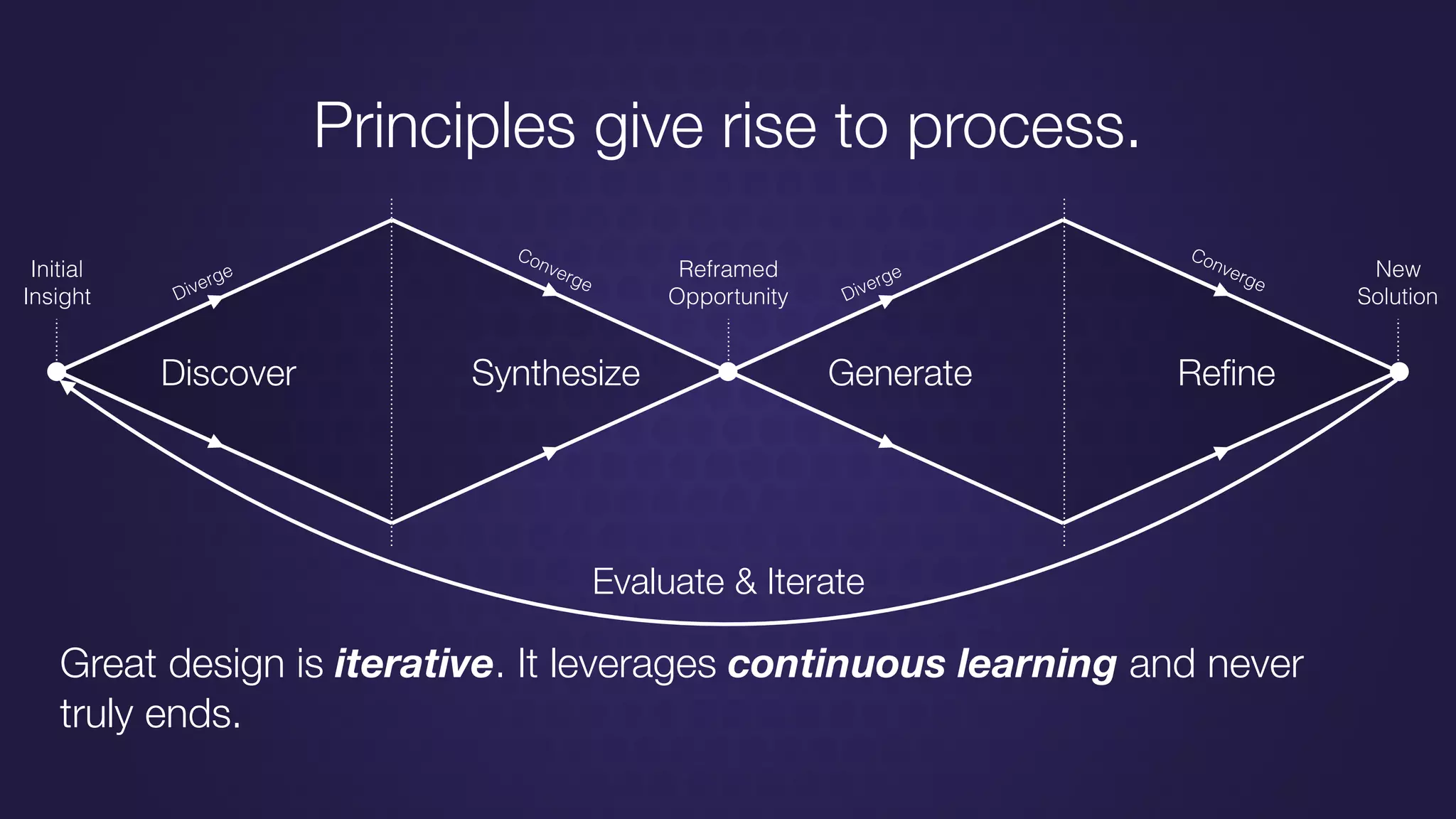
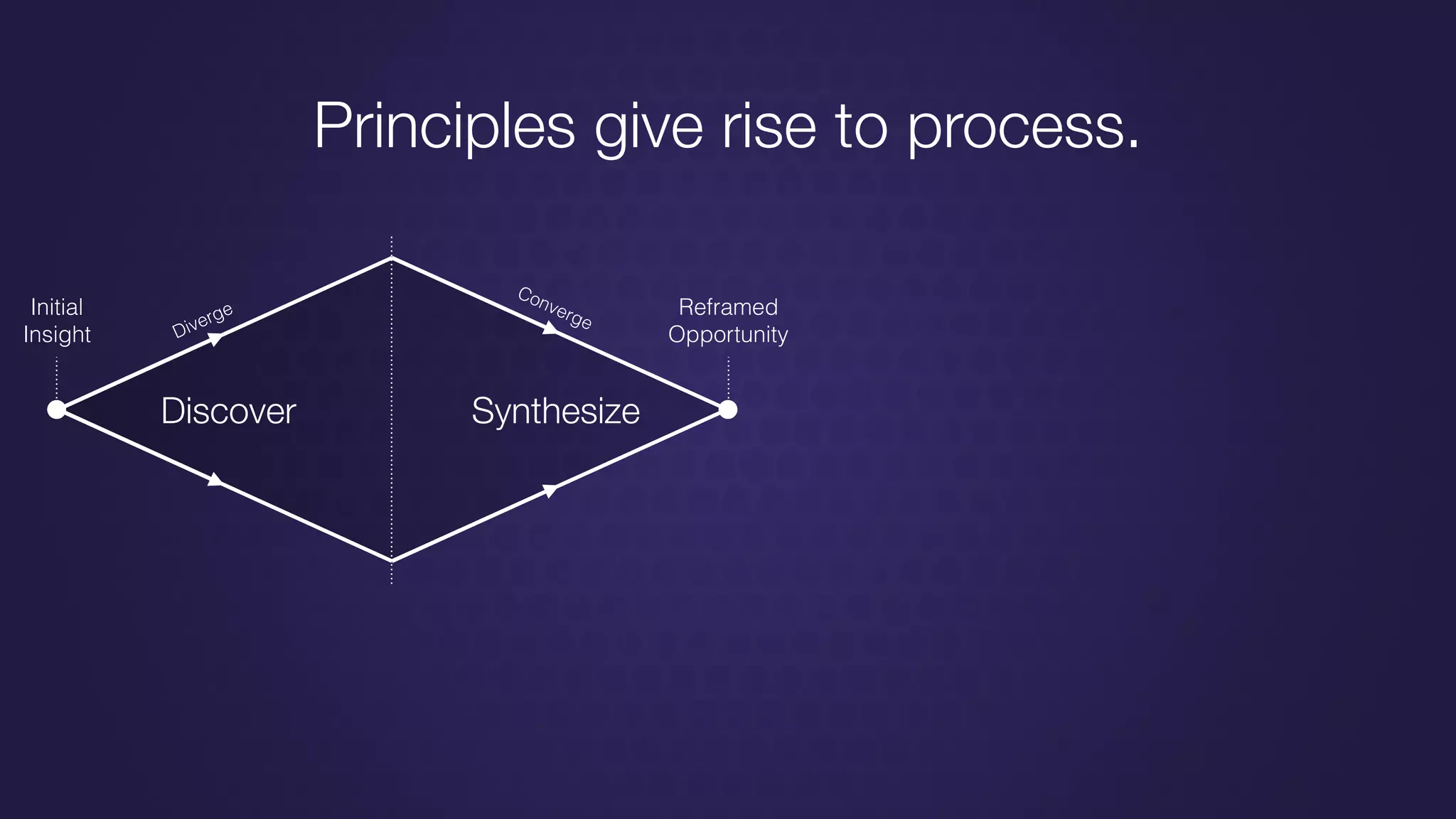
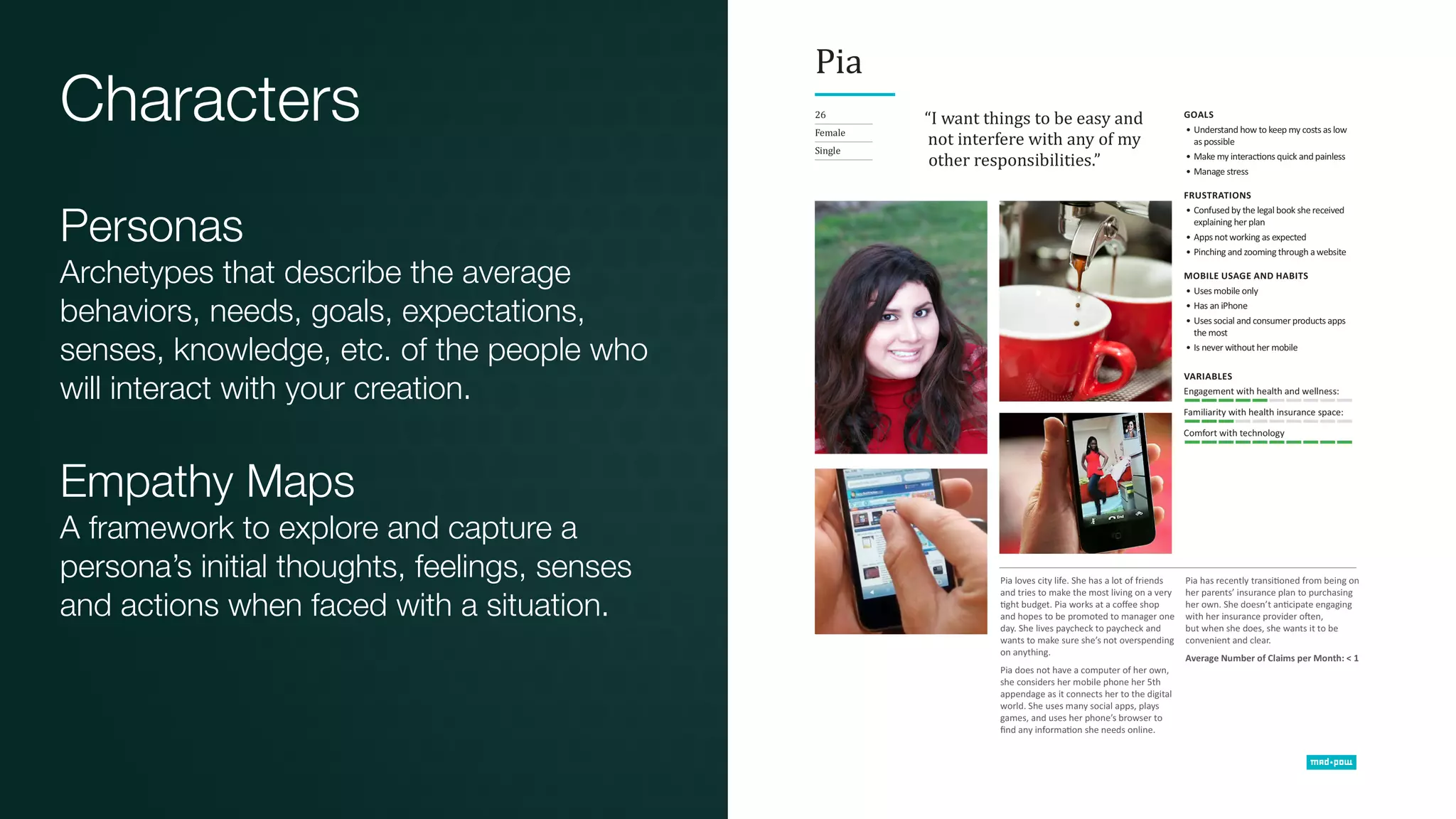
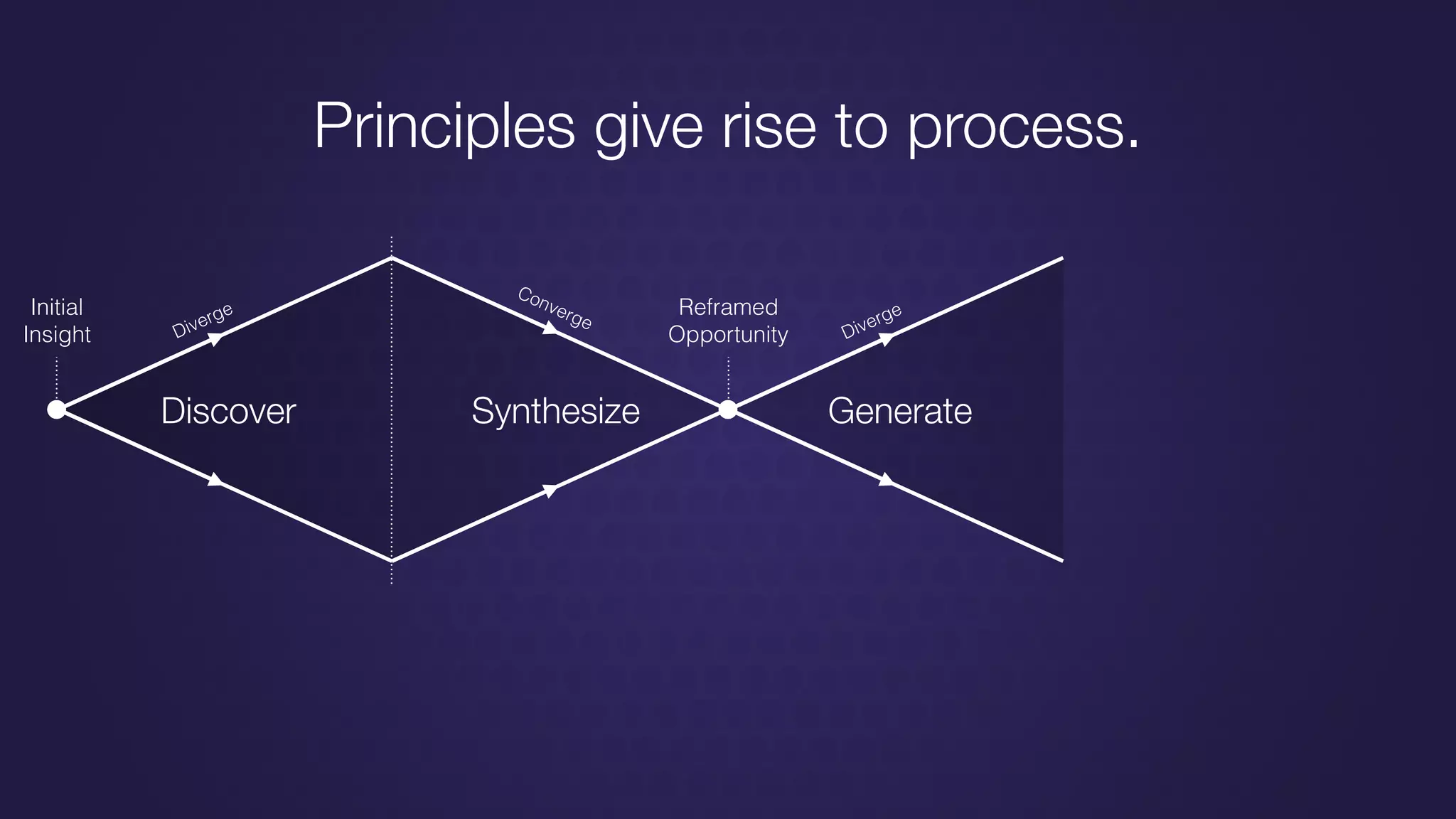
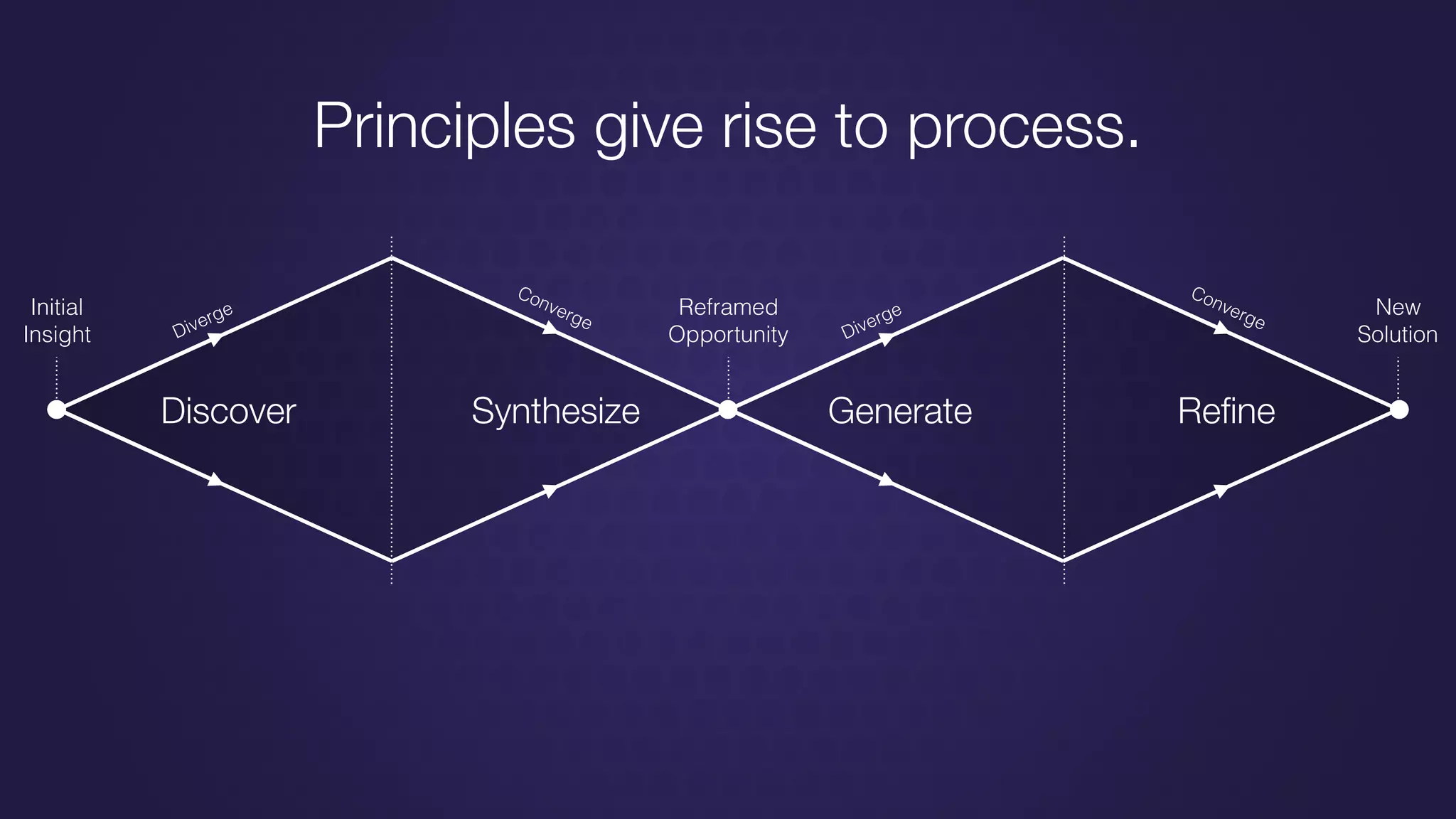
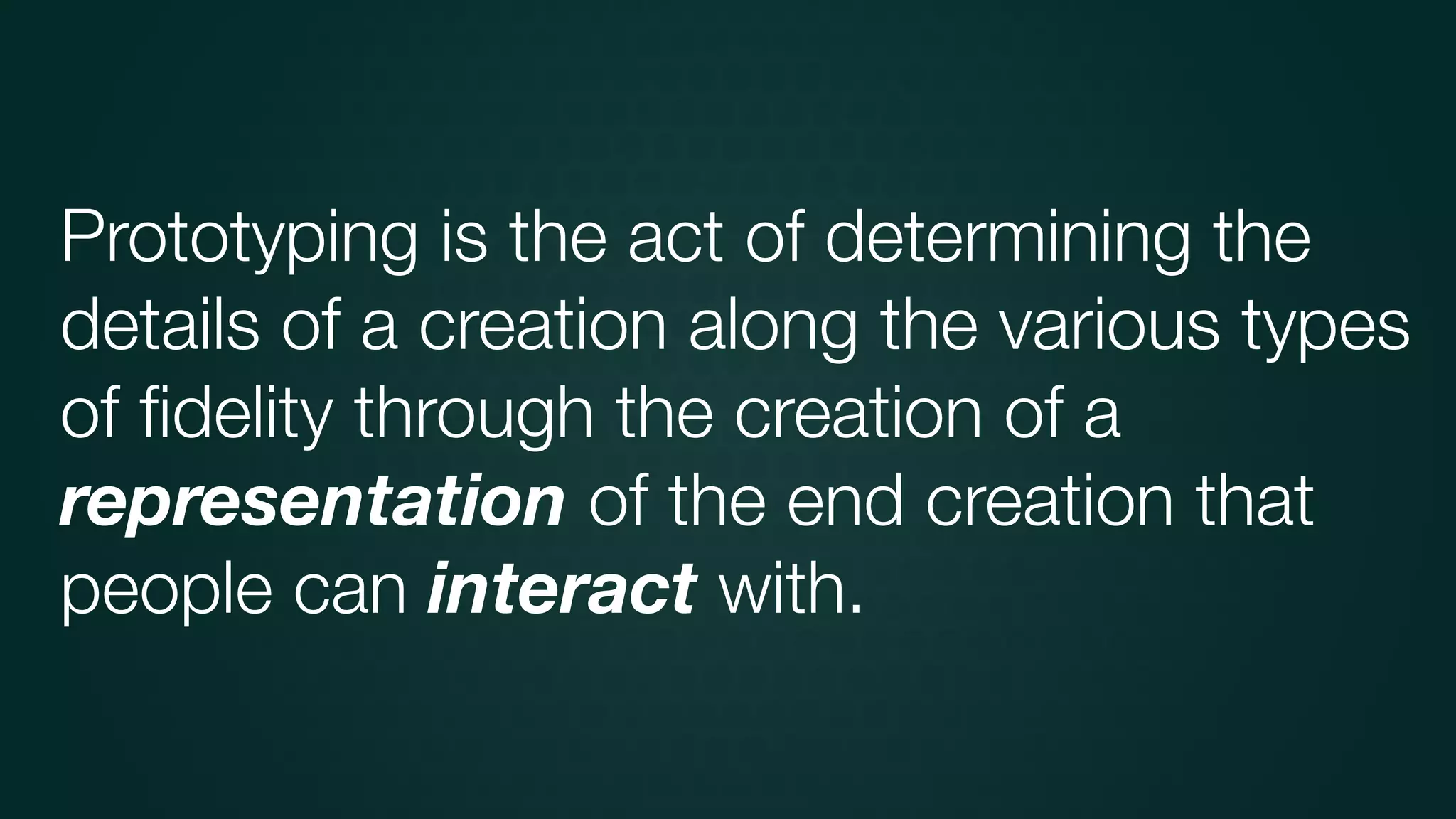
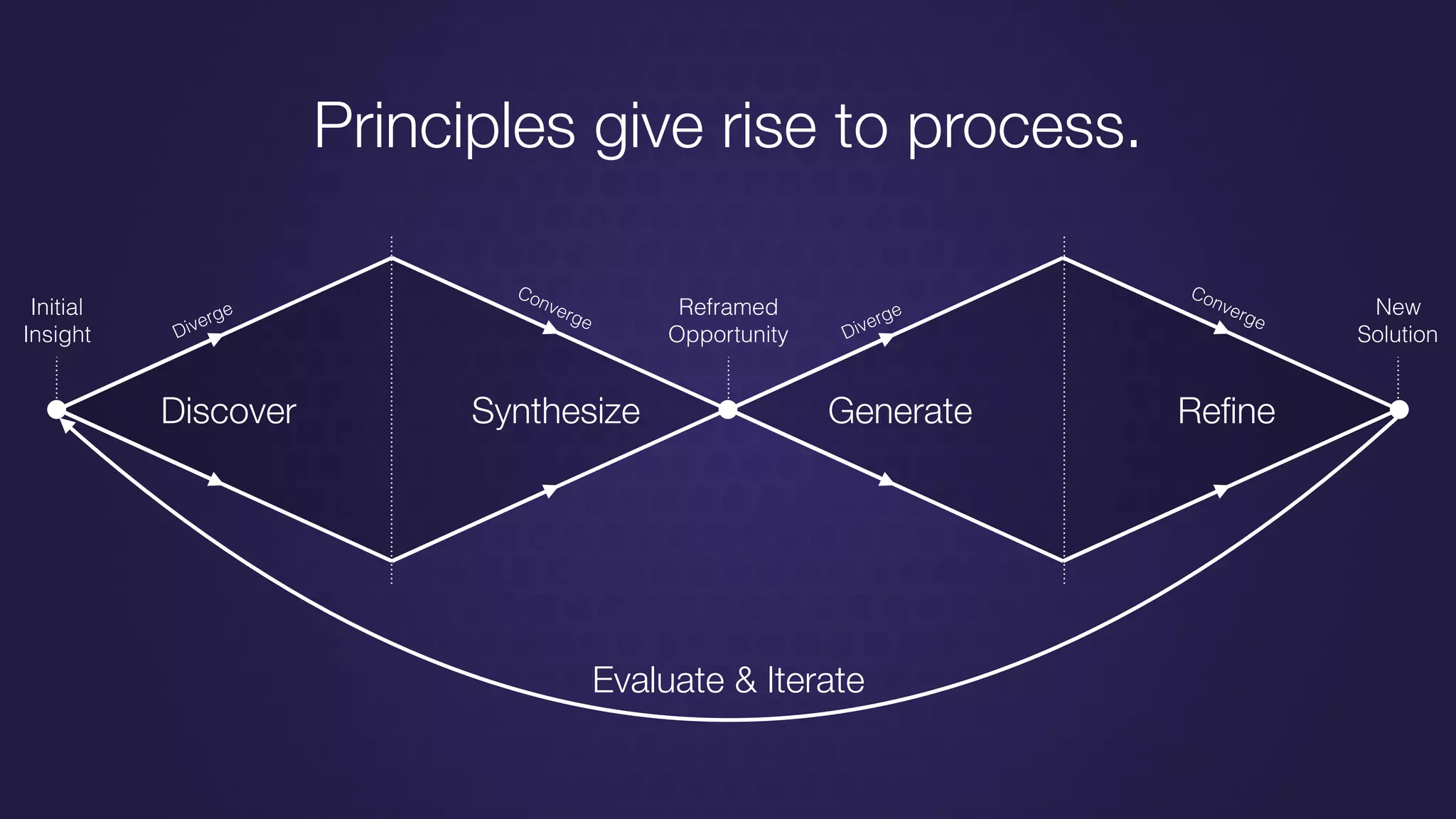
The document discusses design thinking in healthcare, emphasizing the importance of understanding human needs and behaviors to create desirable, feasible, and viable solutions. It outlines principles of design thinking, such as human-centricity, empathy, and the iterative nature of design processes that involve generating and refining ideas. Additionally, it highlights the significance of collaboration, prototyping, and critique in fostering innovation and effective problem-solving.