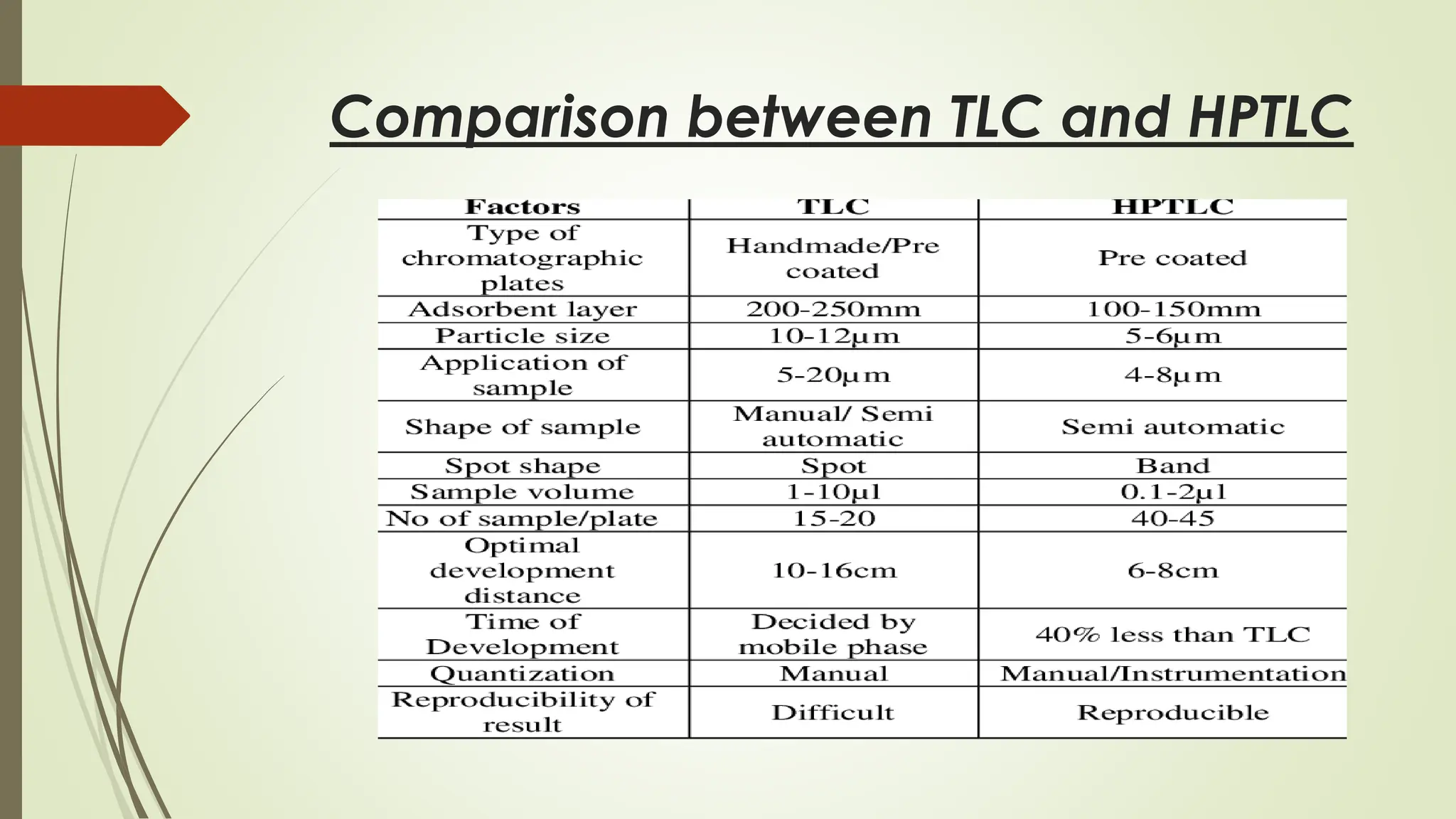
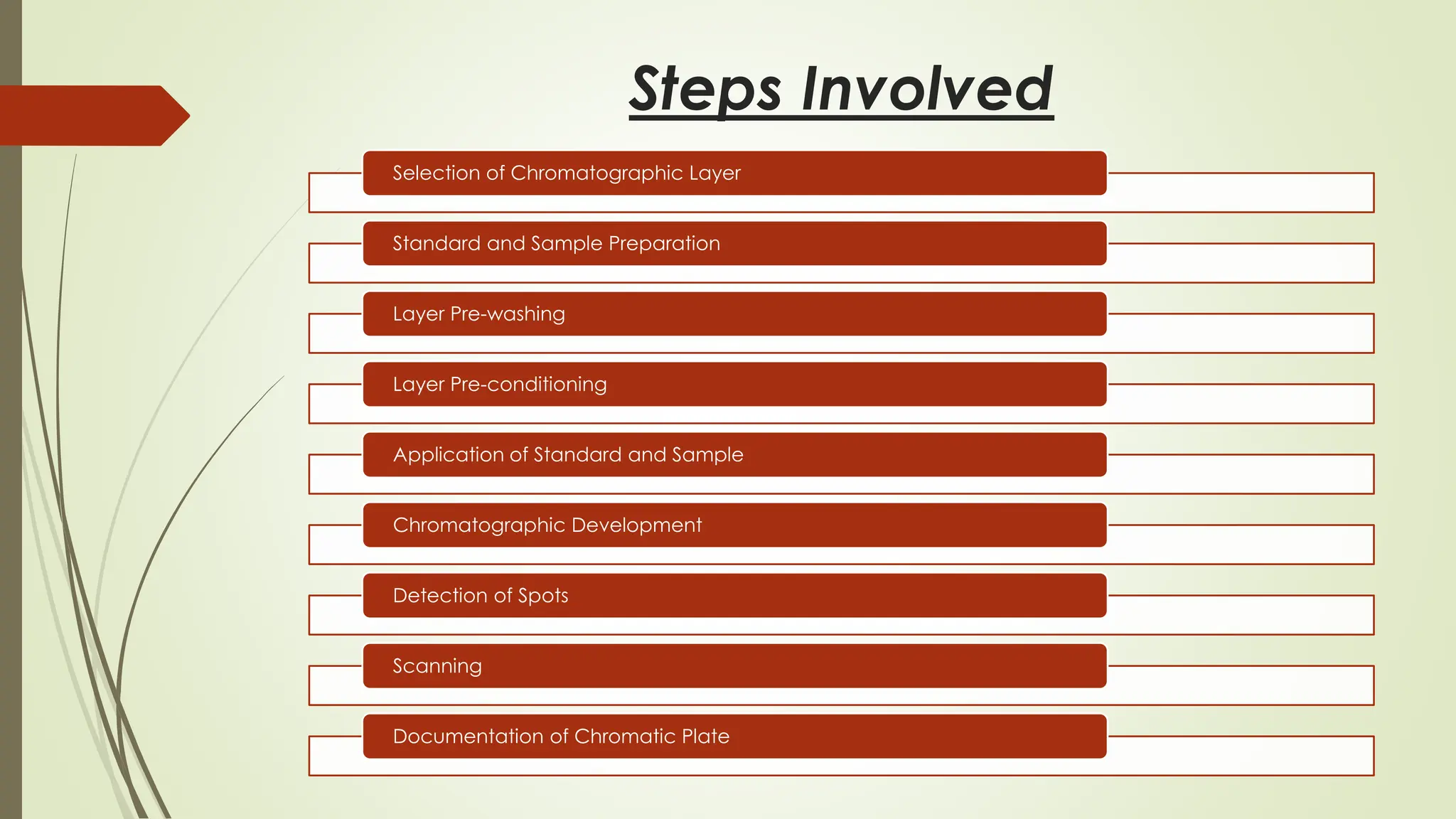
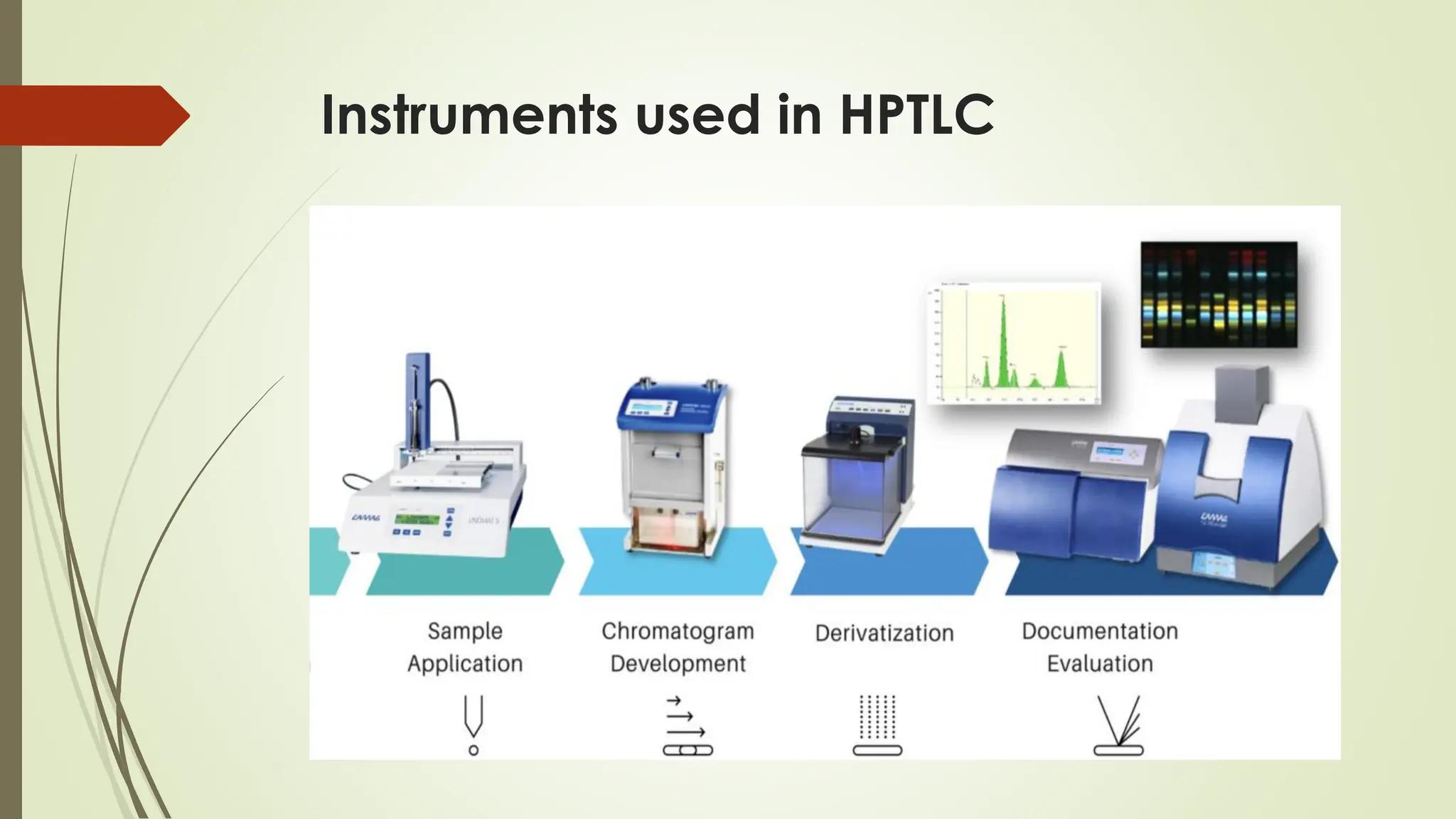
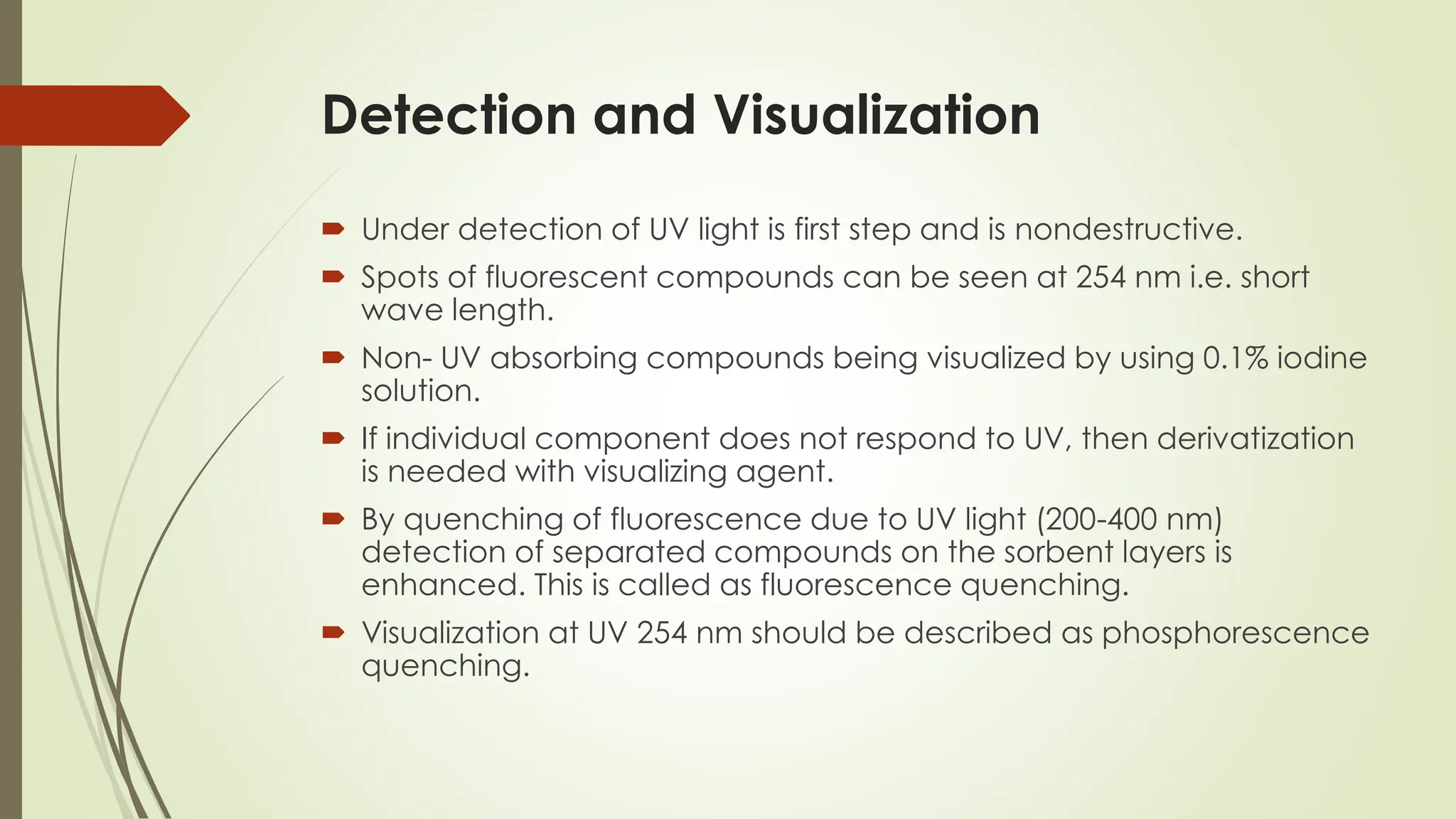
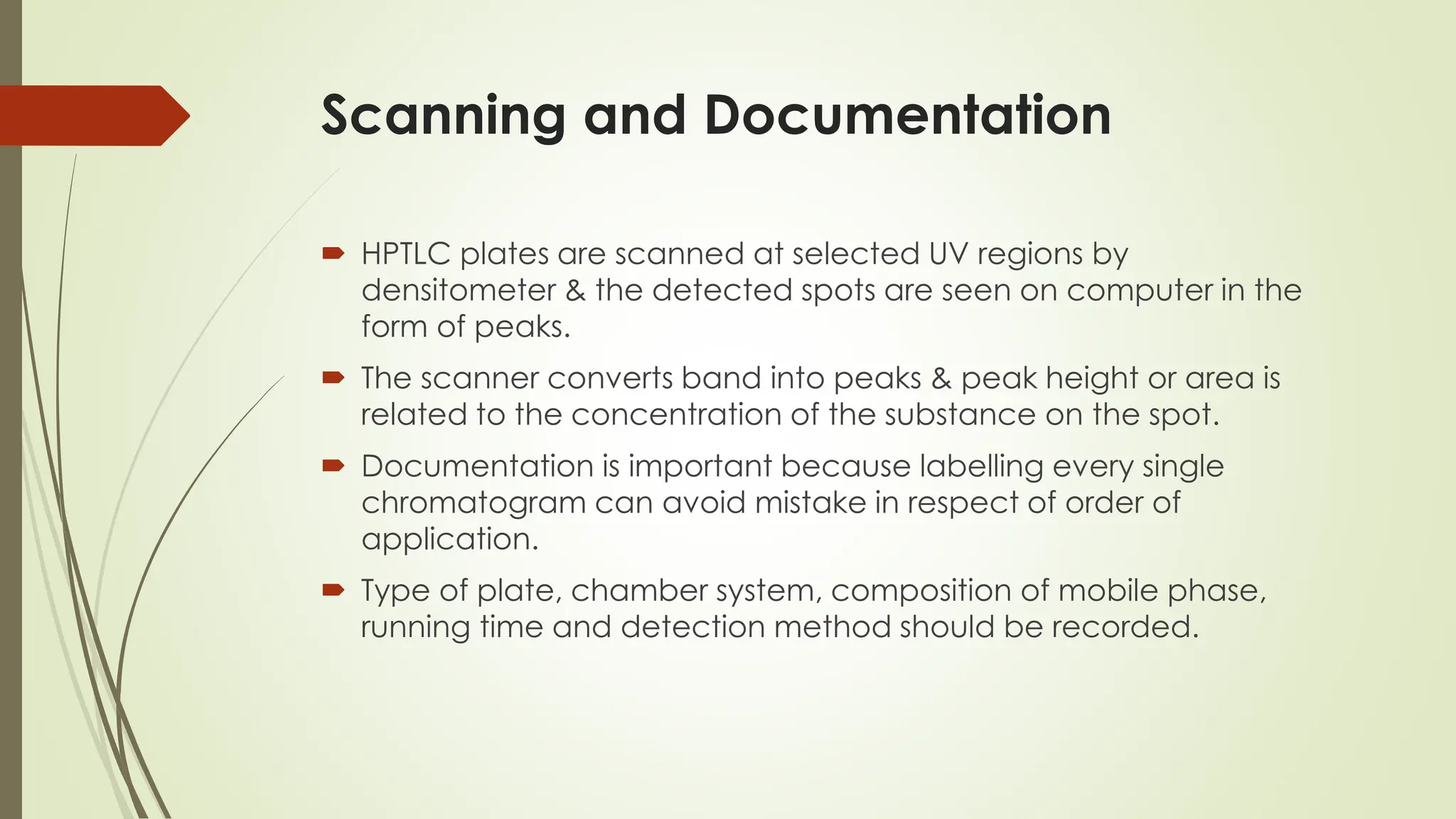
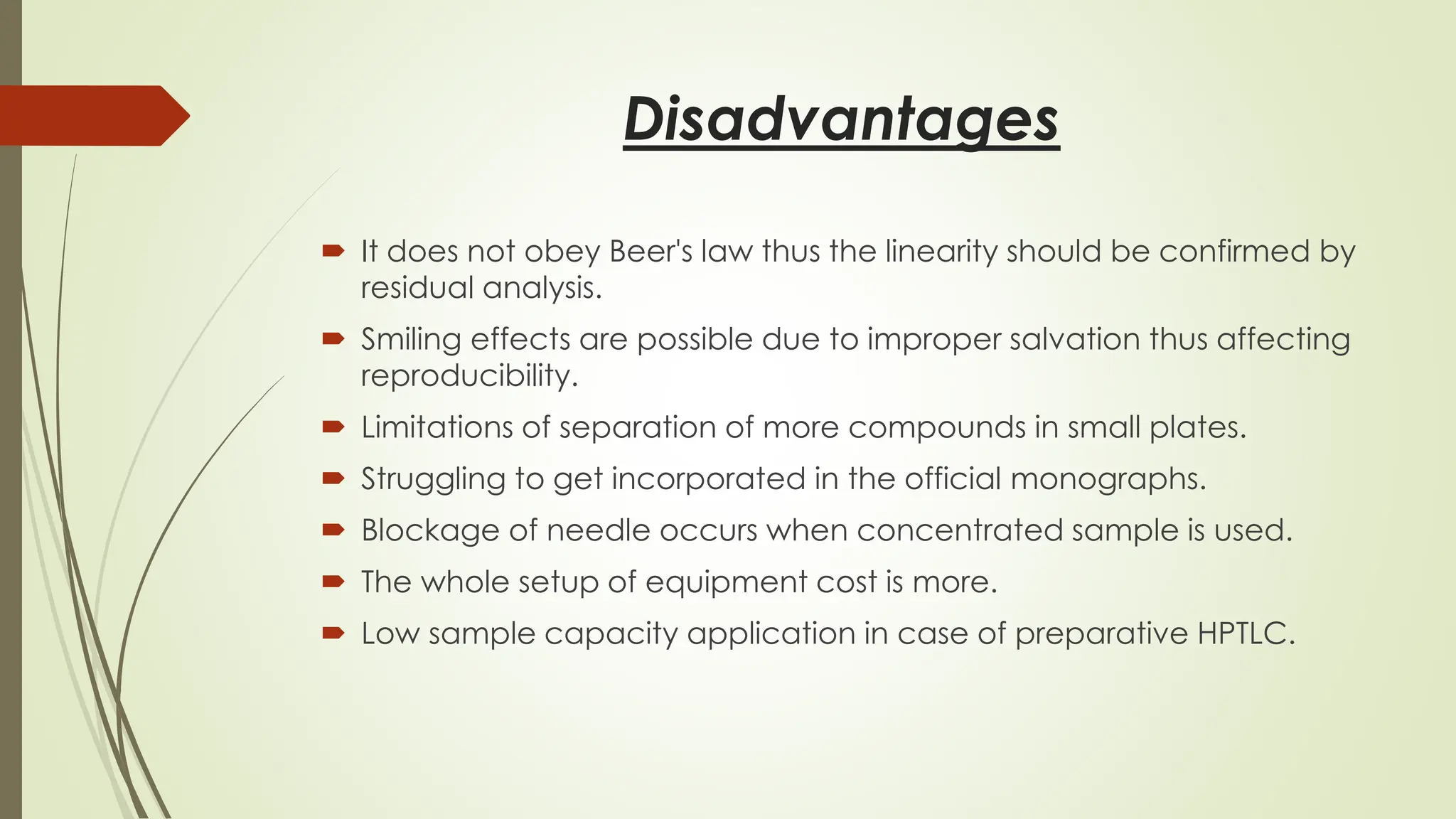
High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography (HPTLC) is an advanced form of conventional Thin-Layer Chromatography that offers enhanced separation efficiency, improved resolution, and precise quantitative analysis. It operates on the principle of differential migration of components between a stationary phase and a mobile phase, but uses superior precoated plates, automated sample application, controlled development chambers, and densitometric scanning to achieve highly reproducible results. HPTLC provides significant advantages over traditional TLC, including higher sensitivity, better accuracy, greater sample throughput, and superior documentation. The technique involves several systematic steps such as sample preparation, automated band application, optimized mobile-phase selection, plate development, derivatization, and densitometric evaluation. Factors such as particle size of the stationary phase, mobile-phase composition, chamber saturation, band width, humidity, and development distance play critical roles in achieving good resolution. Due to its efficiency and versatility, HPTLC finds extensive applications in pharmaceuticals, herbal standardization, food analysis, forensic science, and environmental monitoring. While it offers numerous advantages like low solvent consumption, automation, and simultaneous multi-sample analysis, it also has certain limitations such as higher instrumentation cost and sensitivity to environmental conditions. Overall, HPTLC is a powerful analytical tool providing rapid, reliable, and cost-effective qualitative and quantitative analysis.