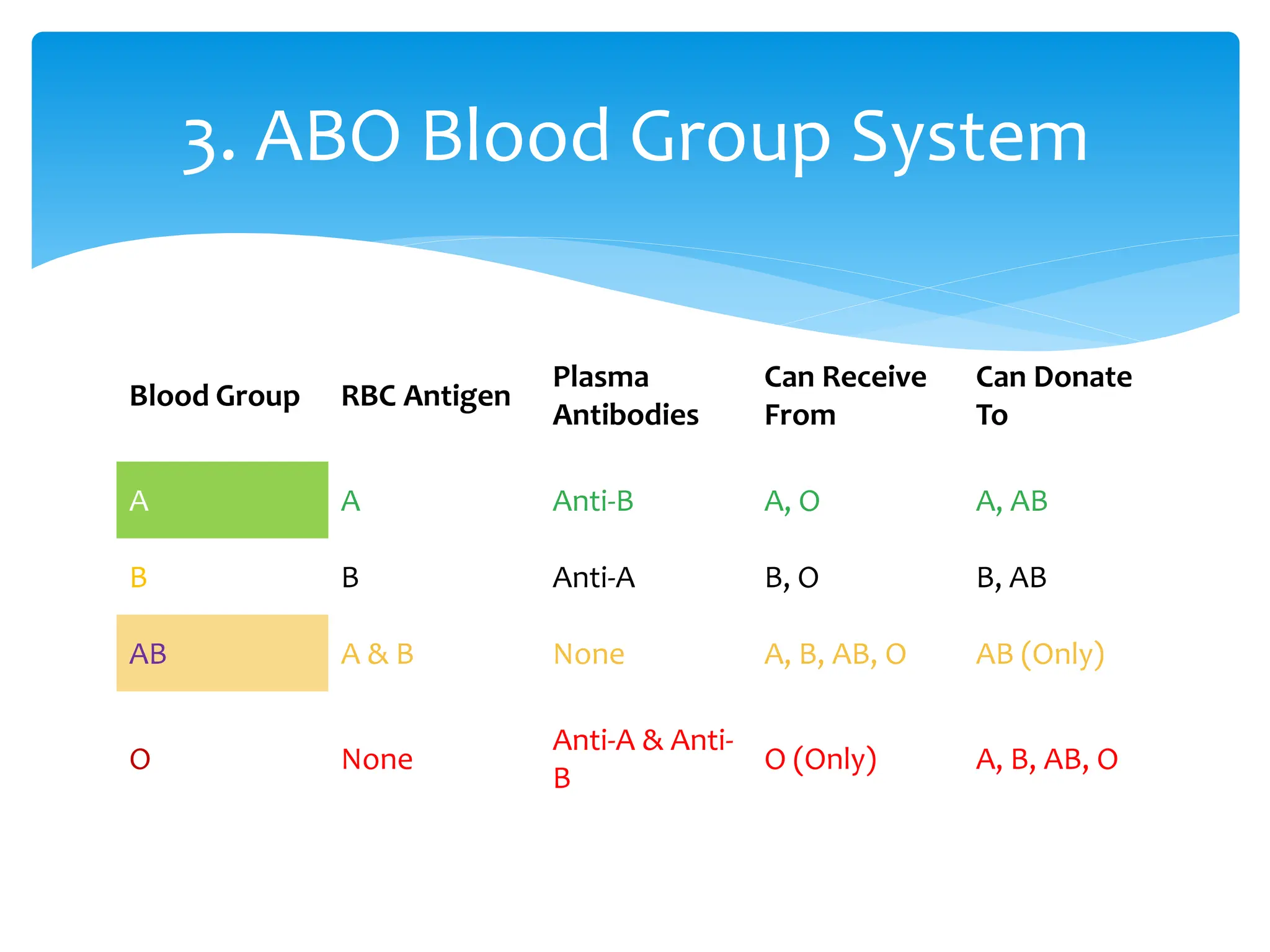
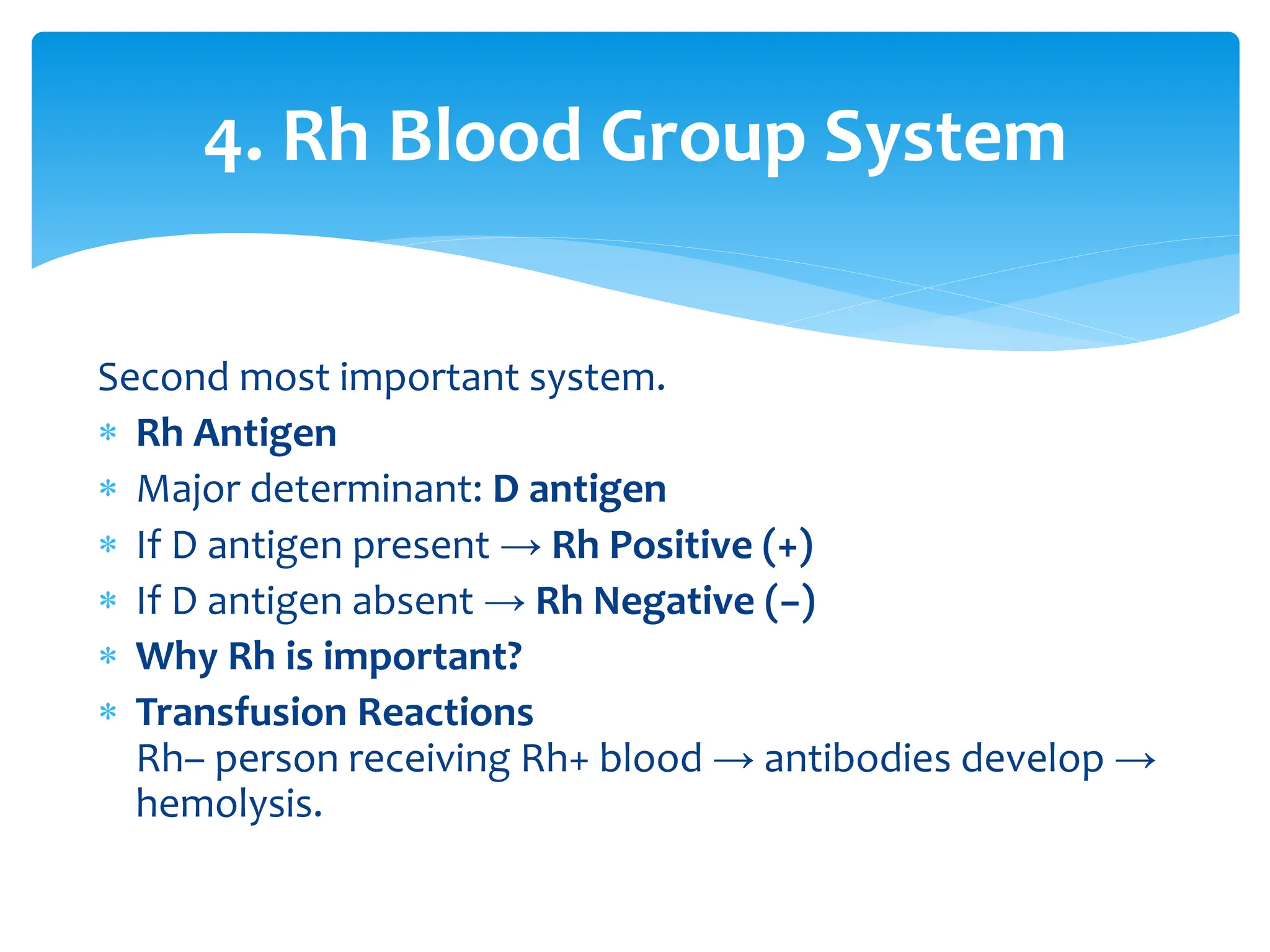
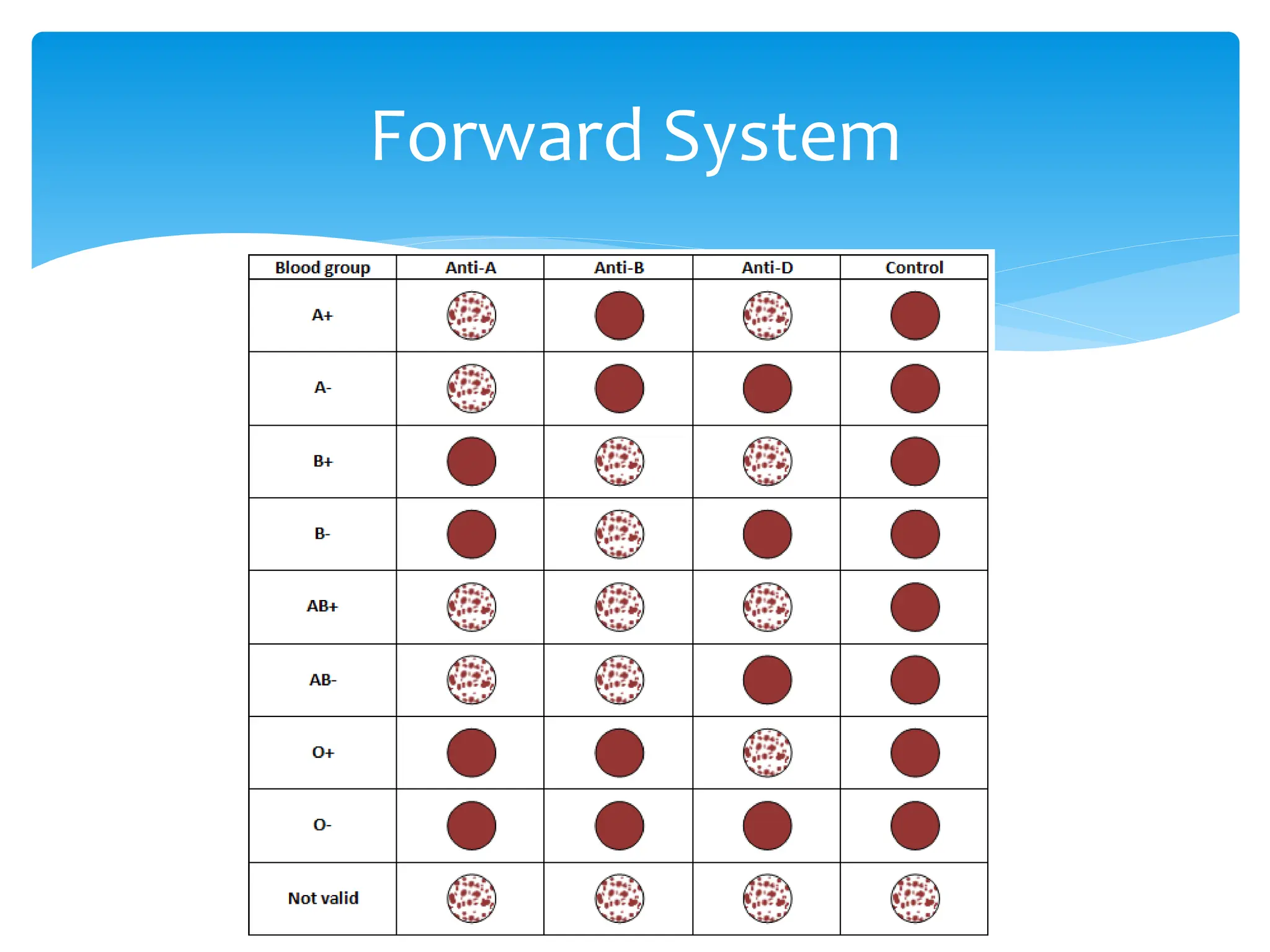
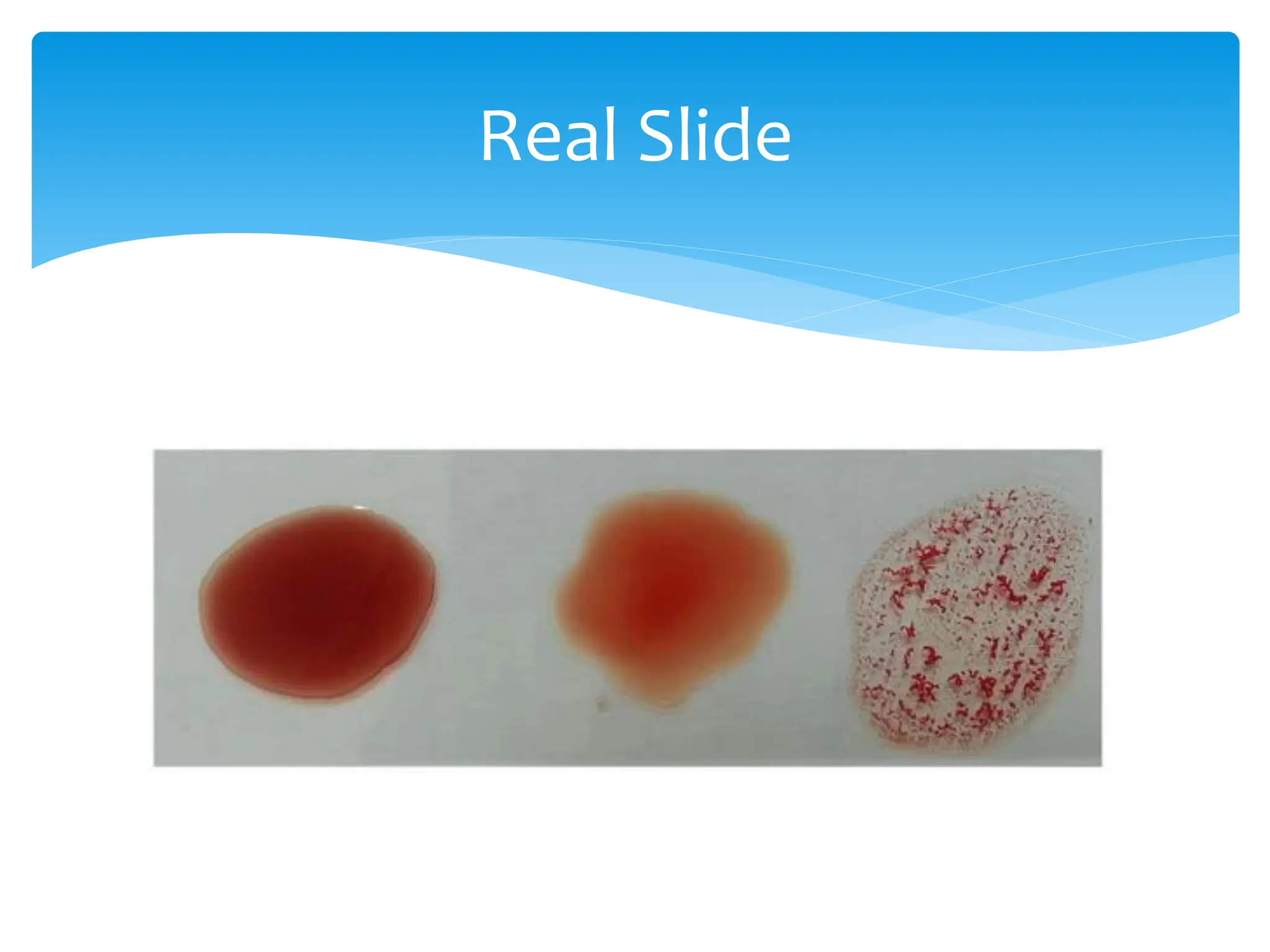
ABO & Rh blood grouping most clinically important systems
Antigens determine blood group; antibodies determine compatibility
O = universal donor (RBCs), AB = universal recipient
Rh disease preventable with Anti-D
Blood typing & crossmatch essential before blood transfusion.