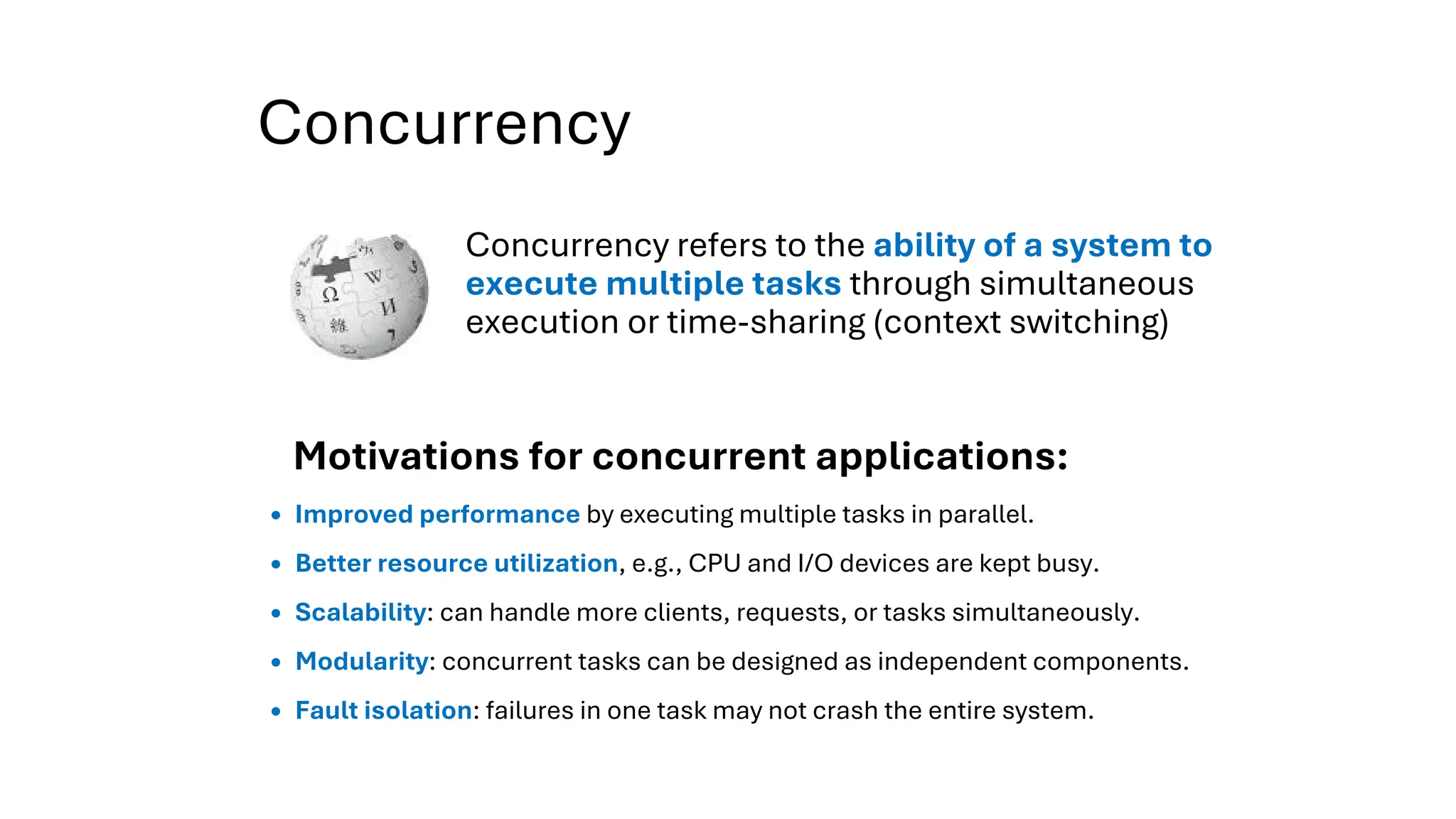
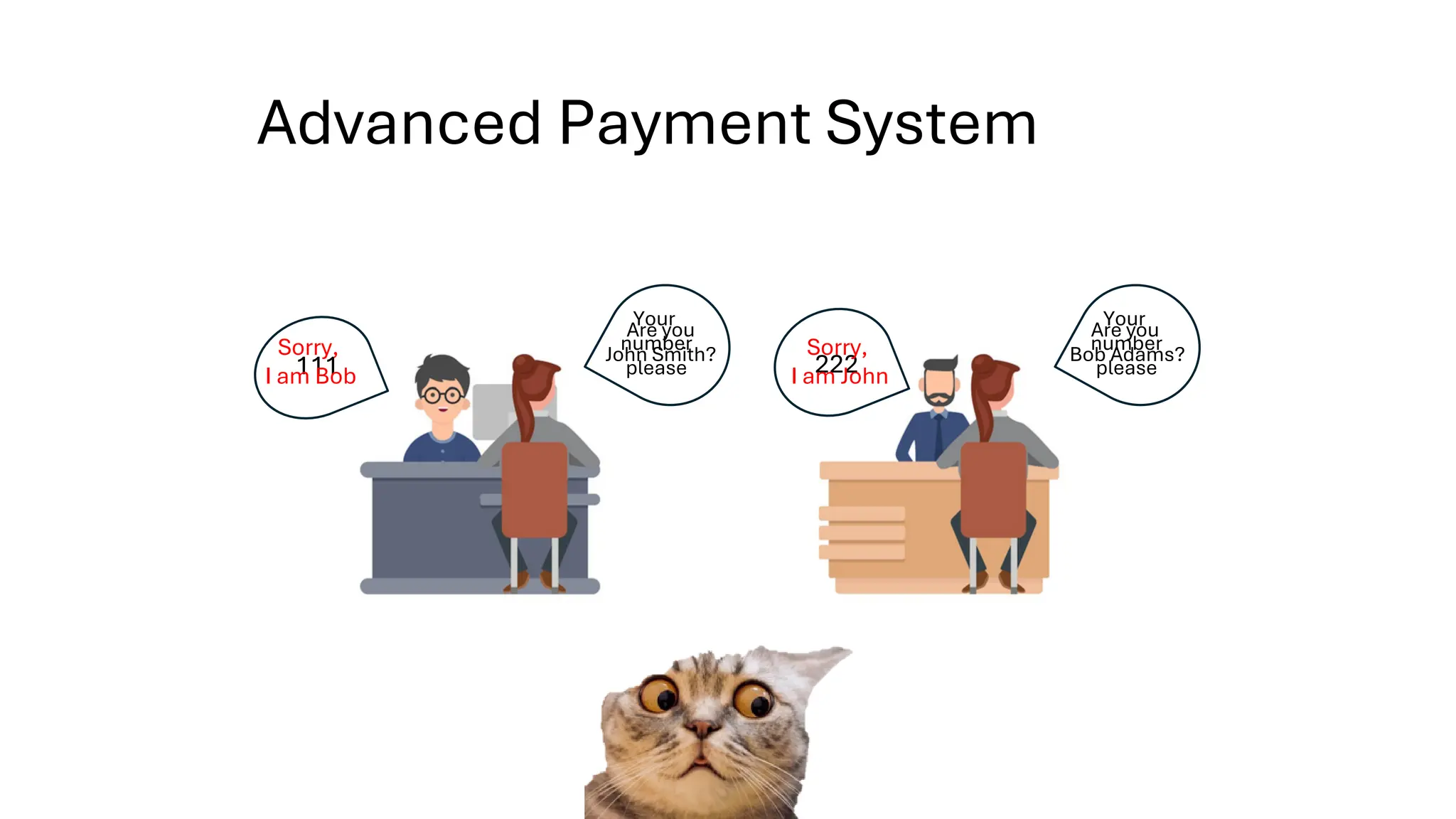
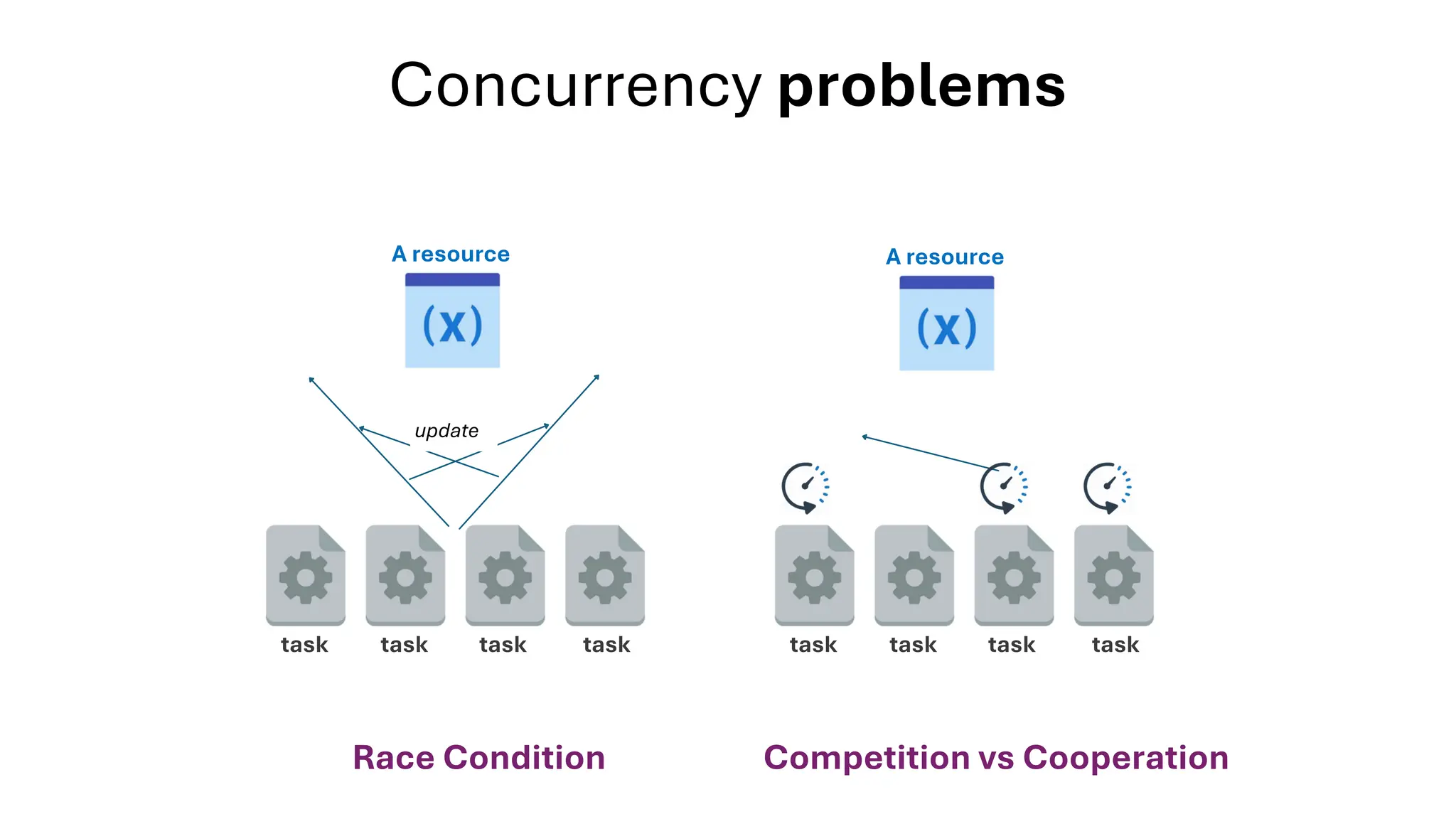
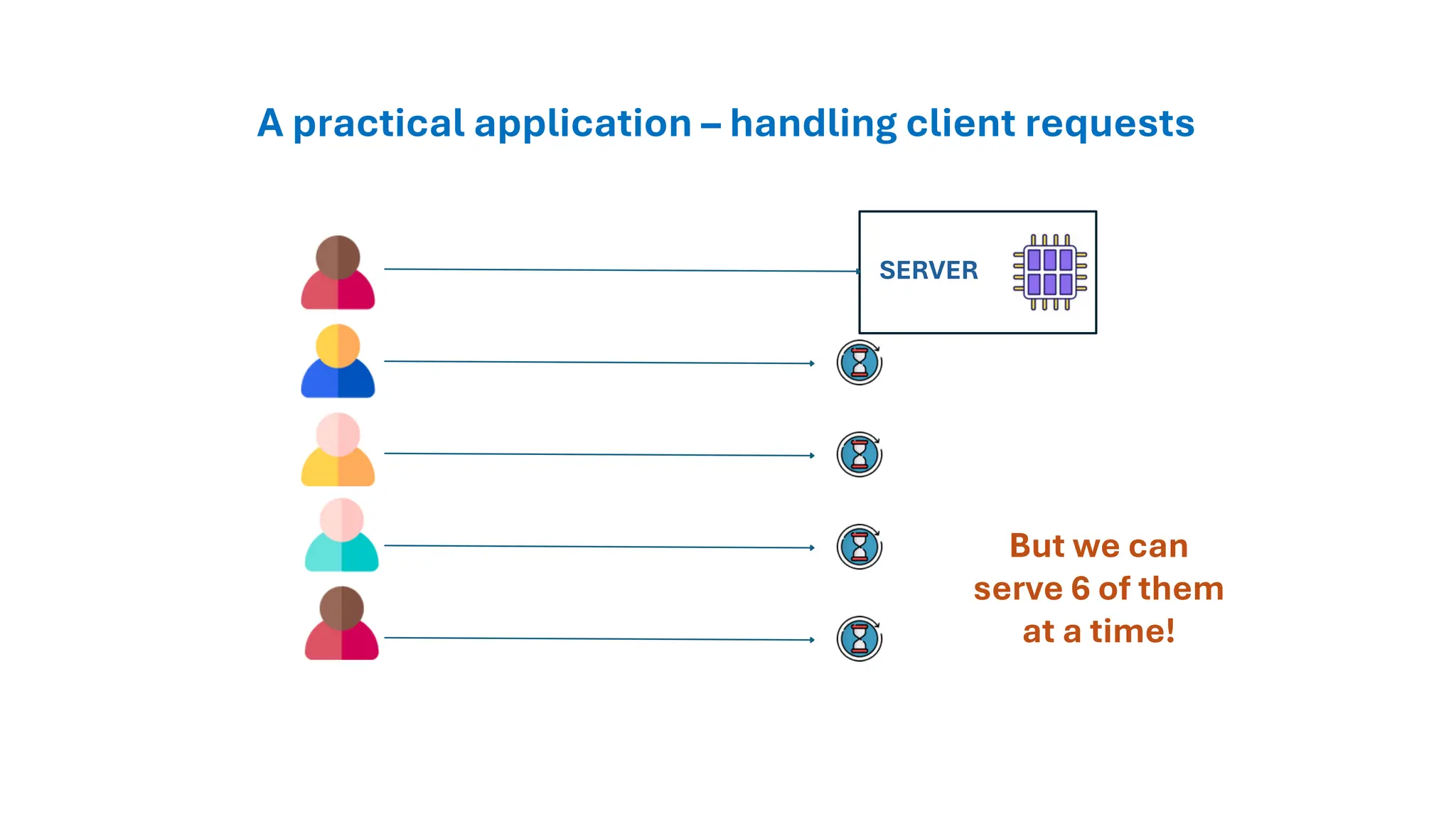
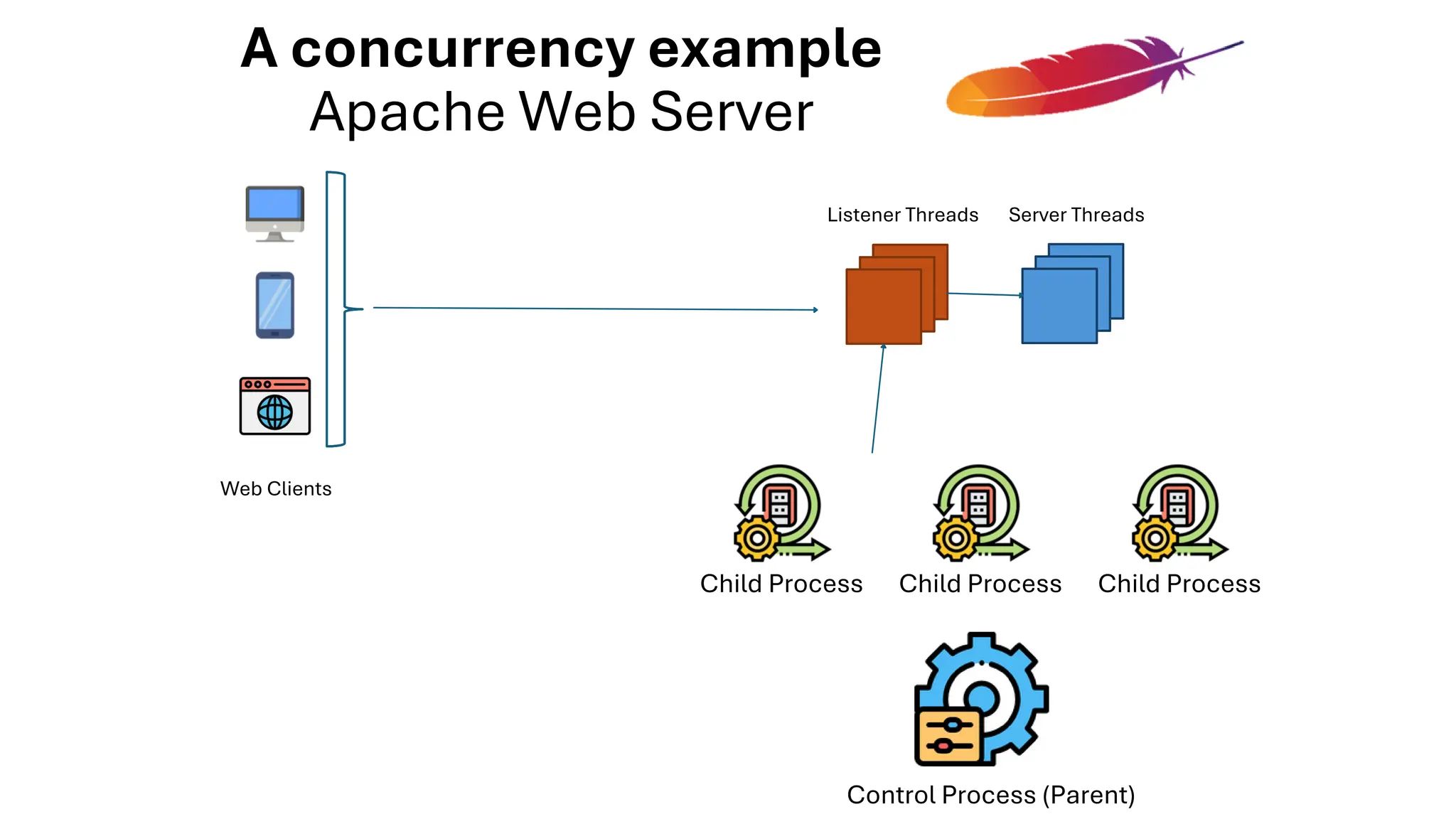
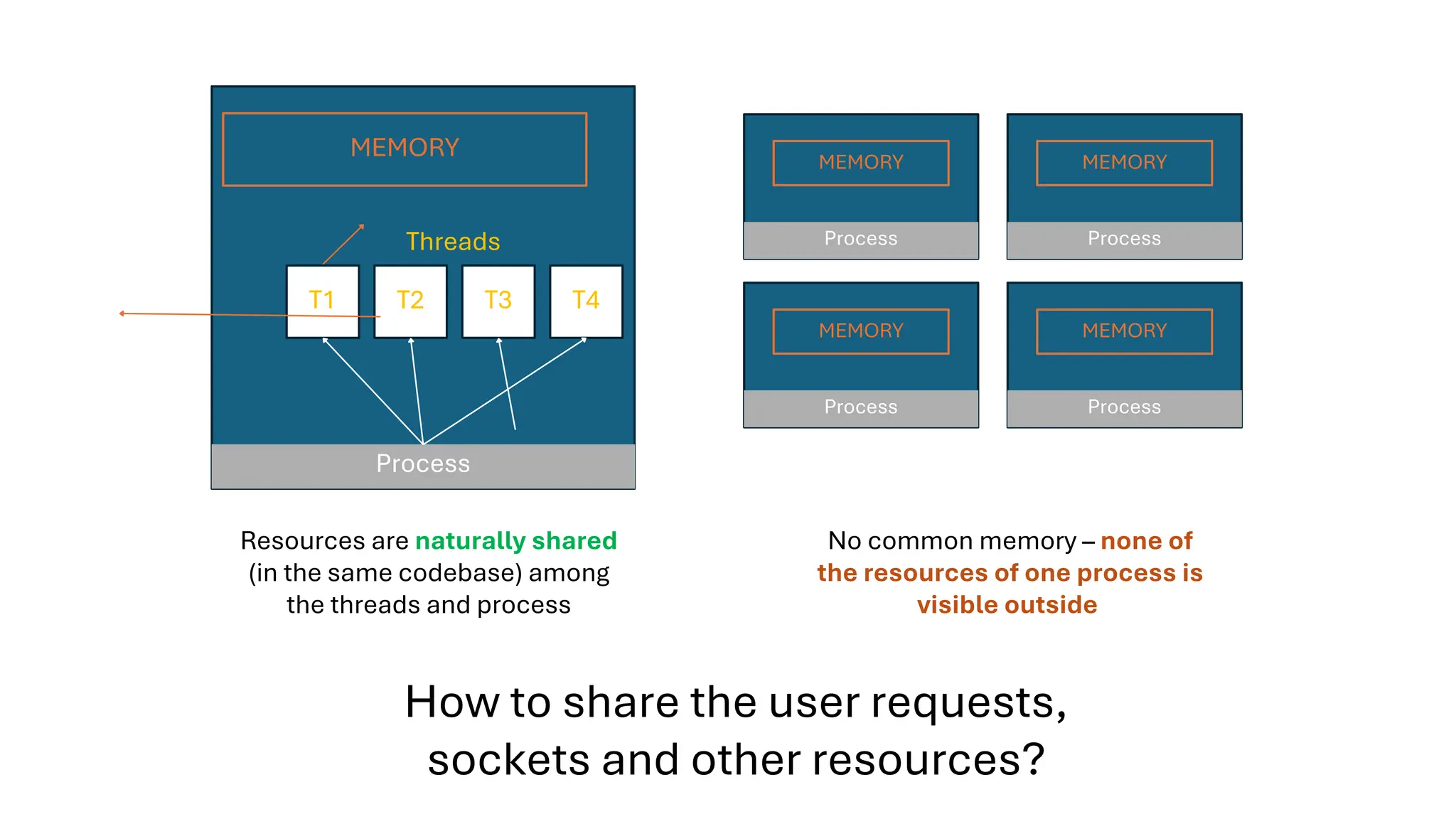
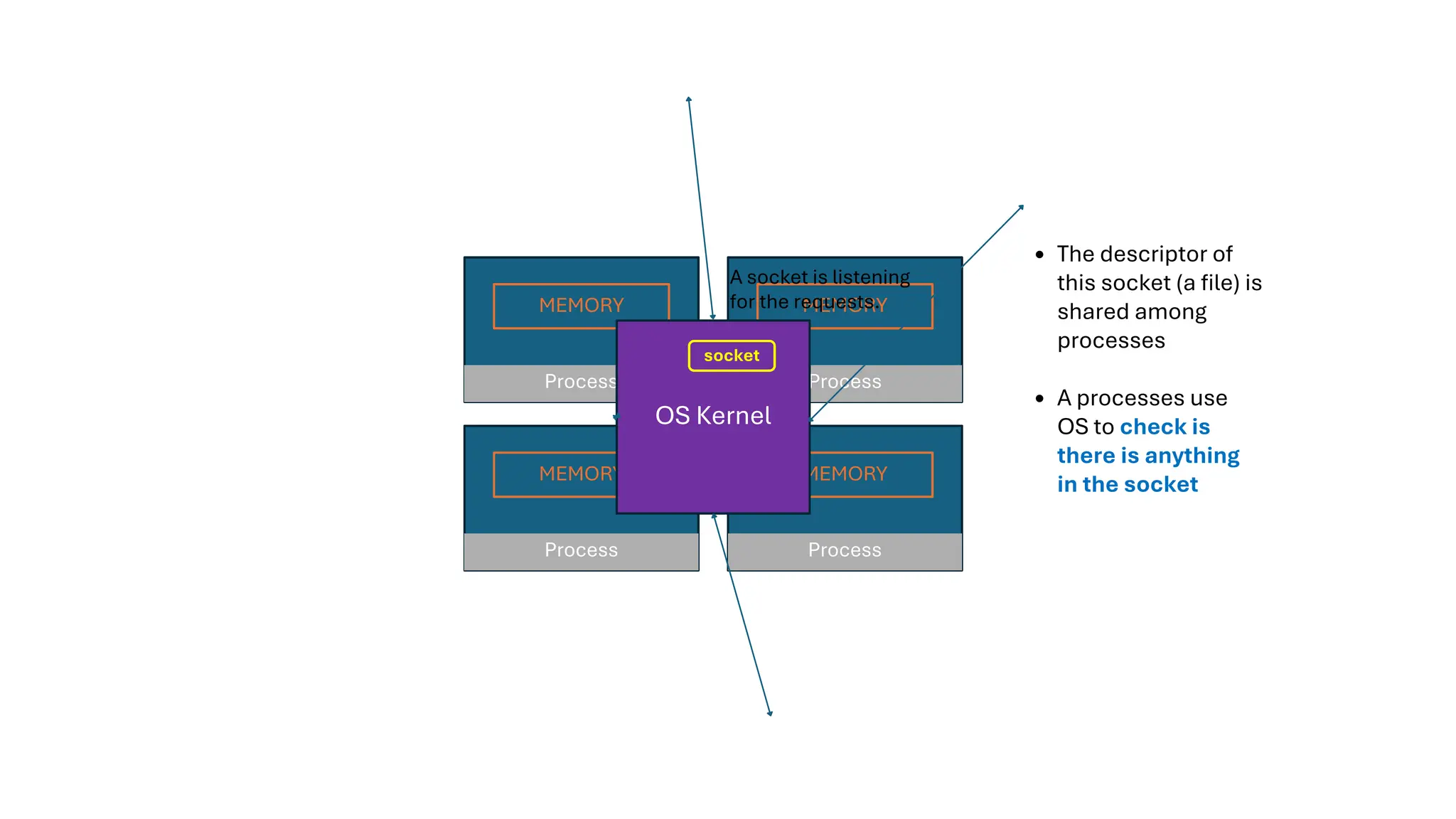
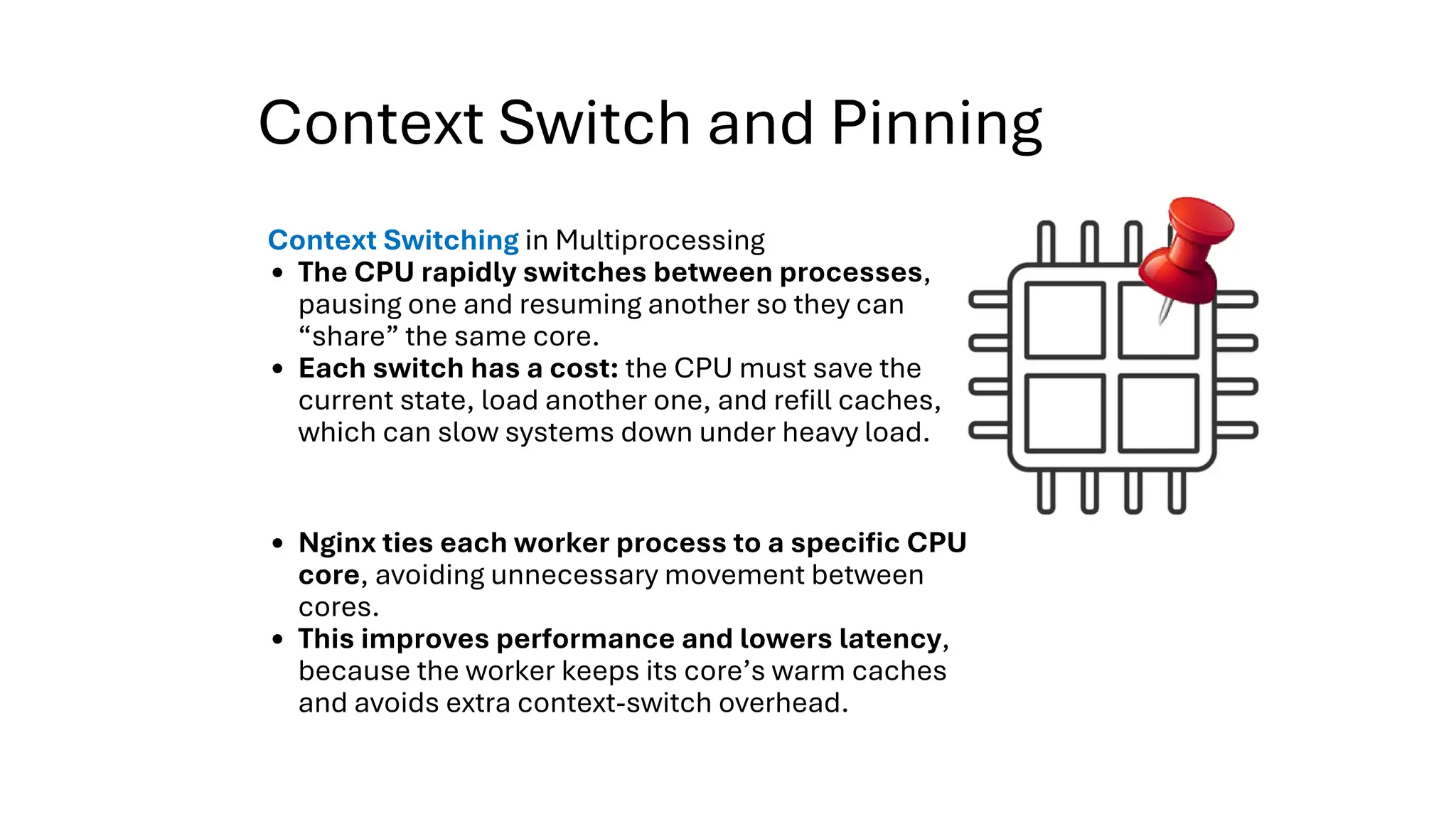
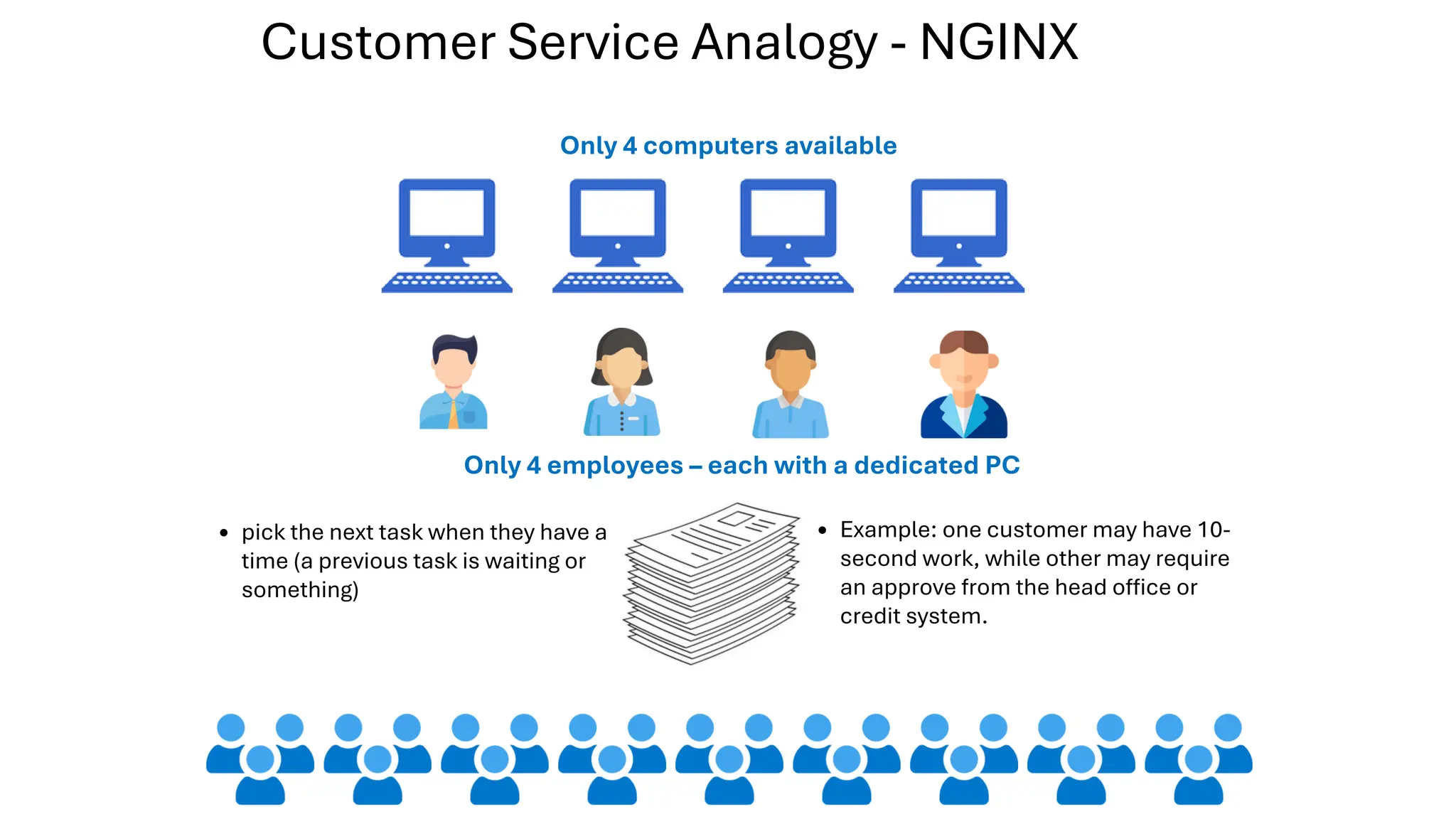
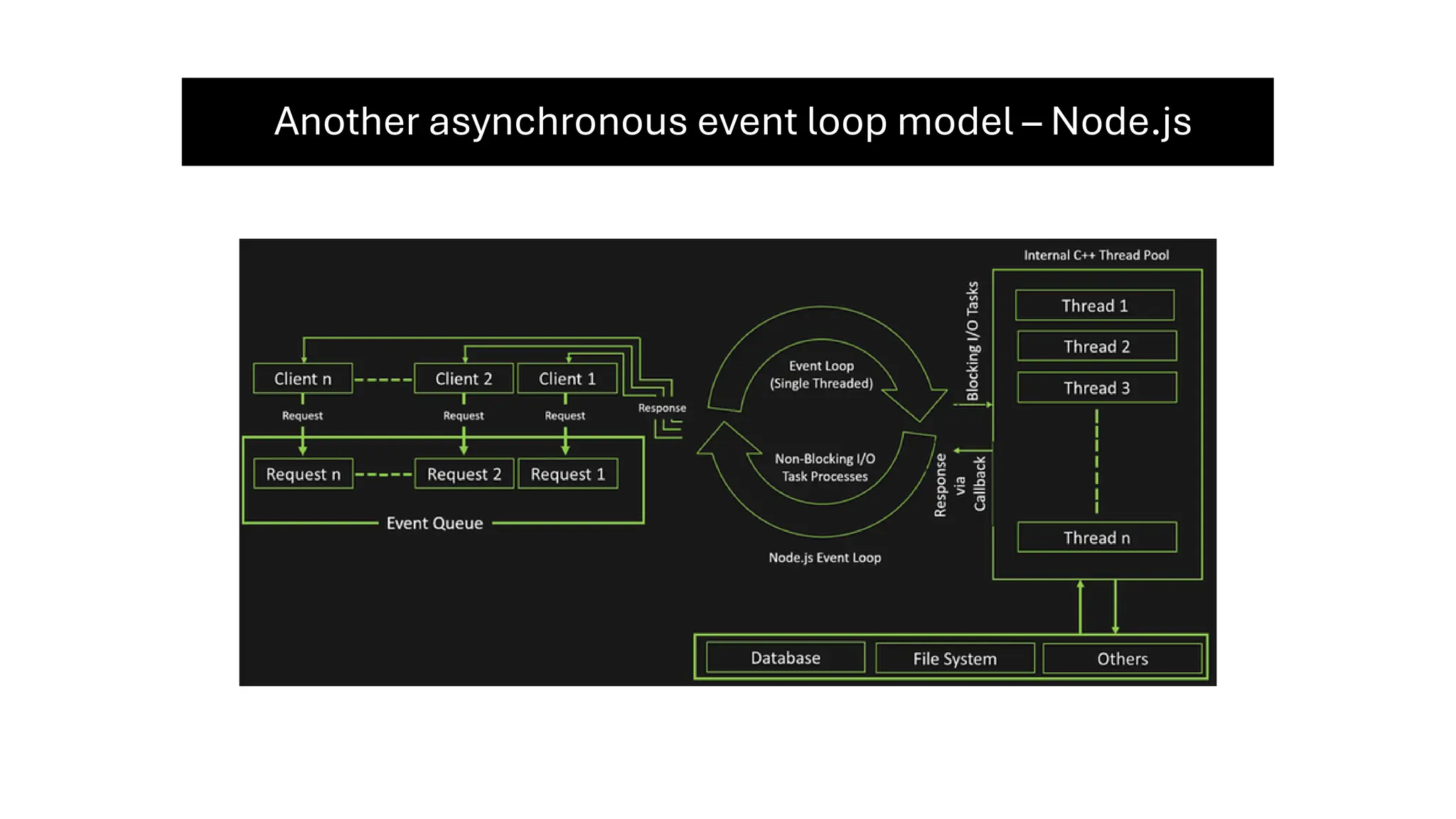
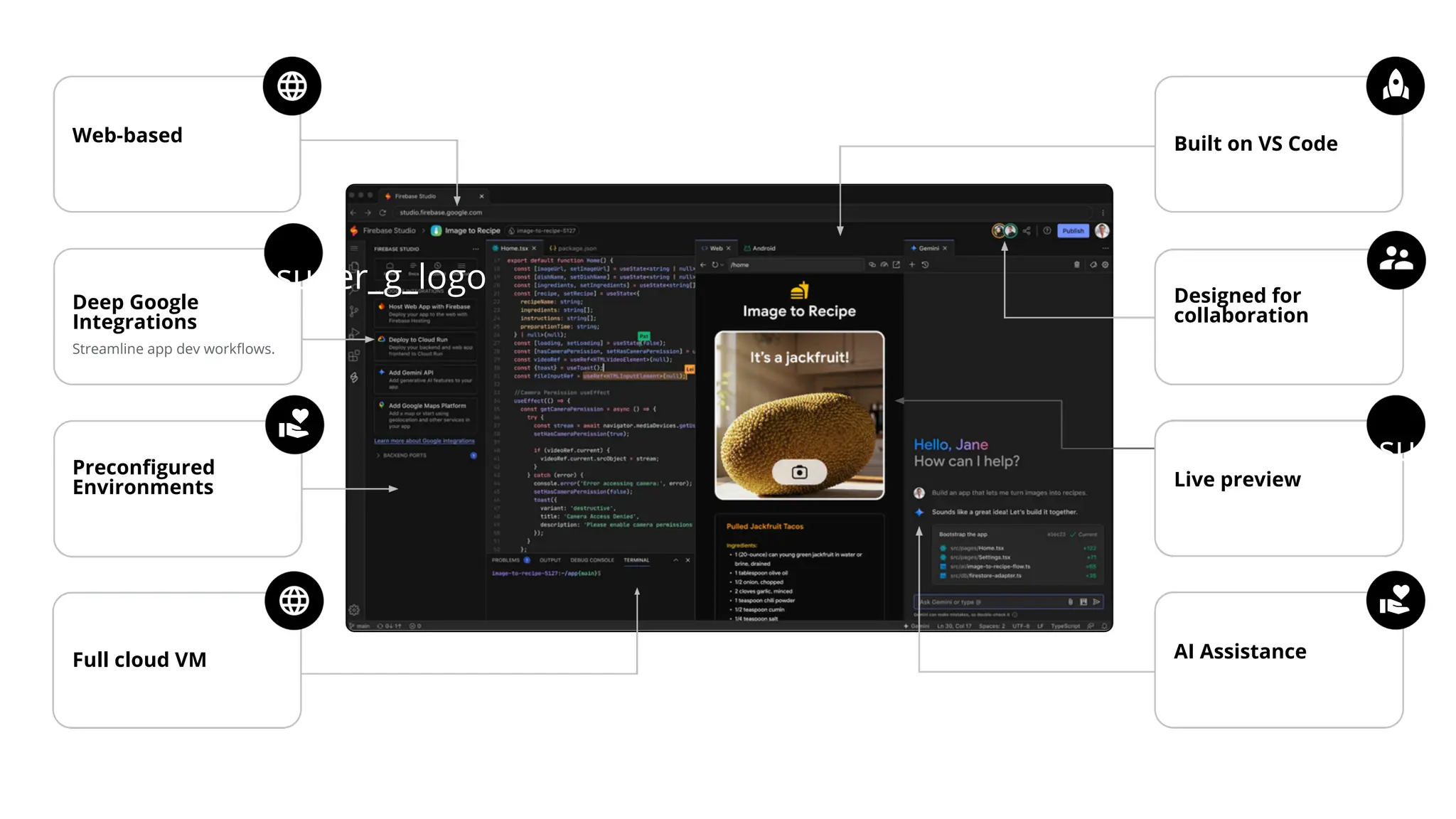
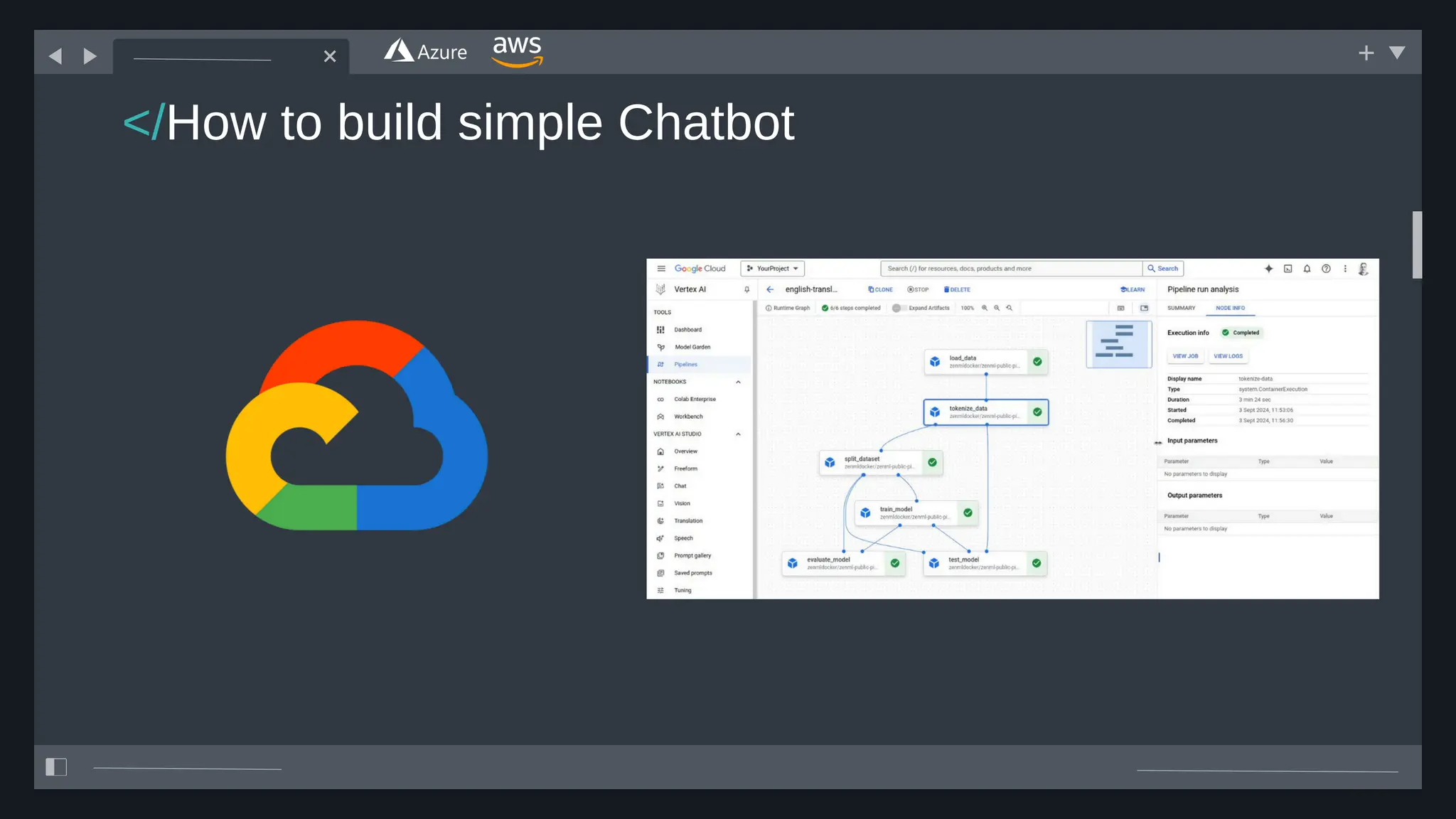
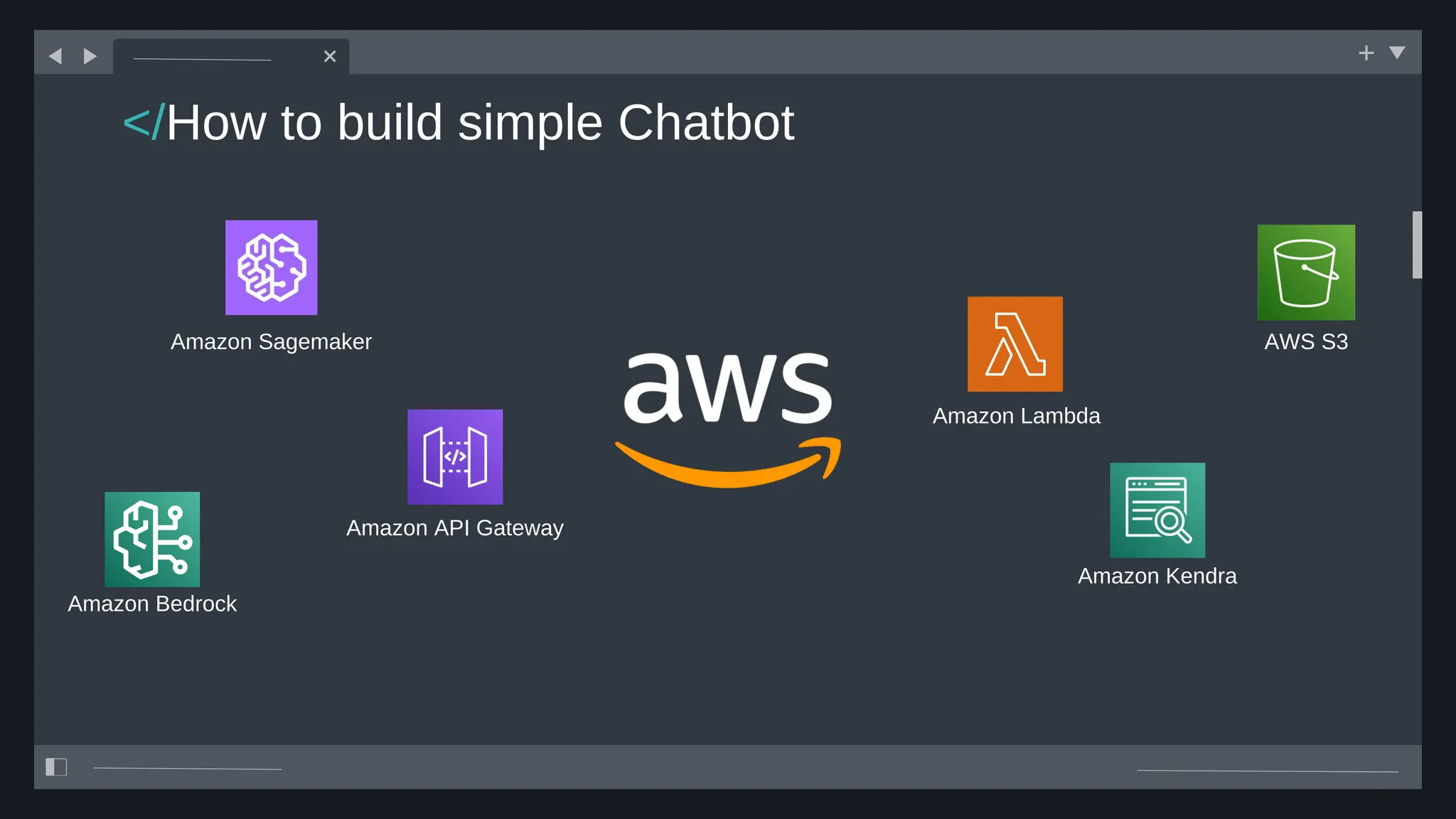
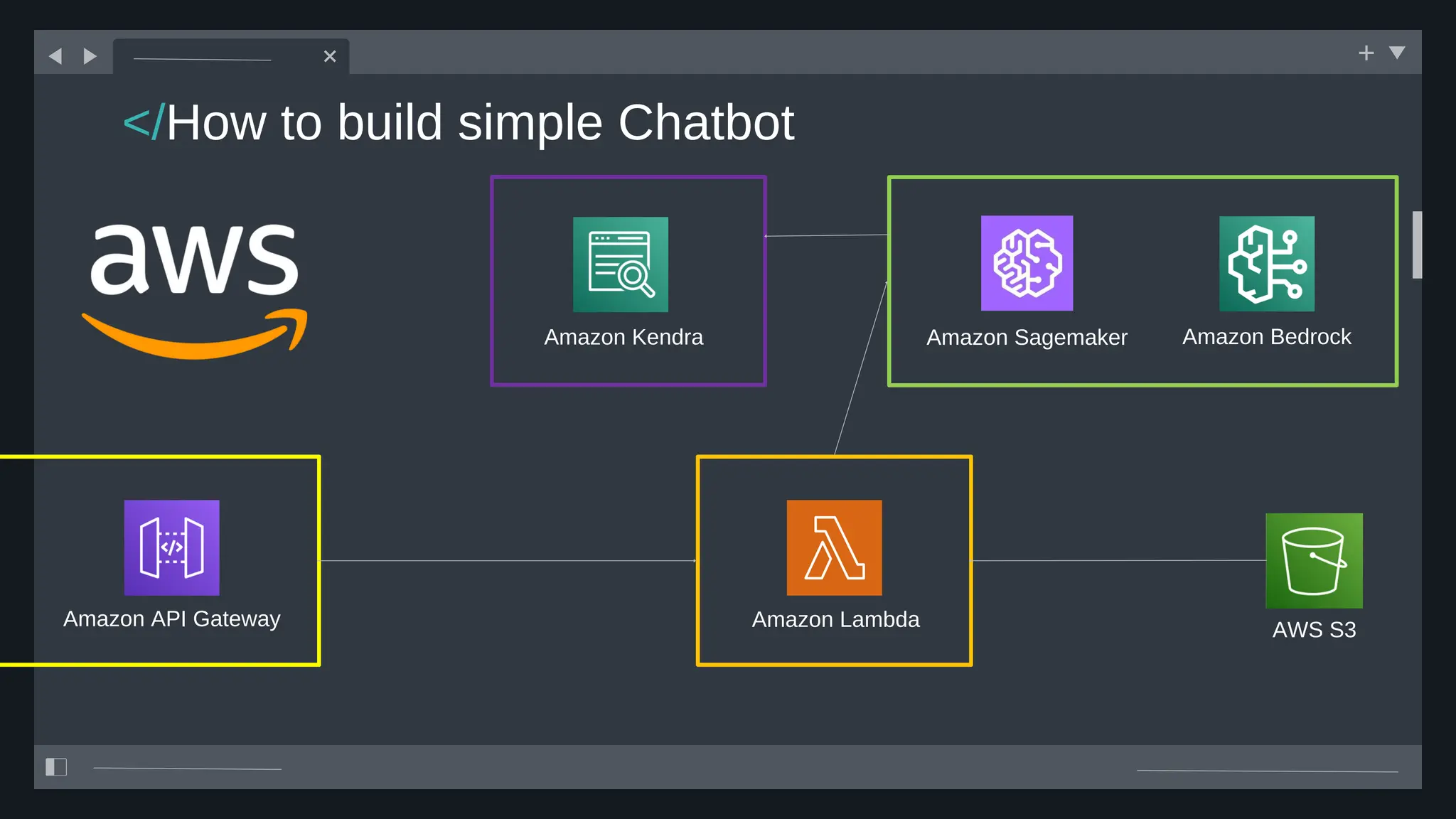
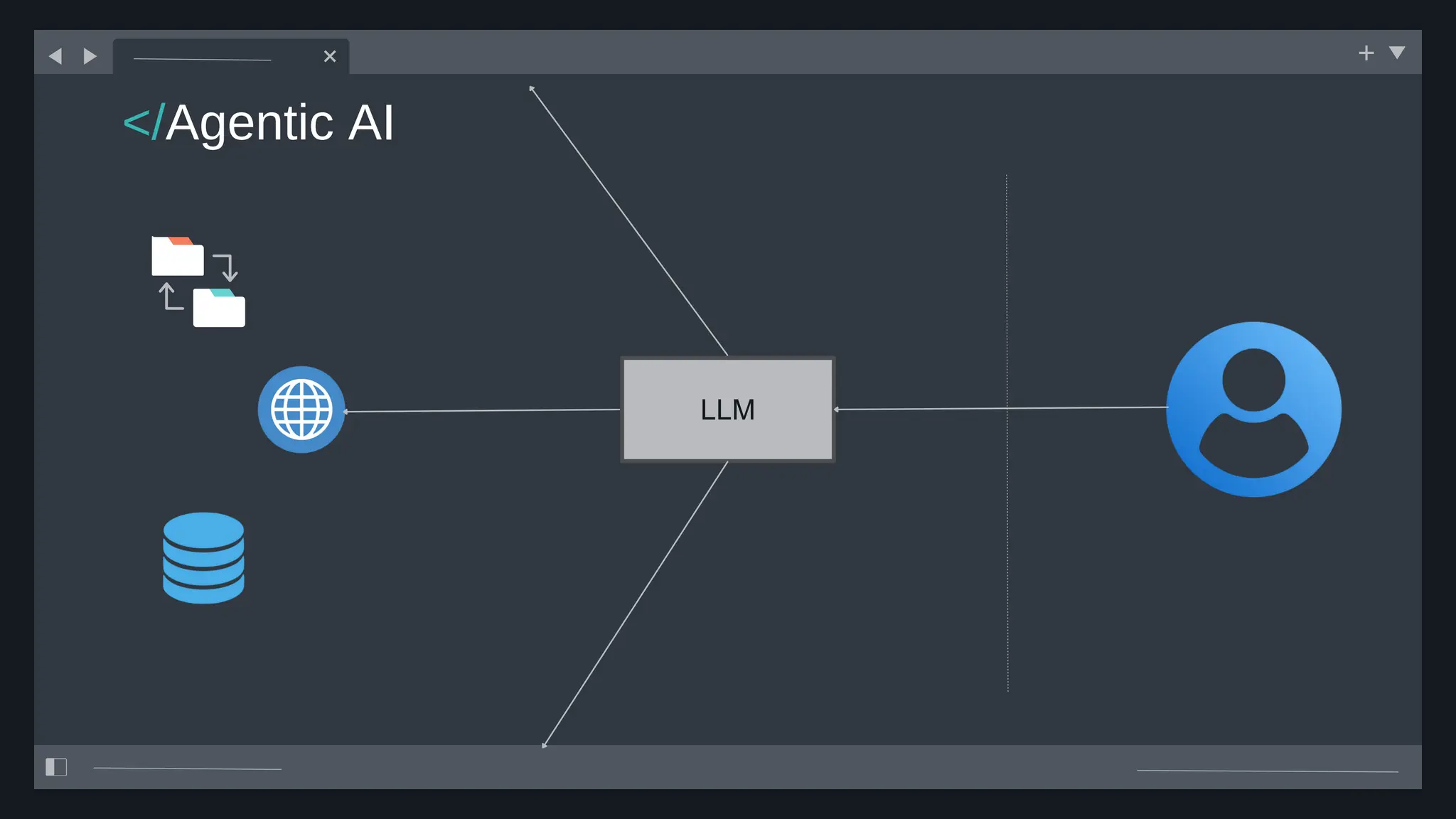
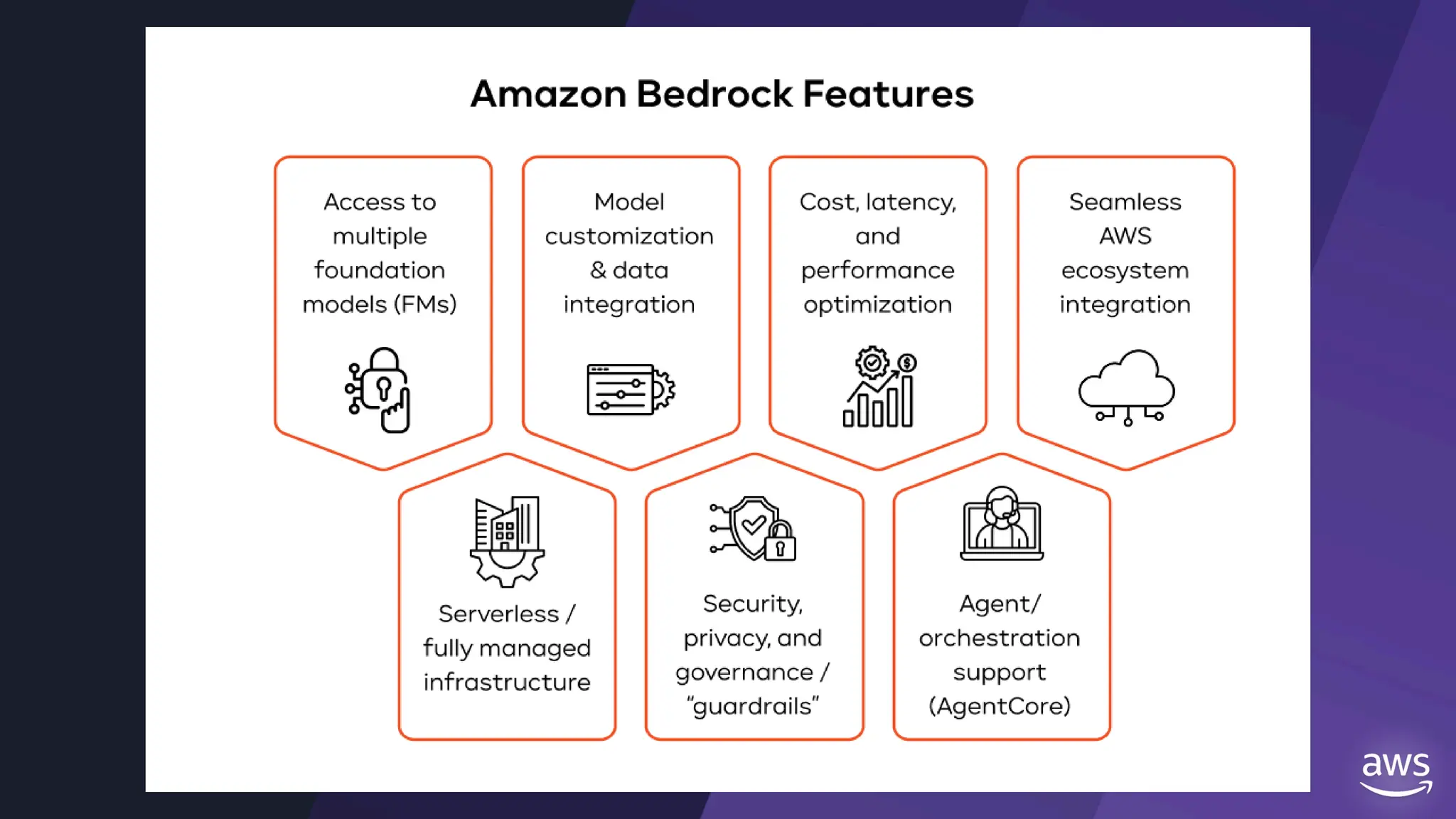
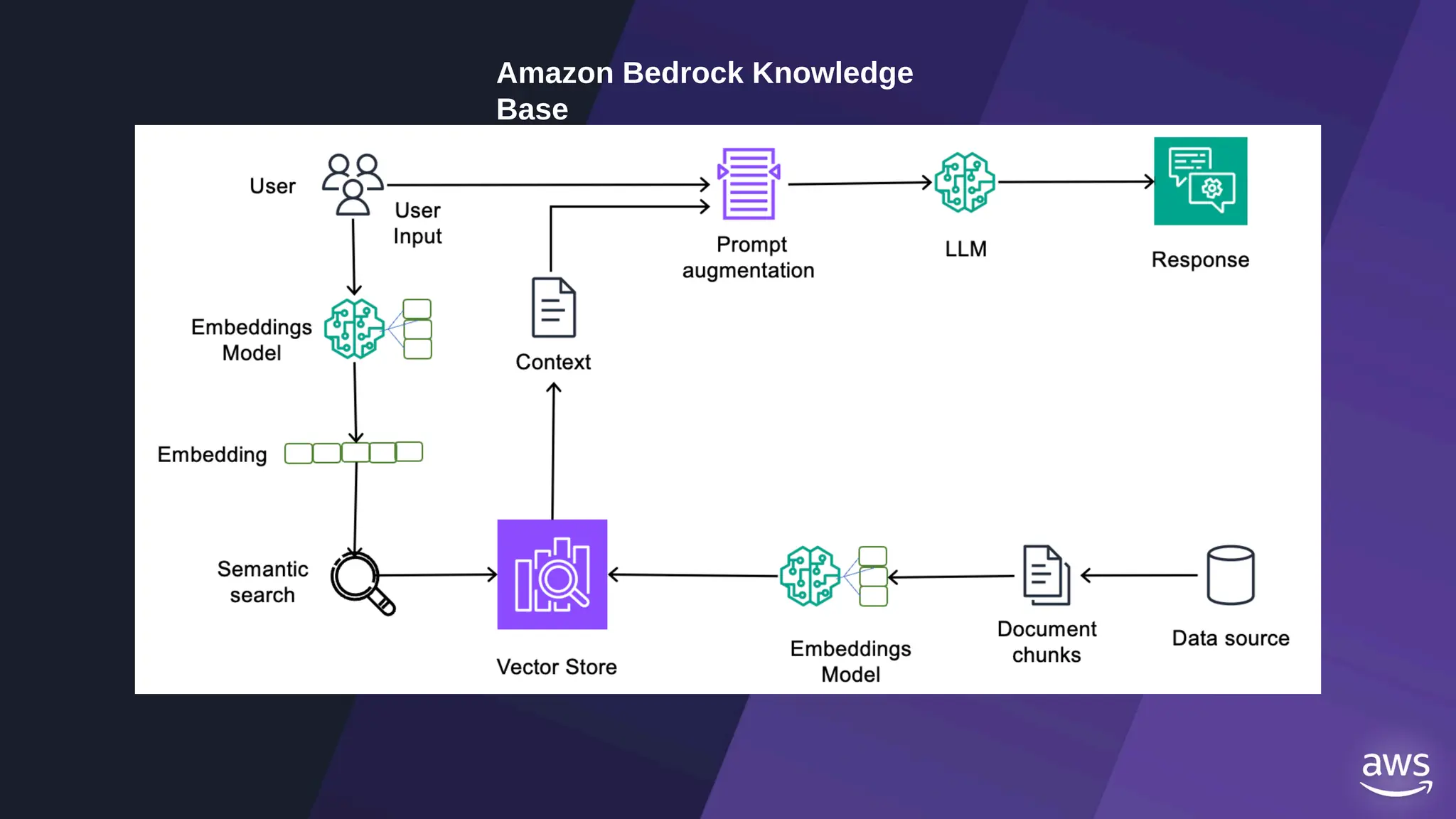
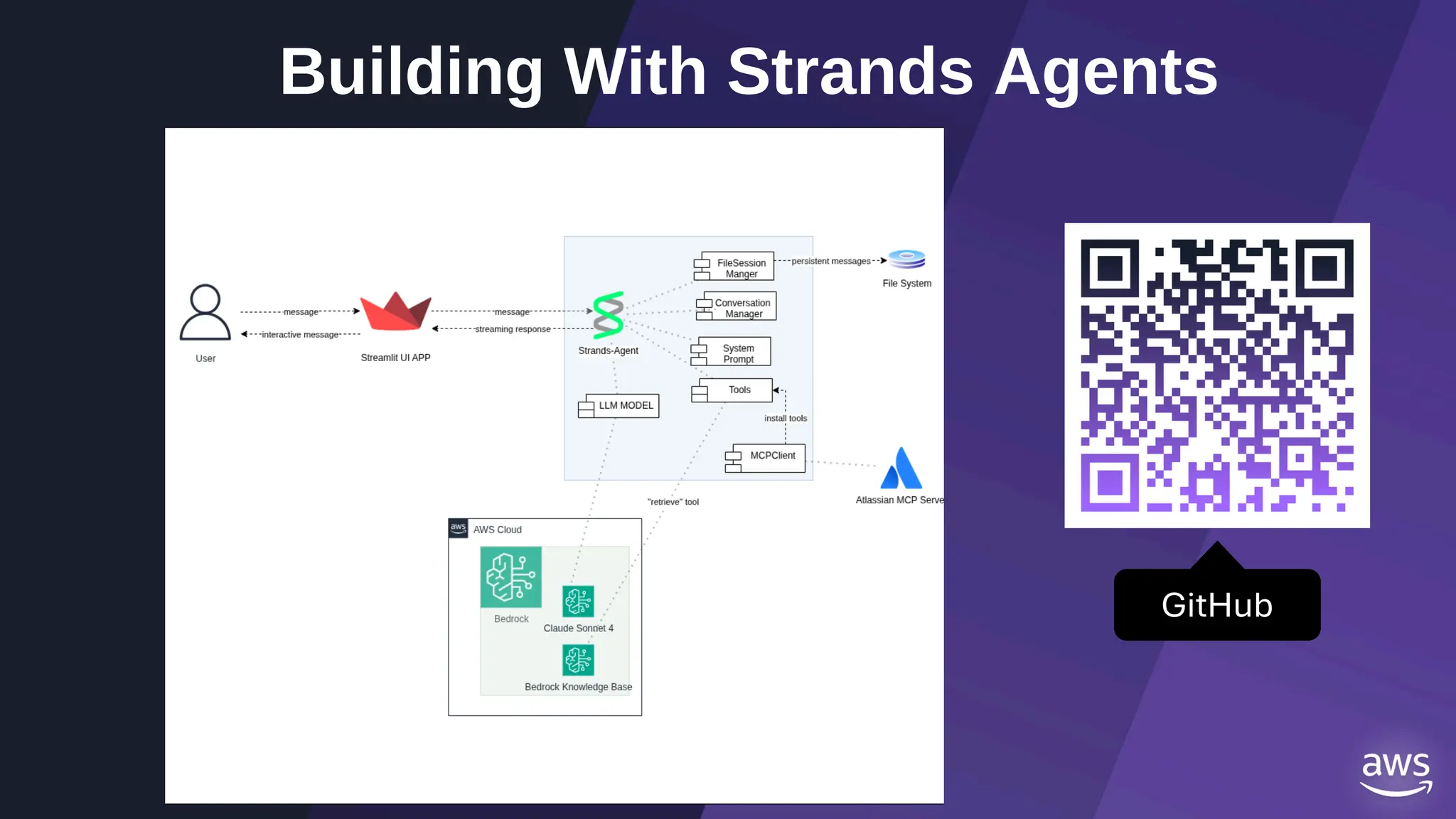
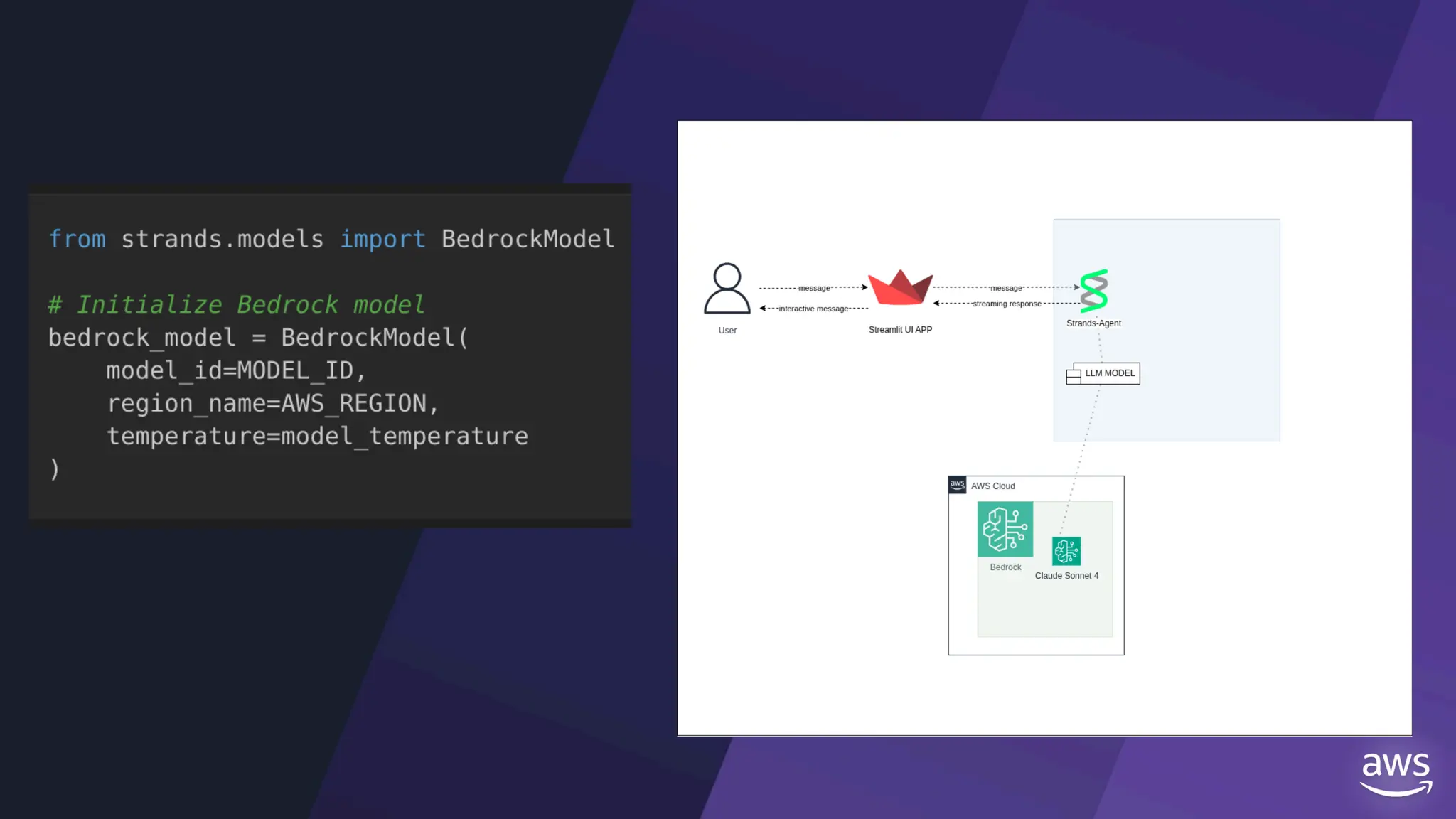
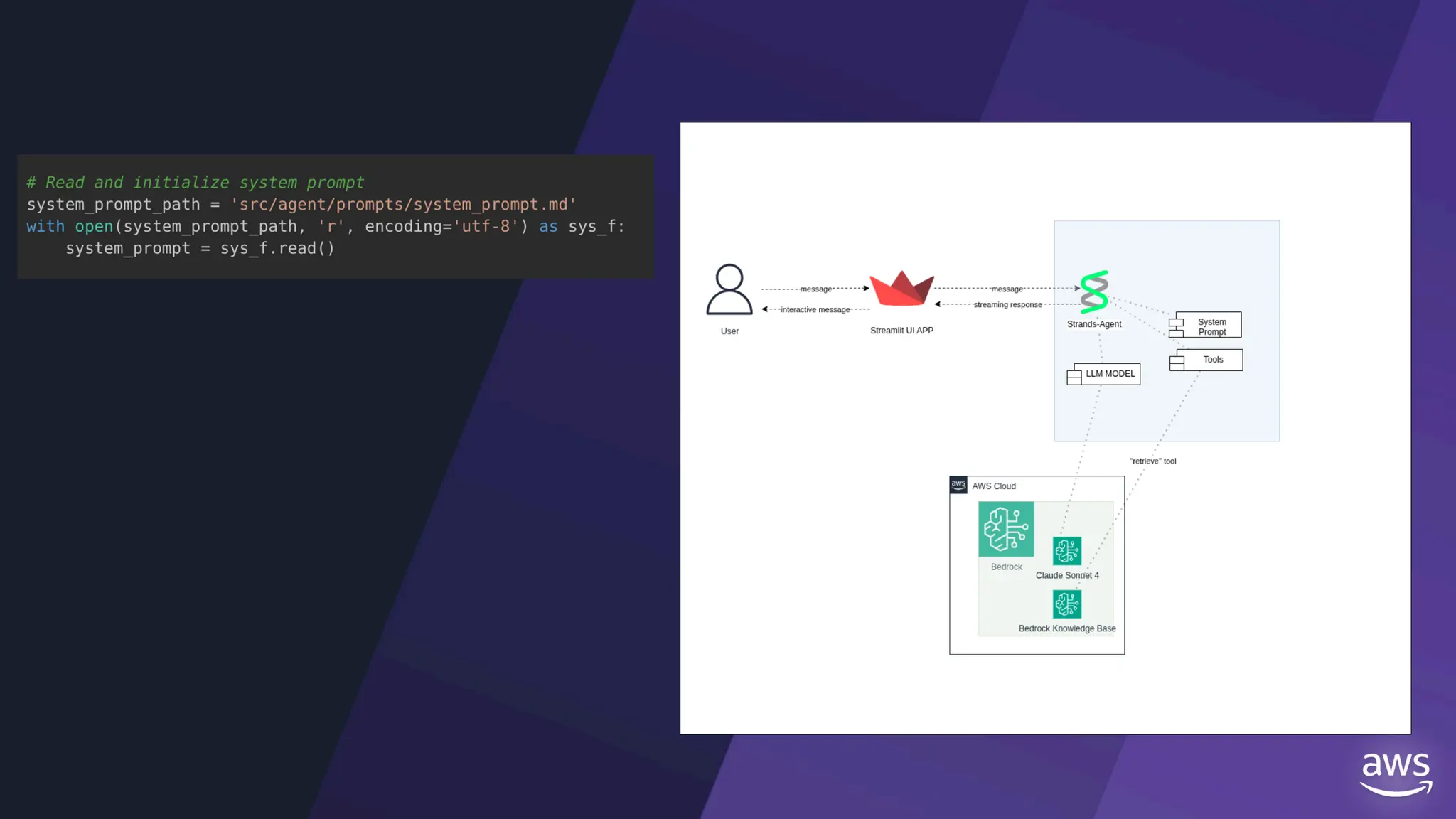
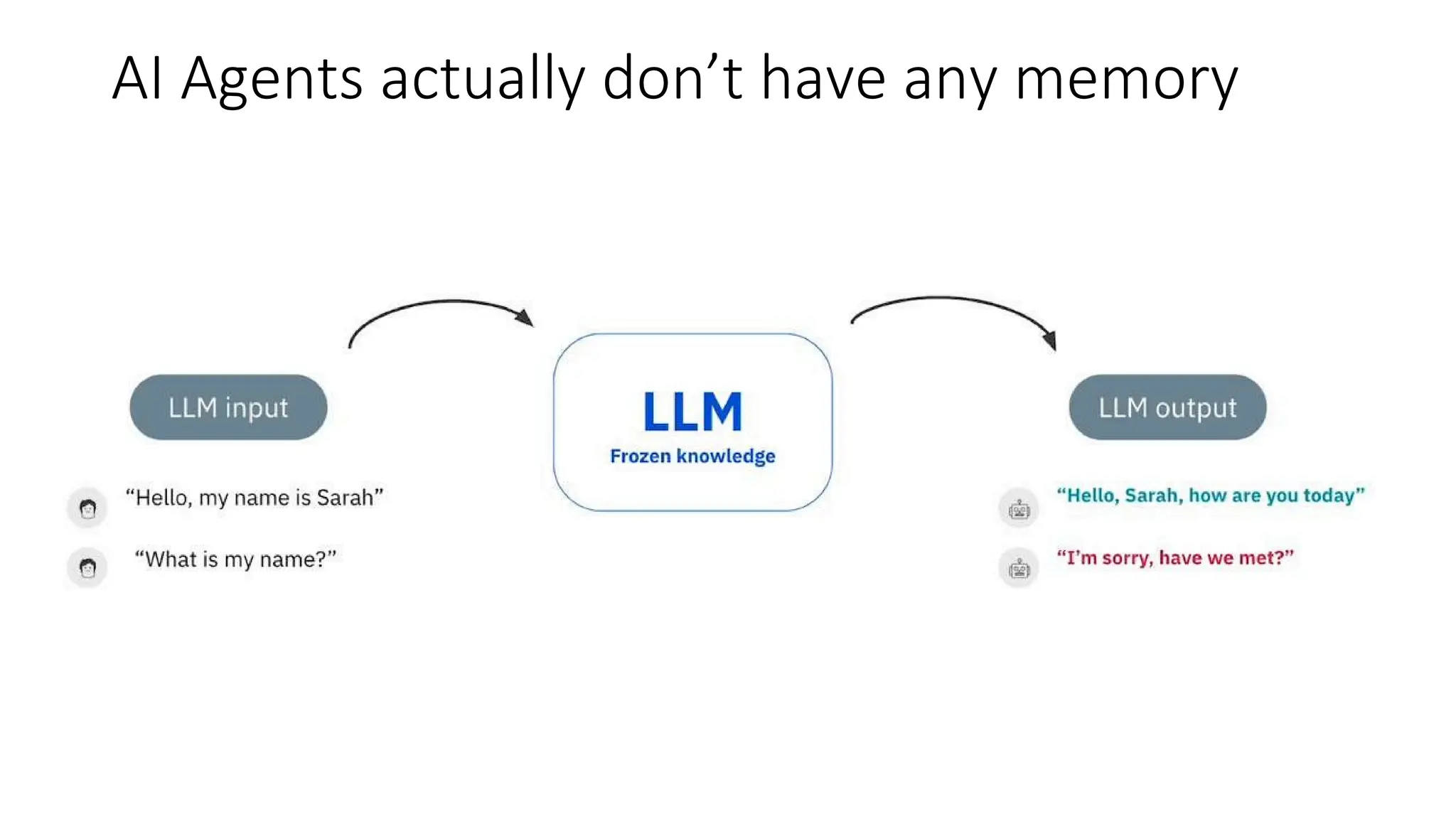
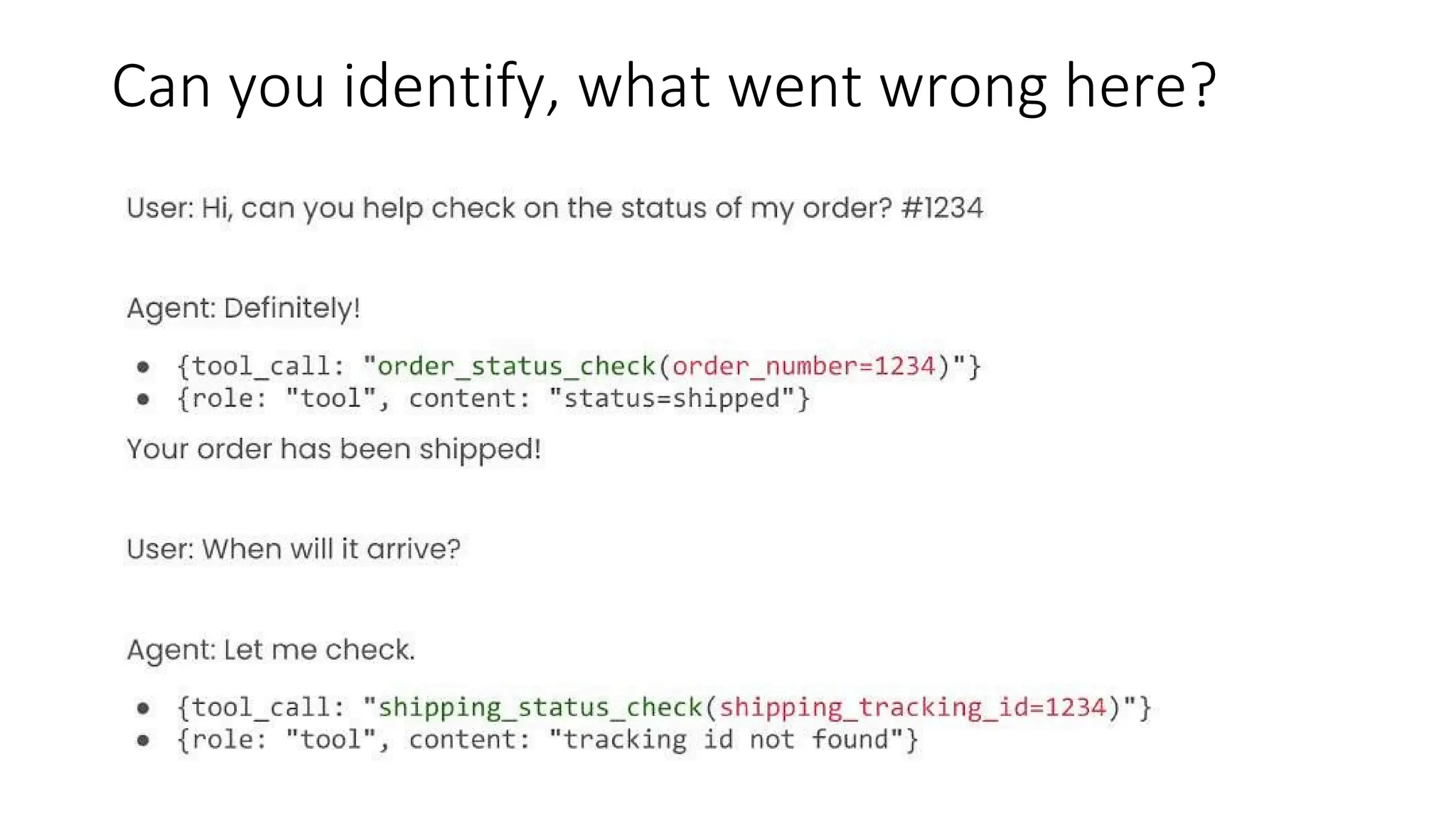
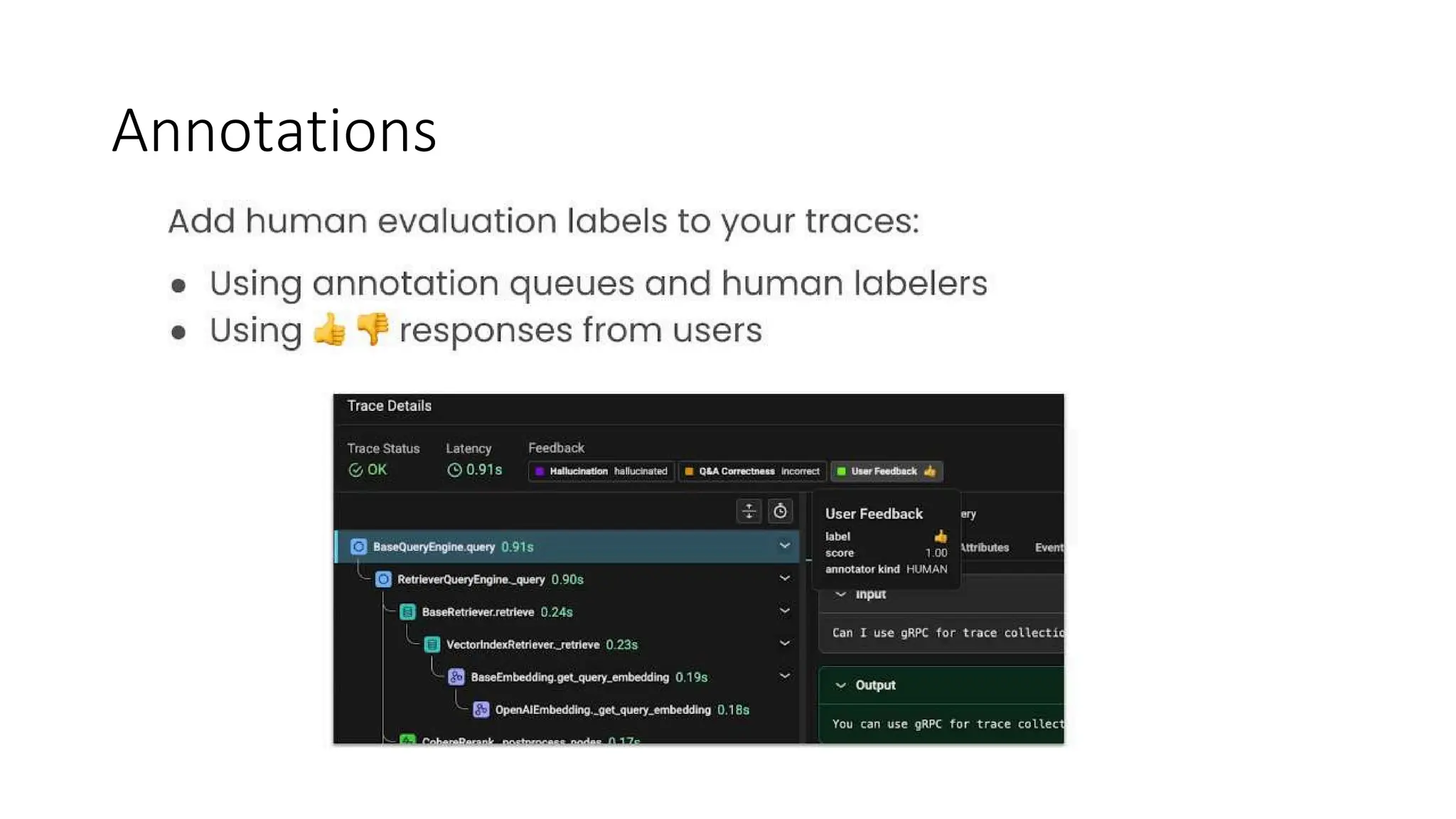
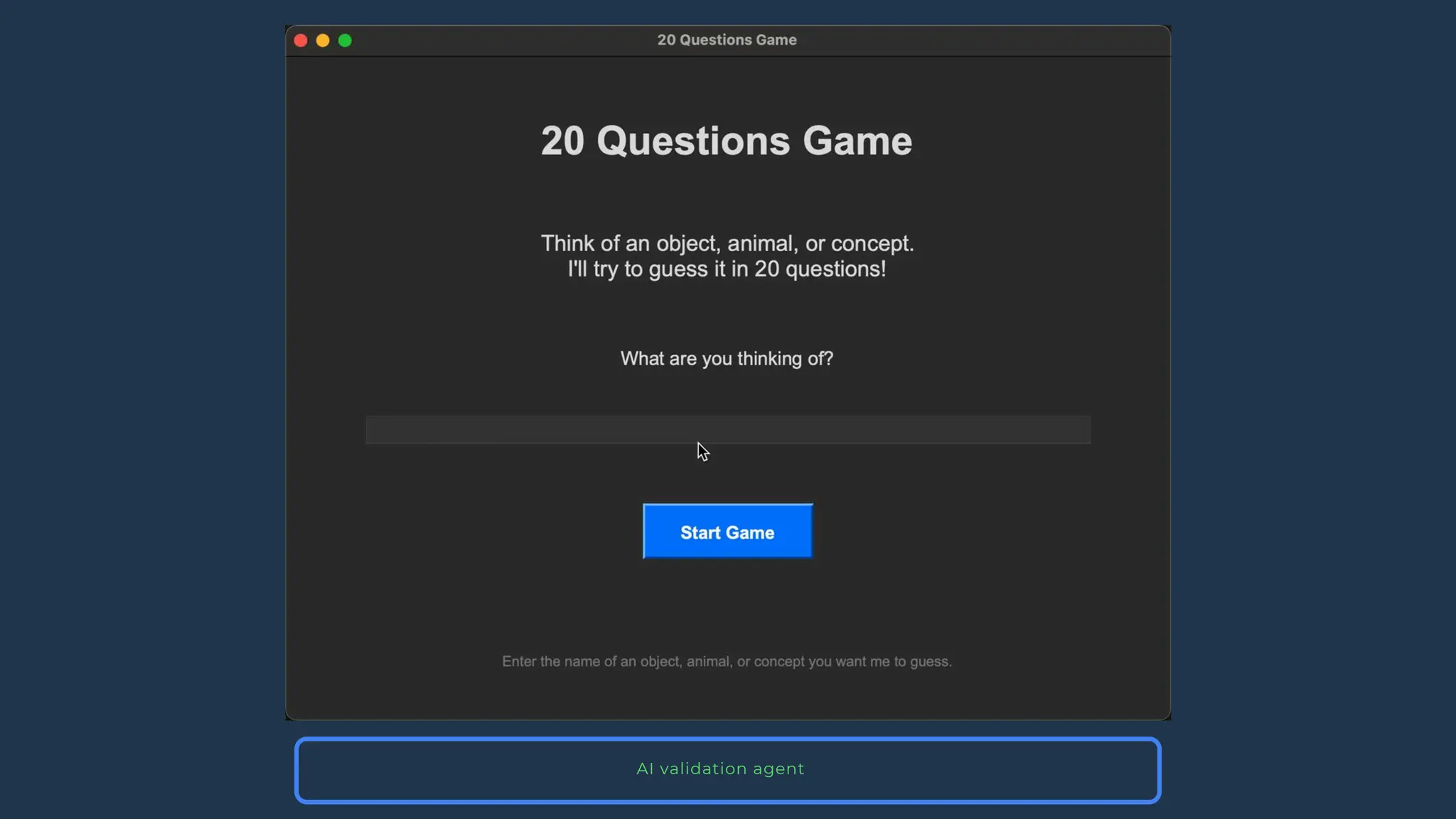
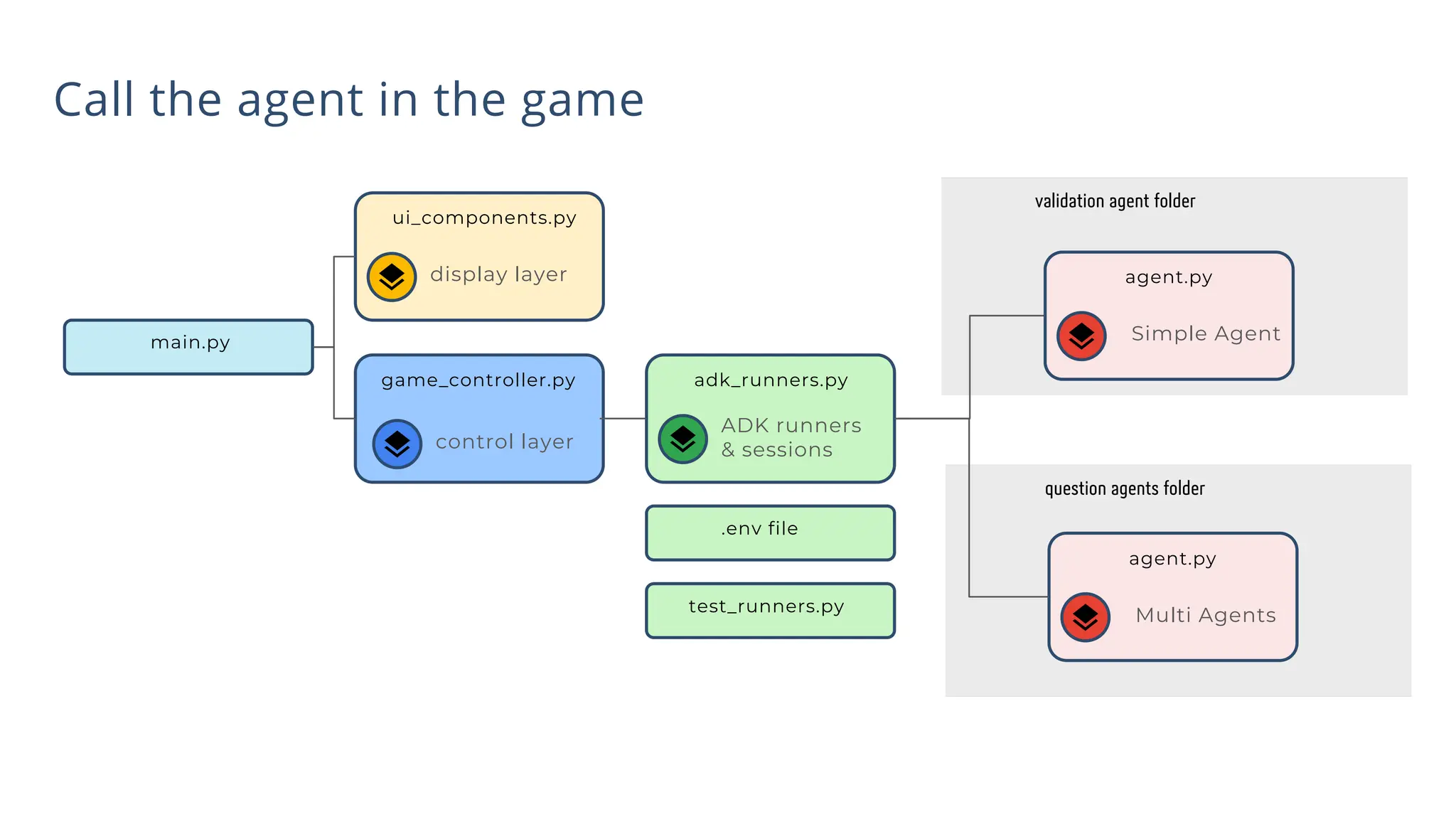
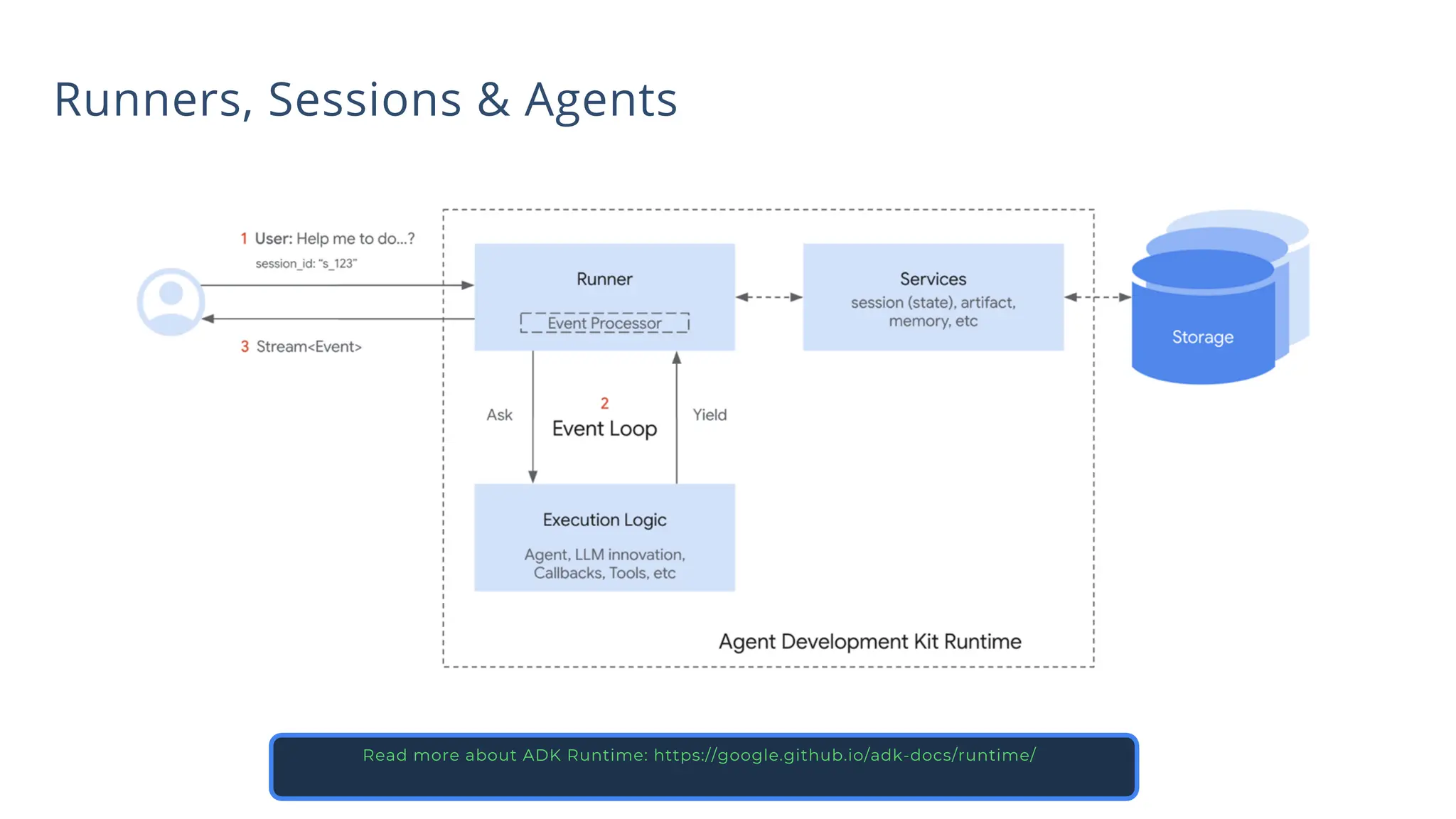
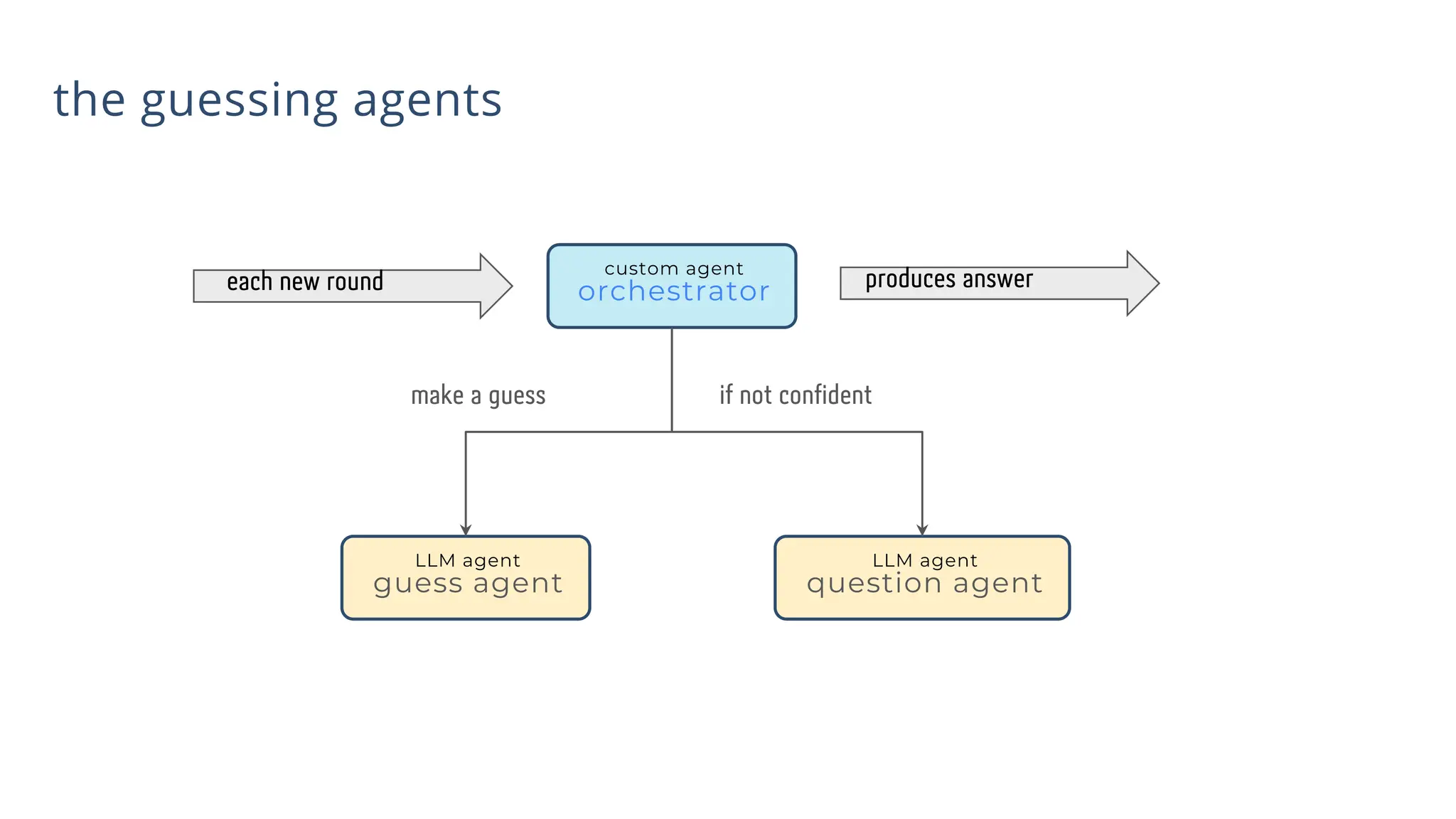
All the DEVFEST Baku 2025 presentations that the speakers shared with us are collected here. Some of them may be missing because not all speakers have shared their presentations.
Berat Göktuğ Özdemir's presentation -> https://medium.com/teamkraken/using-firebase-remote-config-in-flutter-dec10d712c68
https://medium.com/teamkraken/flutterda-firebase-remote-config-kullan%C4%B1m%C4%B1-484c4ffe9666

























































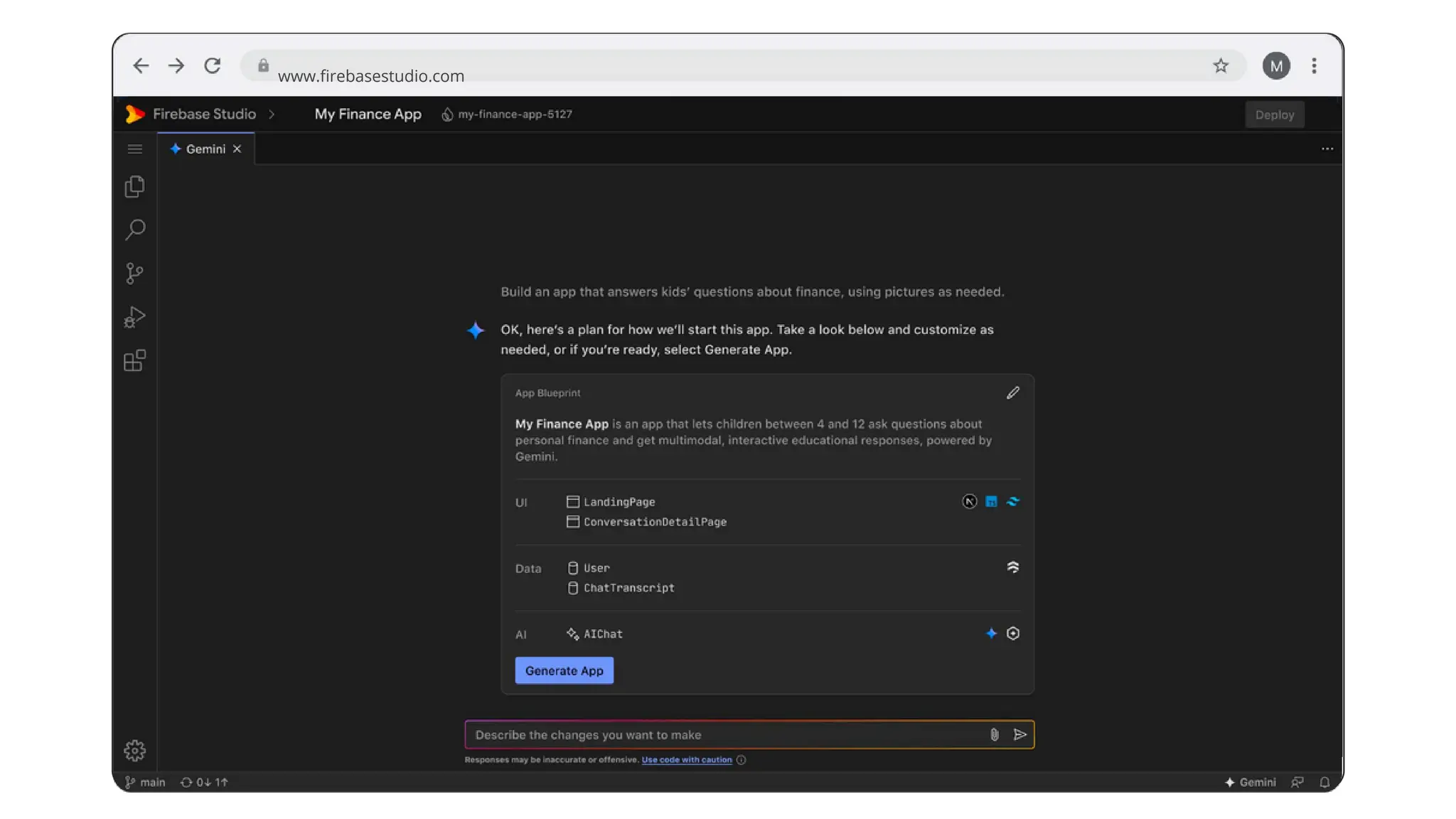



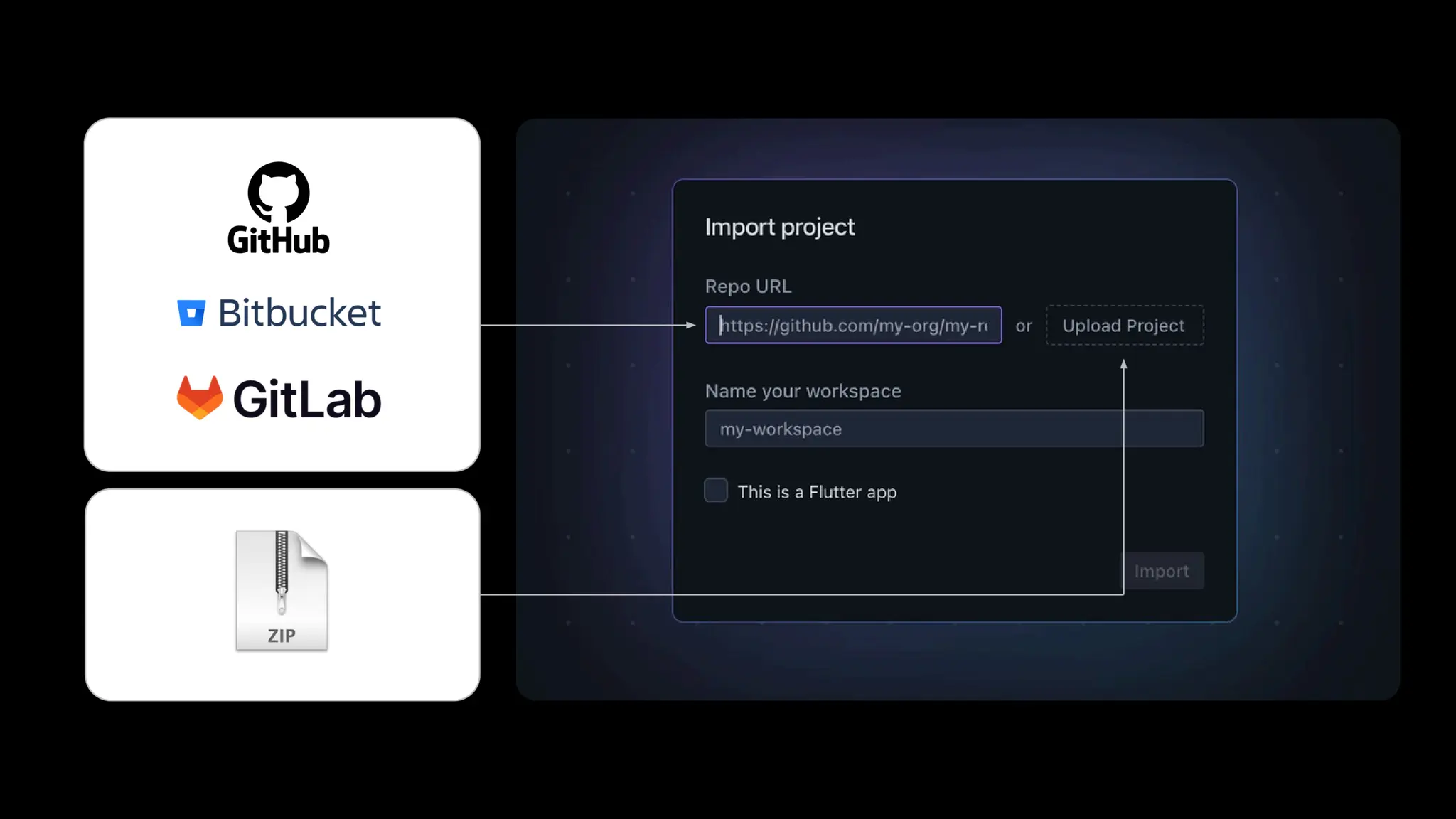
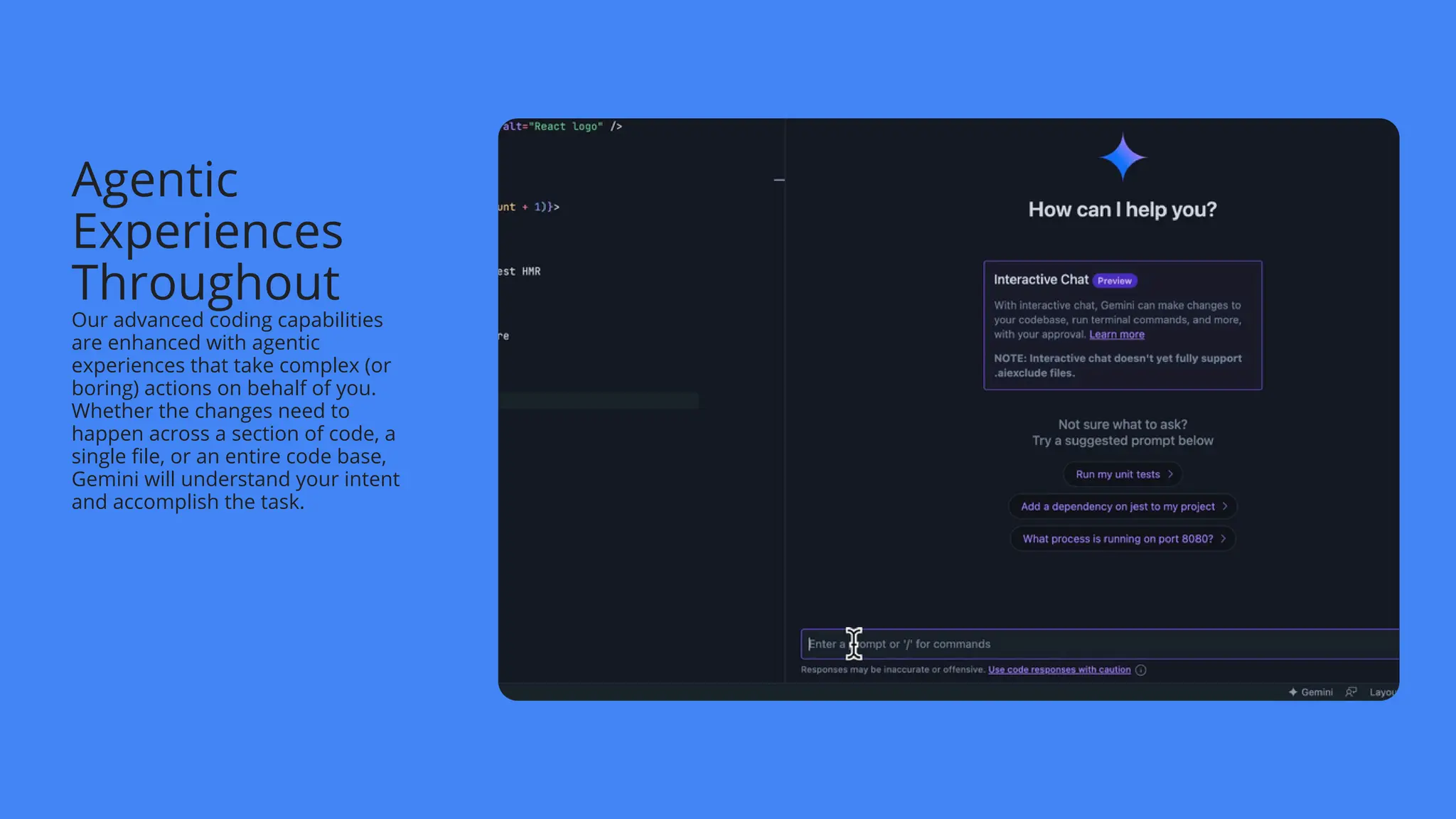

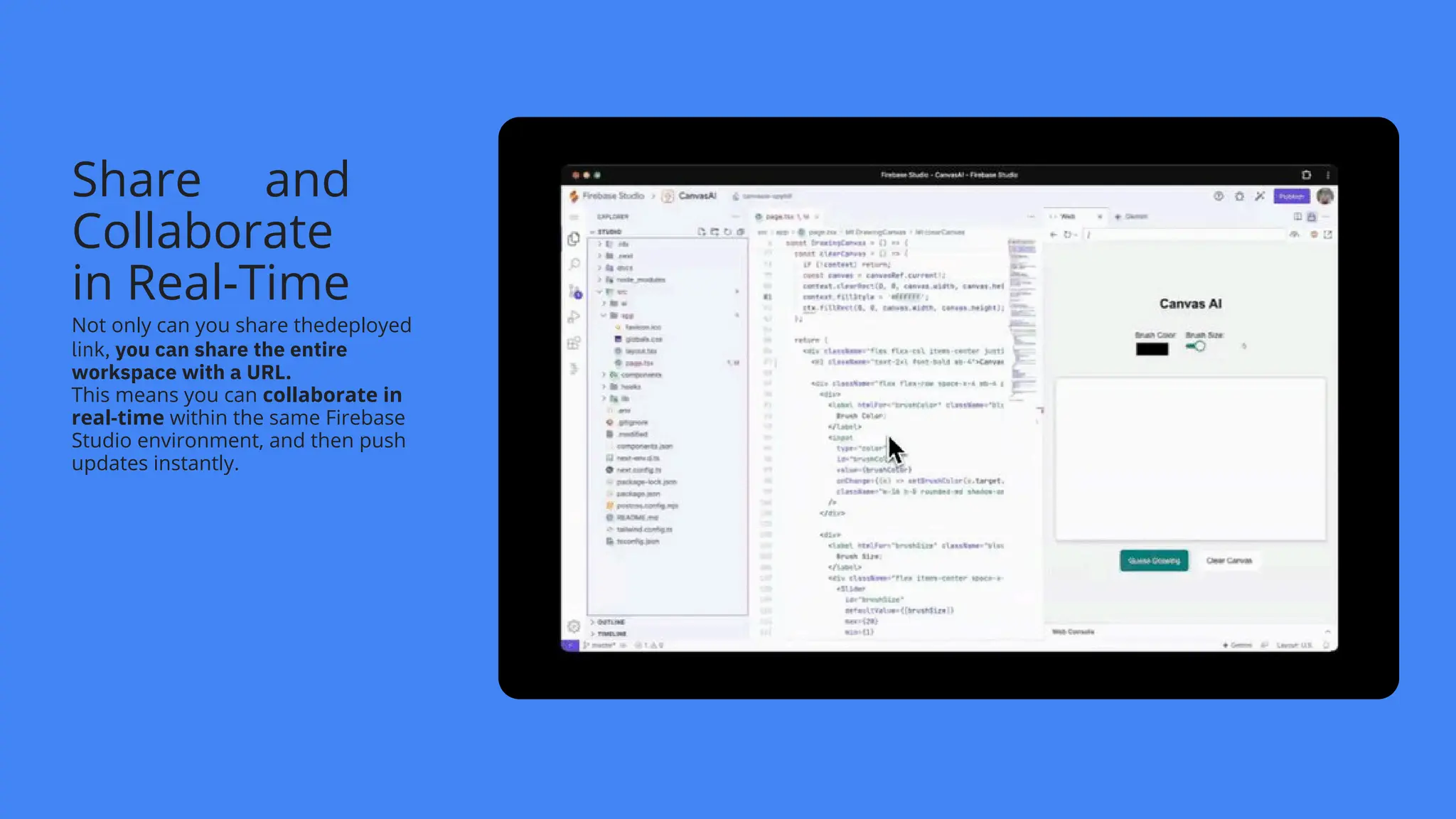
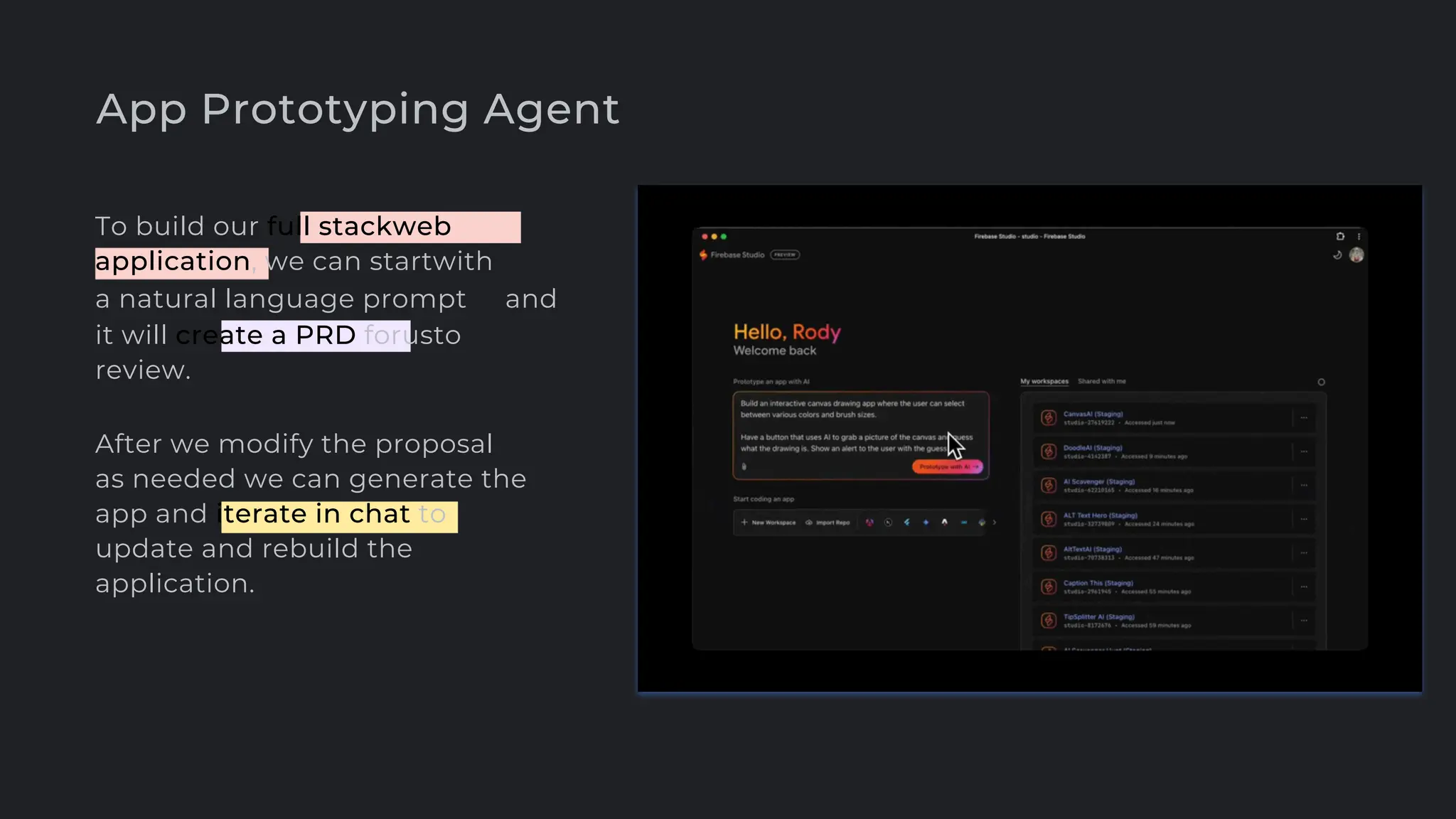

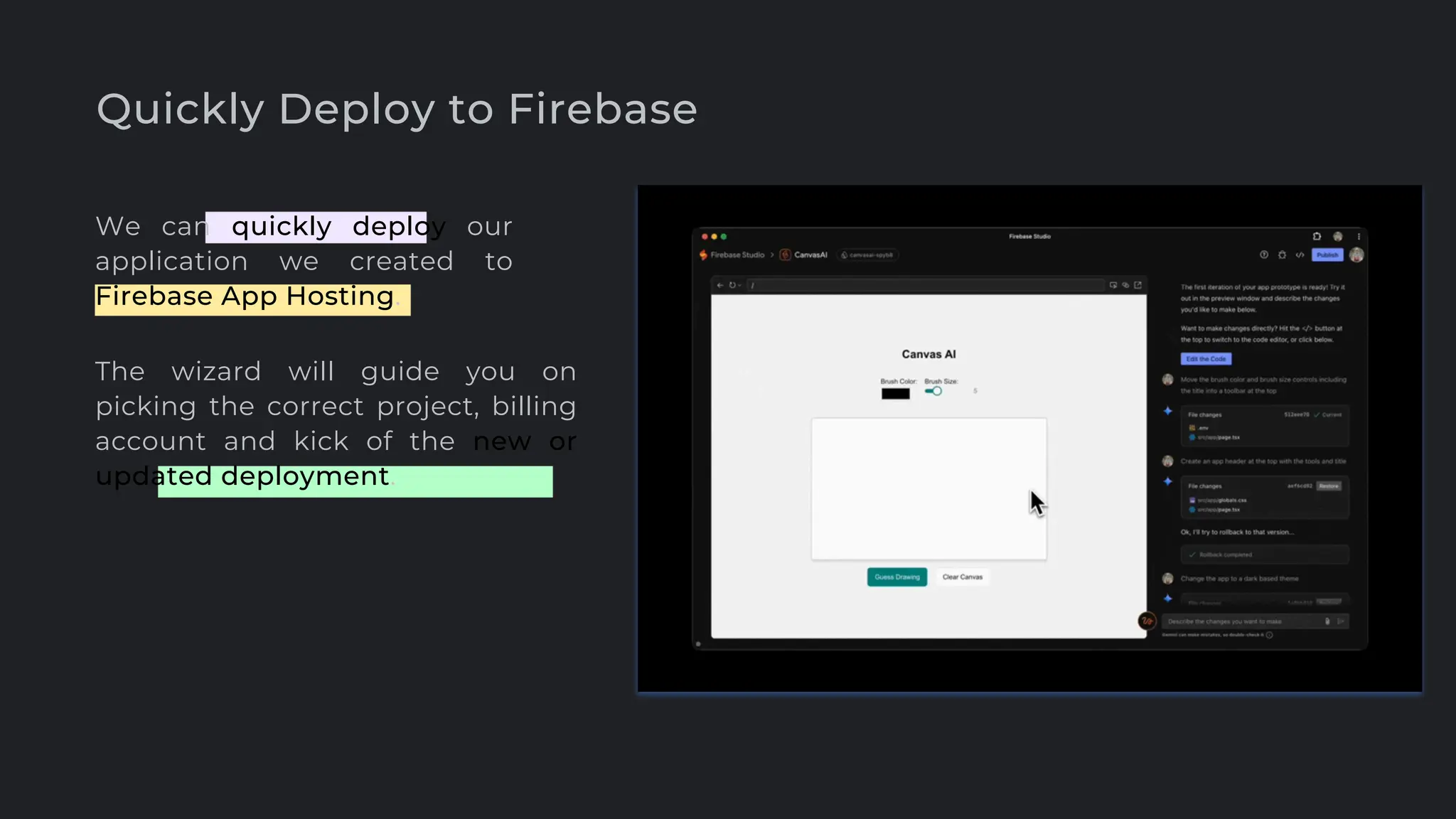


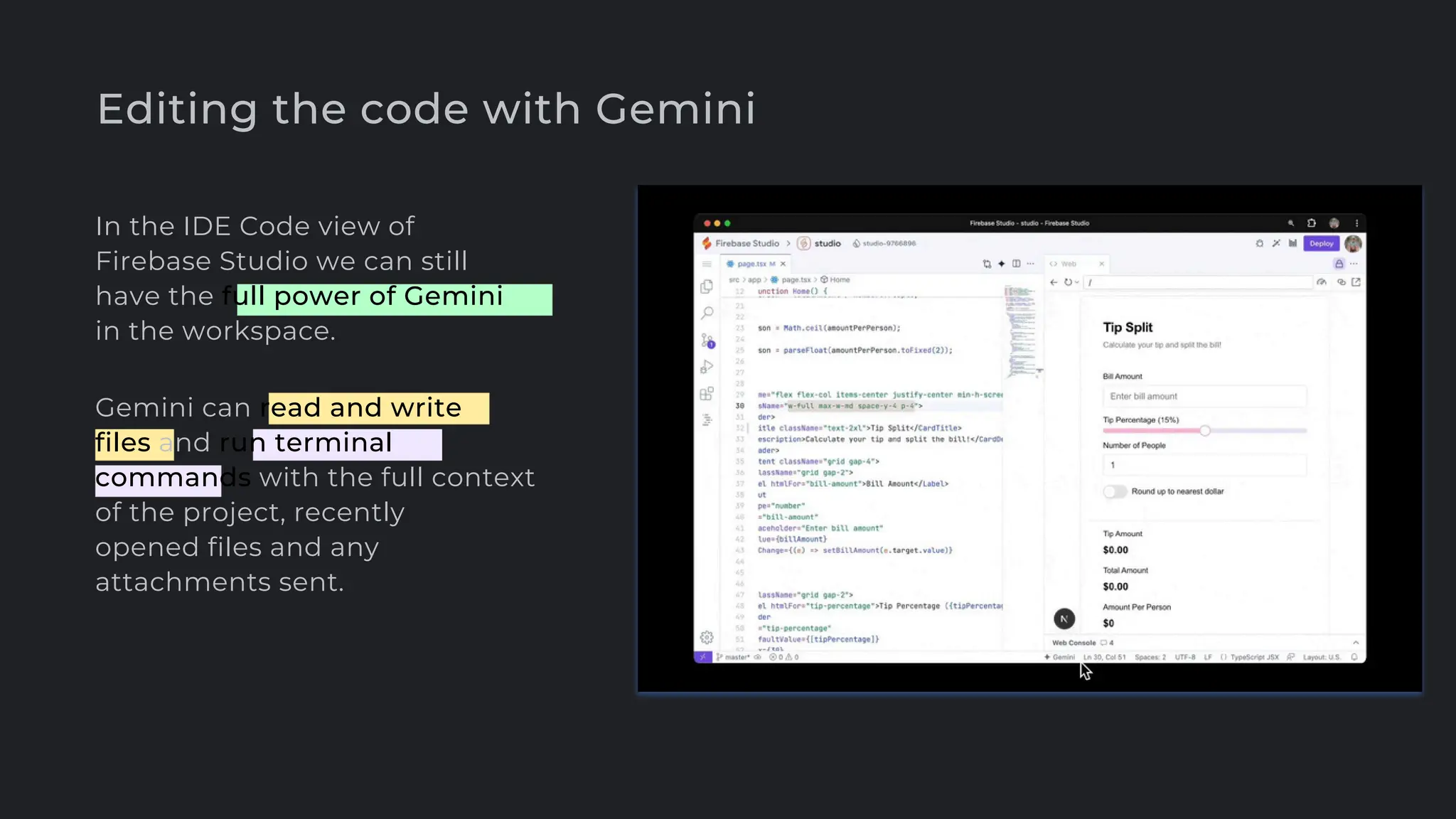










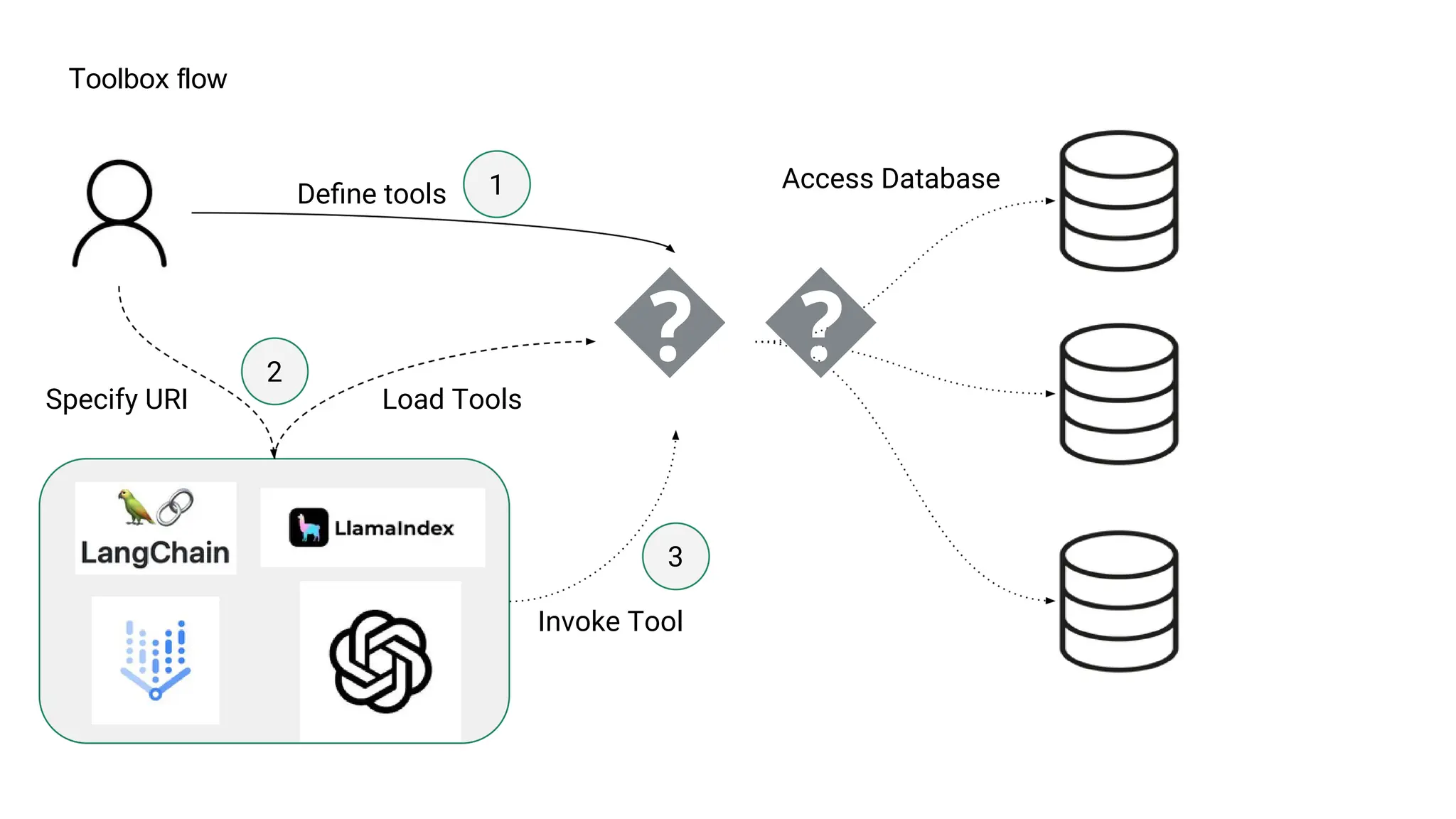
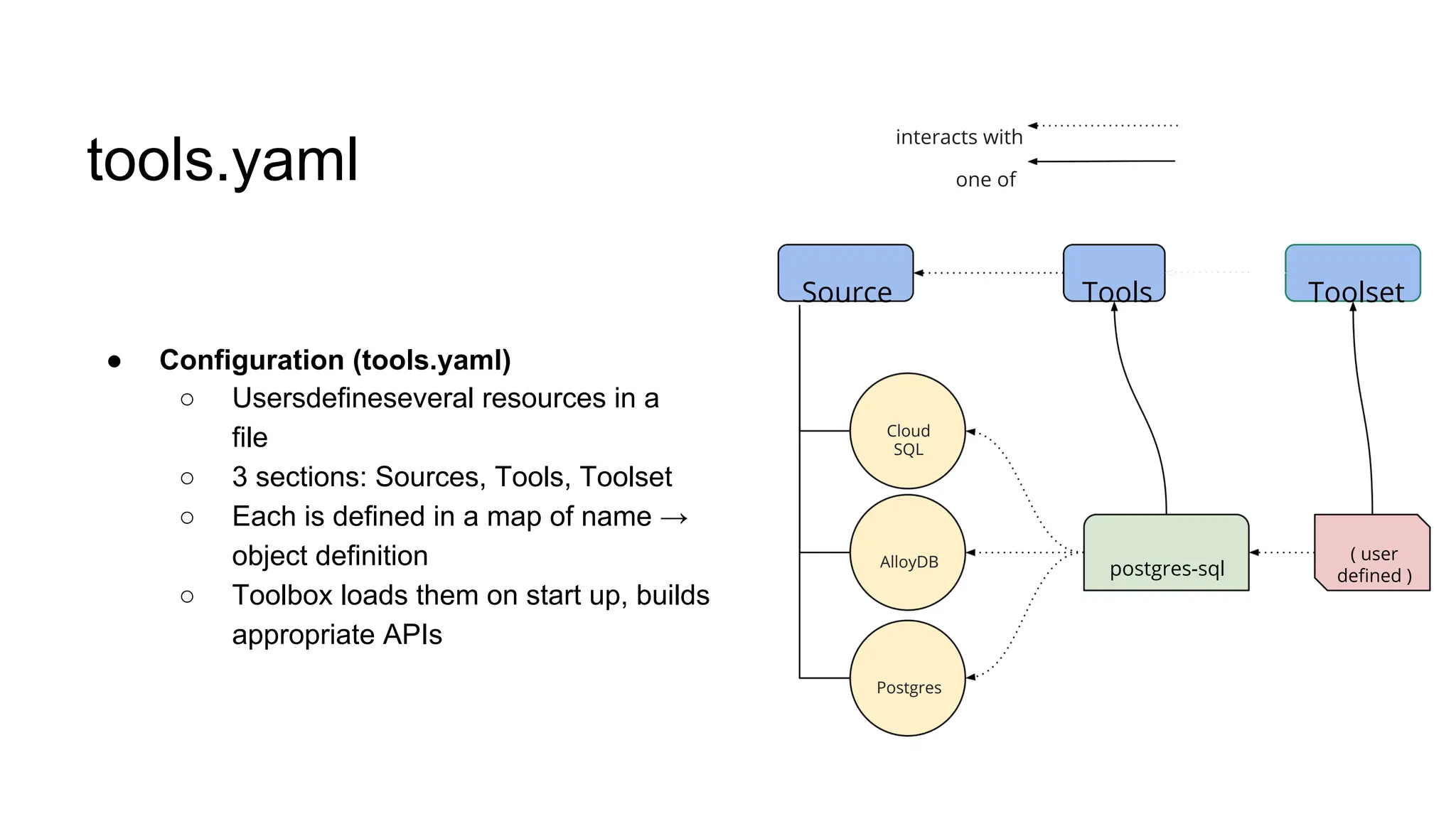
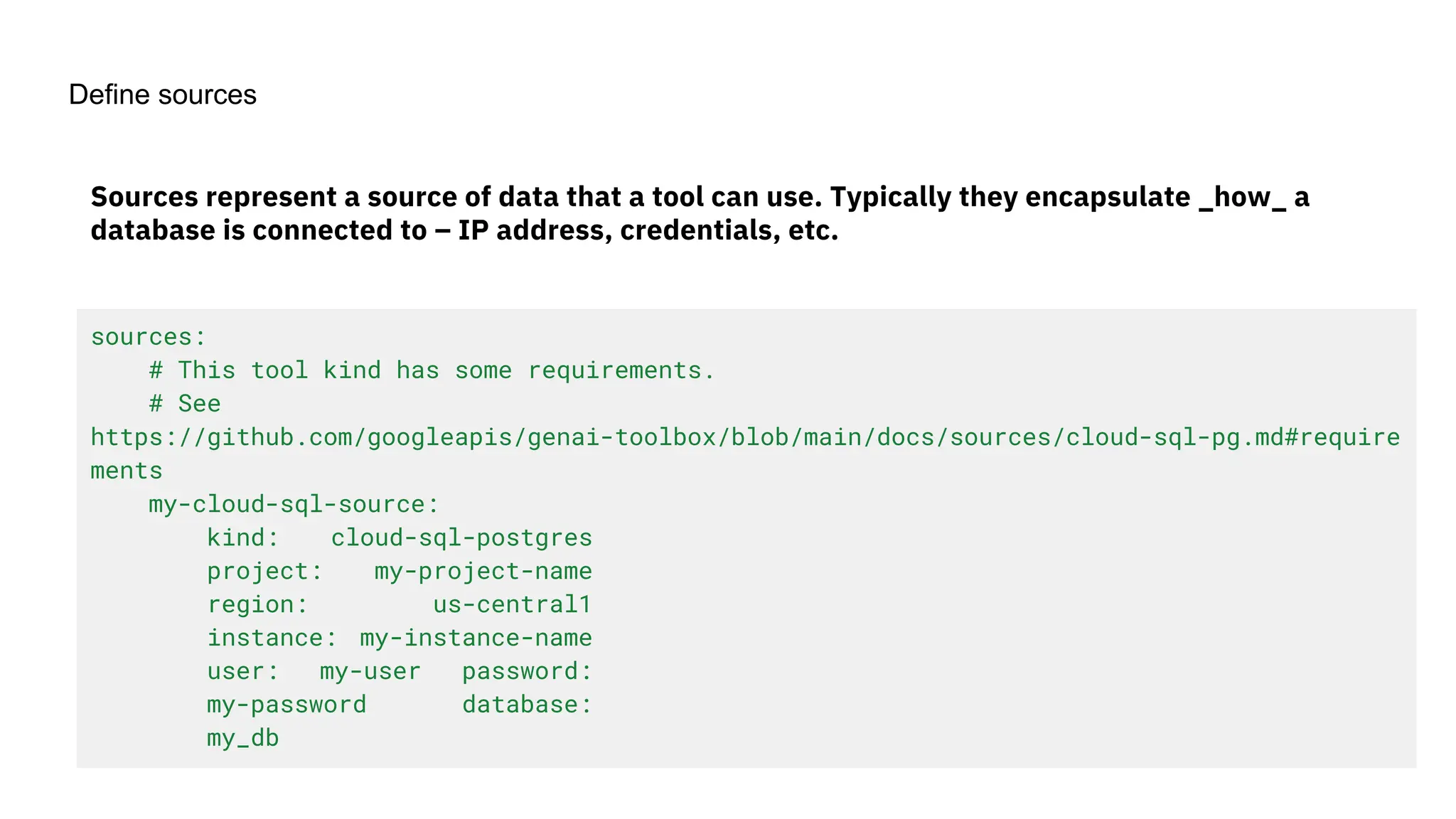


















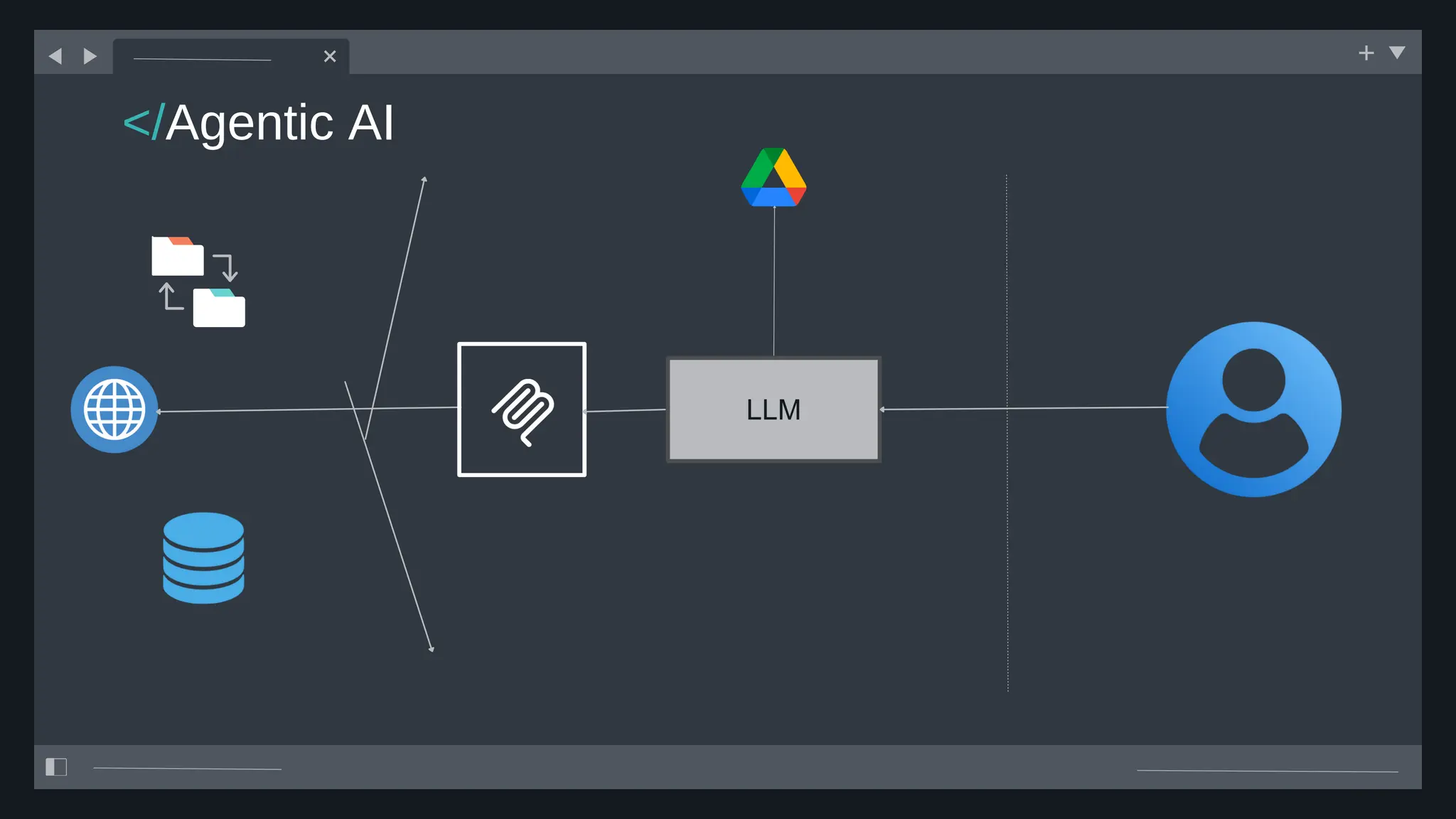



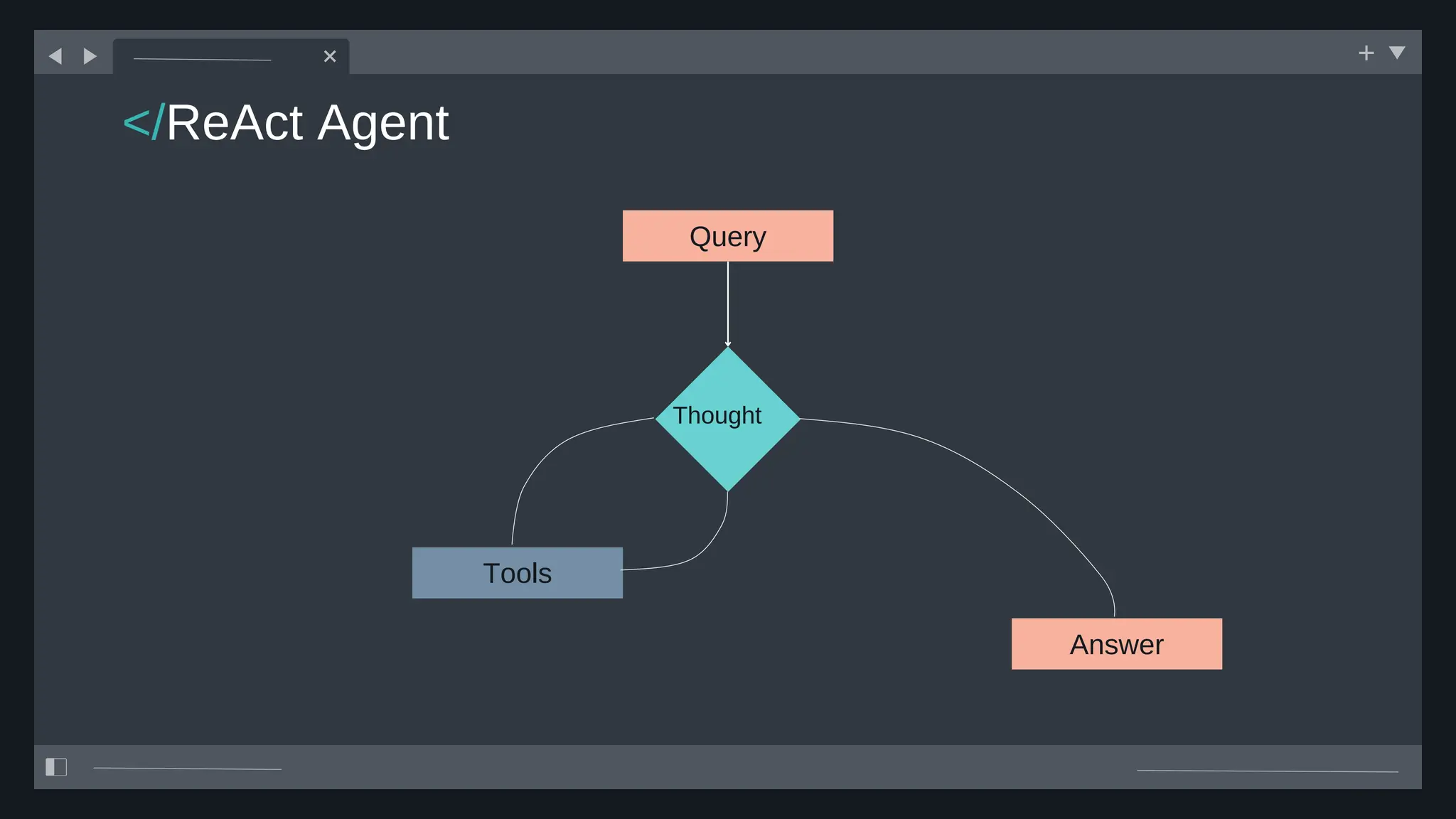





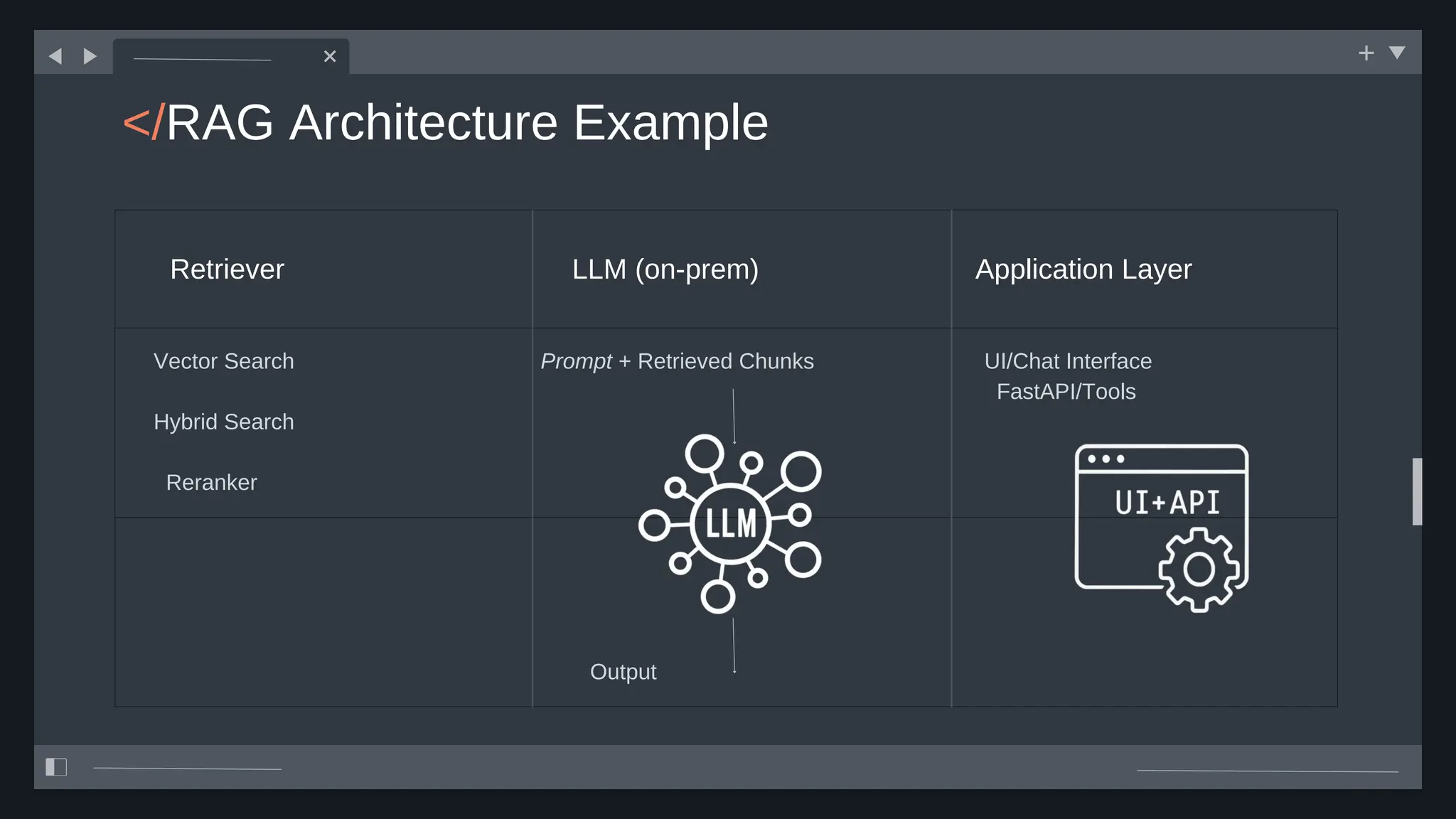

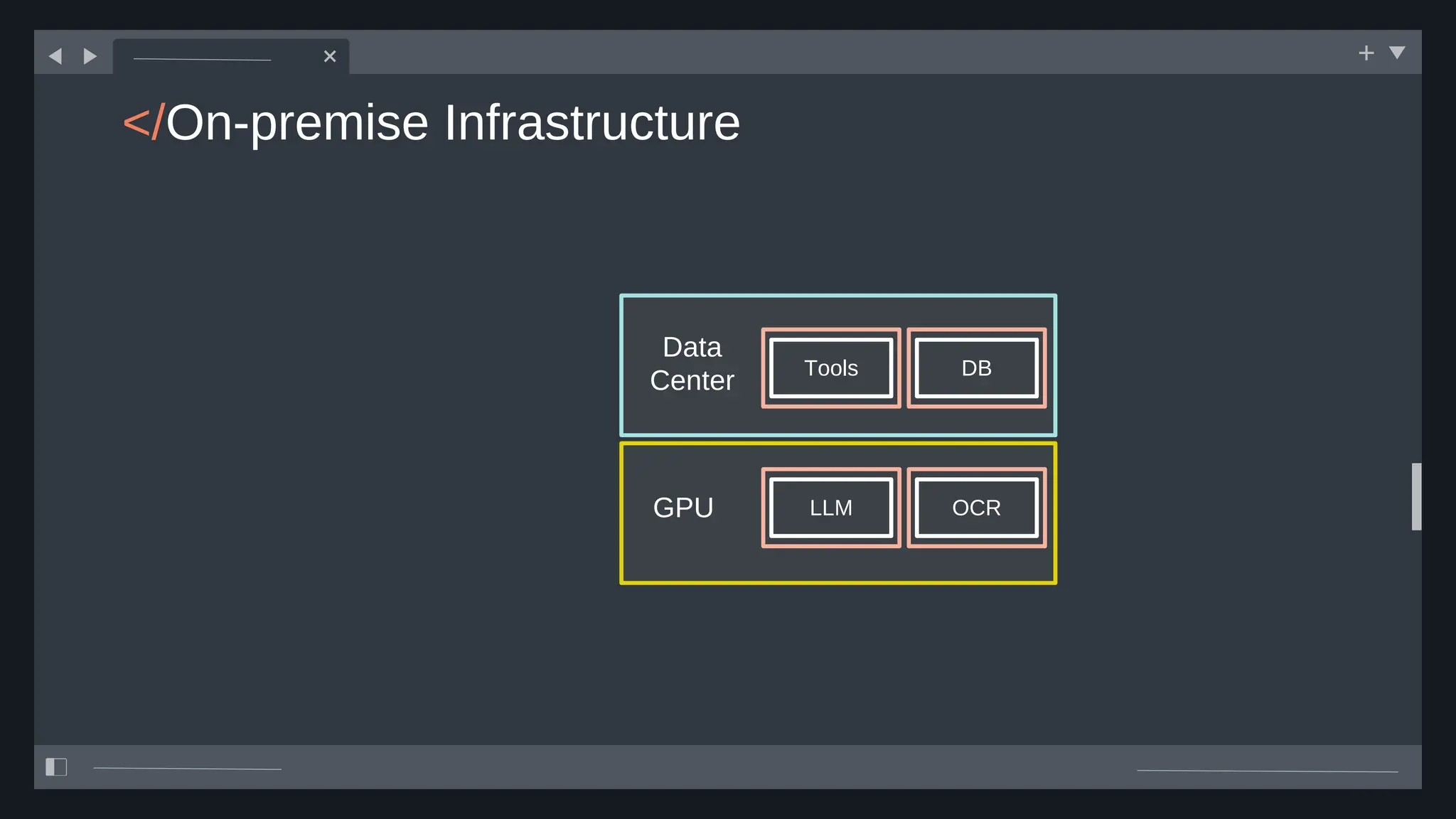

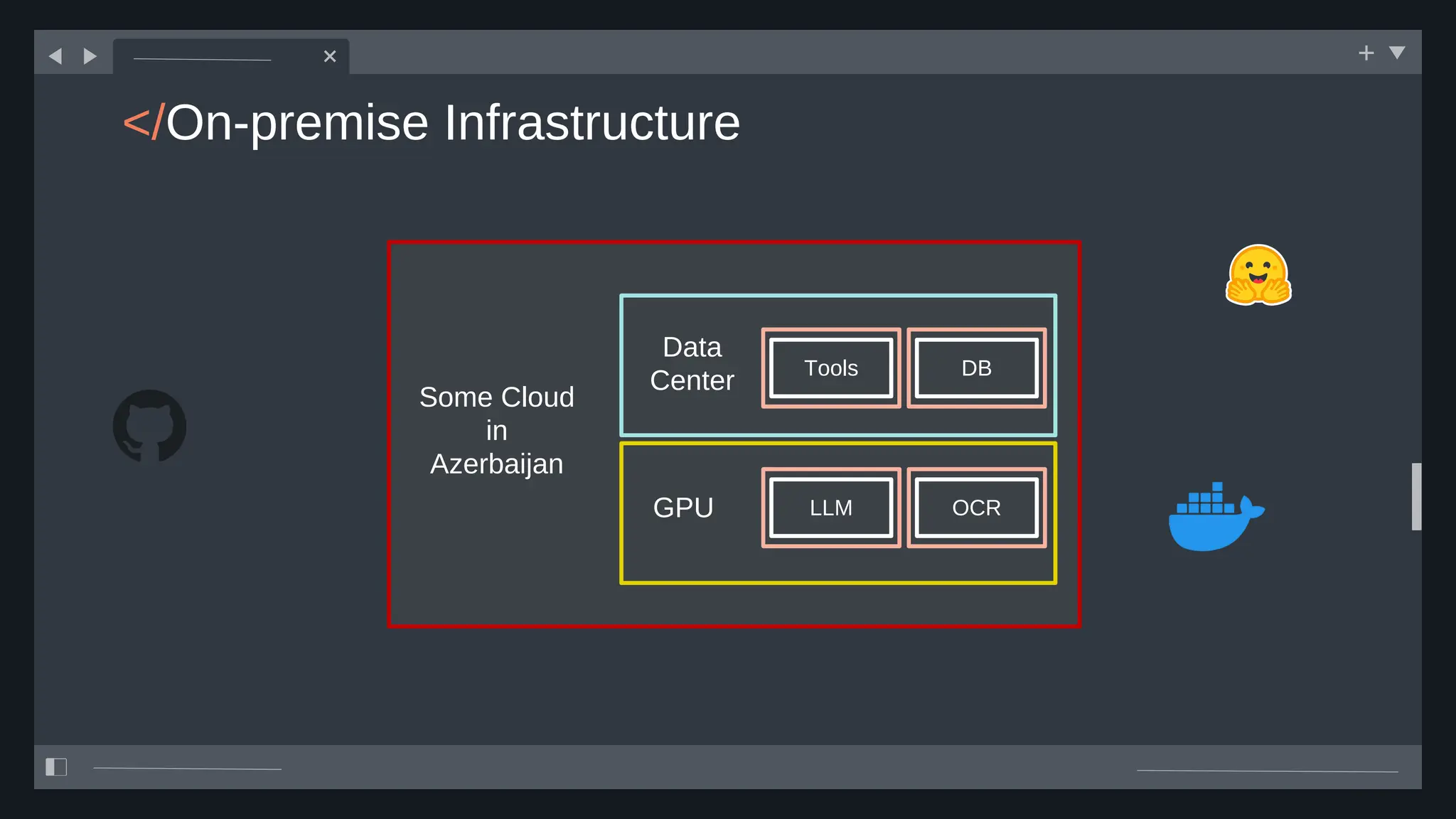




































































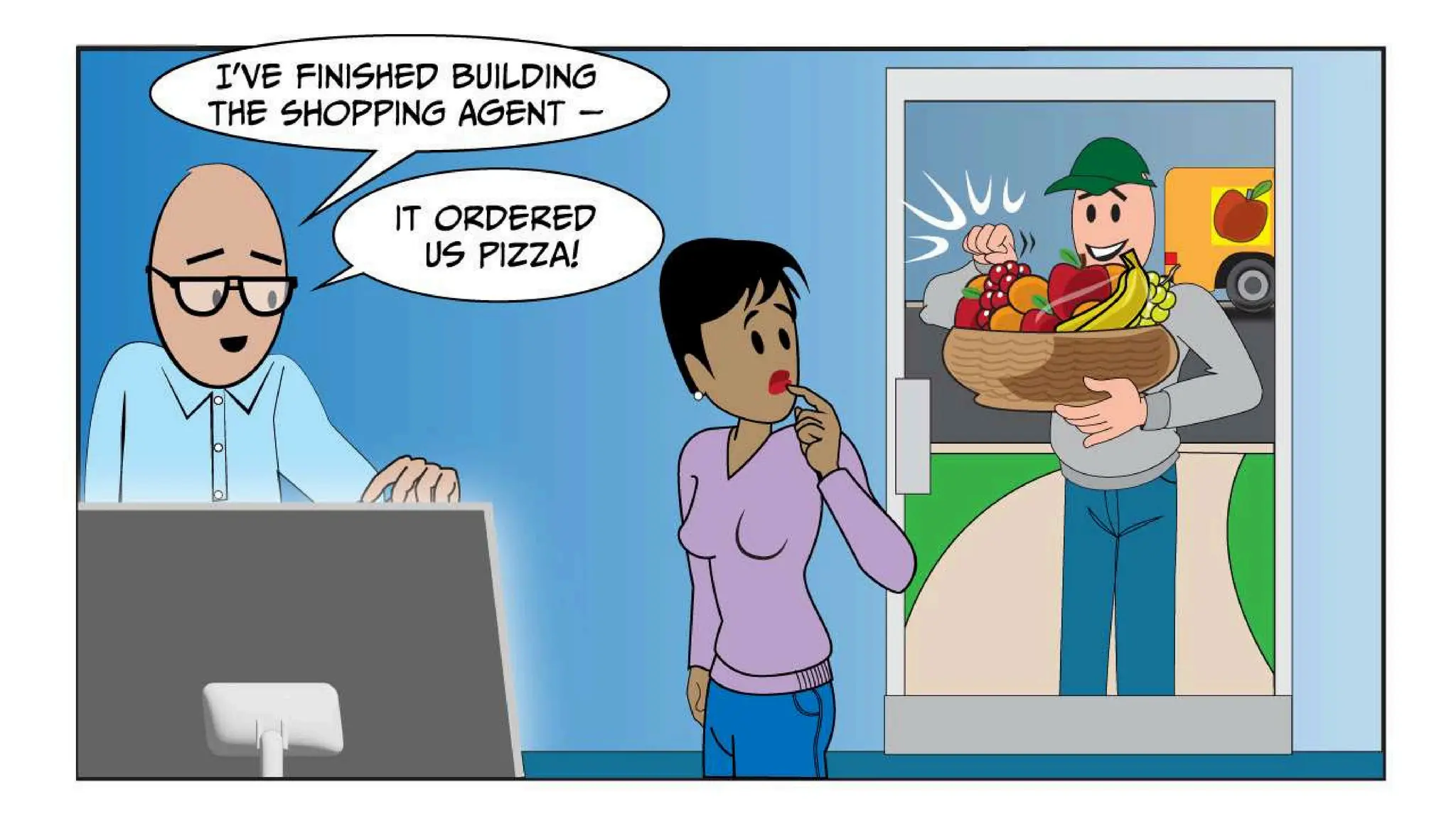






















![create
the Agent
creating the agent using
ADK command line interface
> adk create [agent_name]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ilovepdfmerged3-251125193517-47d6289e/75/DevFest-Baku-2025-Speaker-Presentations-Software-AI-Workshop-tracks-279-2048.jpg)

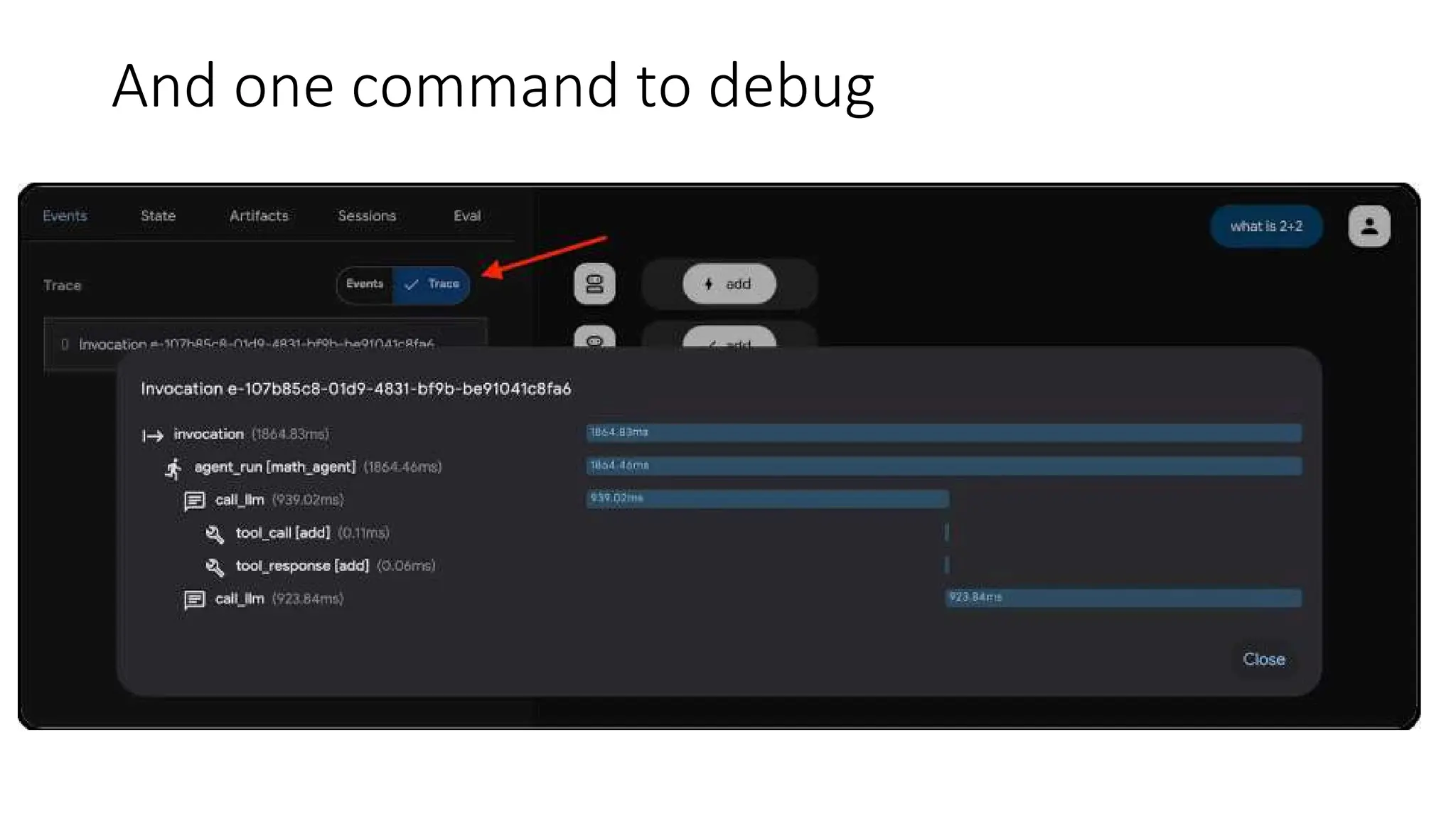
![debug
the Agent
debugging the agent
in browser
debugging the agent using
ADK command line interface
> adk web
> adk run [agent_name]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ilovepdfmerged3-251125193517-47d6289e/75/DevFest-Baku-2025-Speaker-Presentations-Software-AI-Workshop-tracks-281-2048.jpg)

![if(event.is_final_response()):
logger.debug(event.content.parts[0].text)
return json.loads(event.content.parts[0].text)
else:
pass
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error during validation: {e}")
return None
async def validate_input(self,user_input="elephant"):
try:
asyncforevent inself.validation_agent_runner.run_async(
user_id="test_user",
session_id=self.validation_agent_session.id,
new_message=types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=user_input)])
):
https://github.com/yoyu777/adk-game-demo-public/blob/main/adk_runners.py](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ilovepdfmerged3-251125193517-47d6289e/75/DevFest-Baku-2025-Speaker-Presentations-Software-AI-Workshop-tracks-285-2048.jpg)

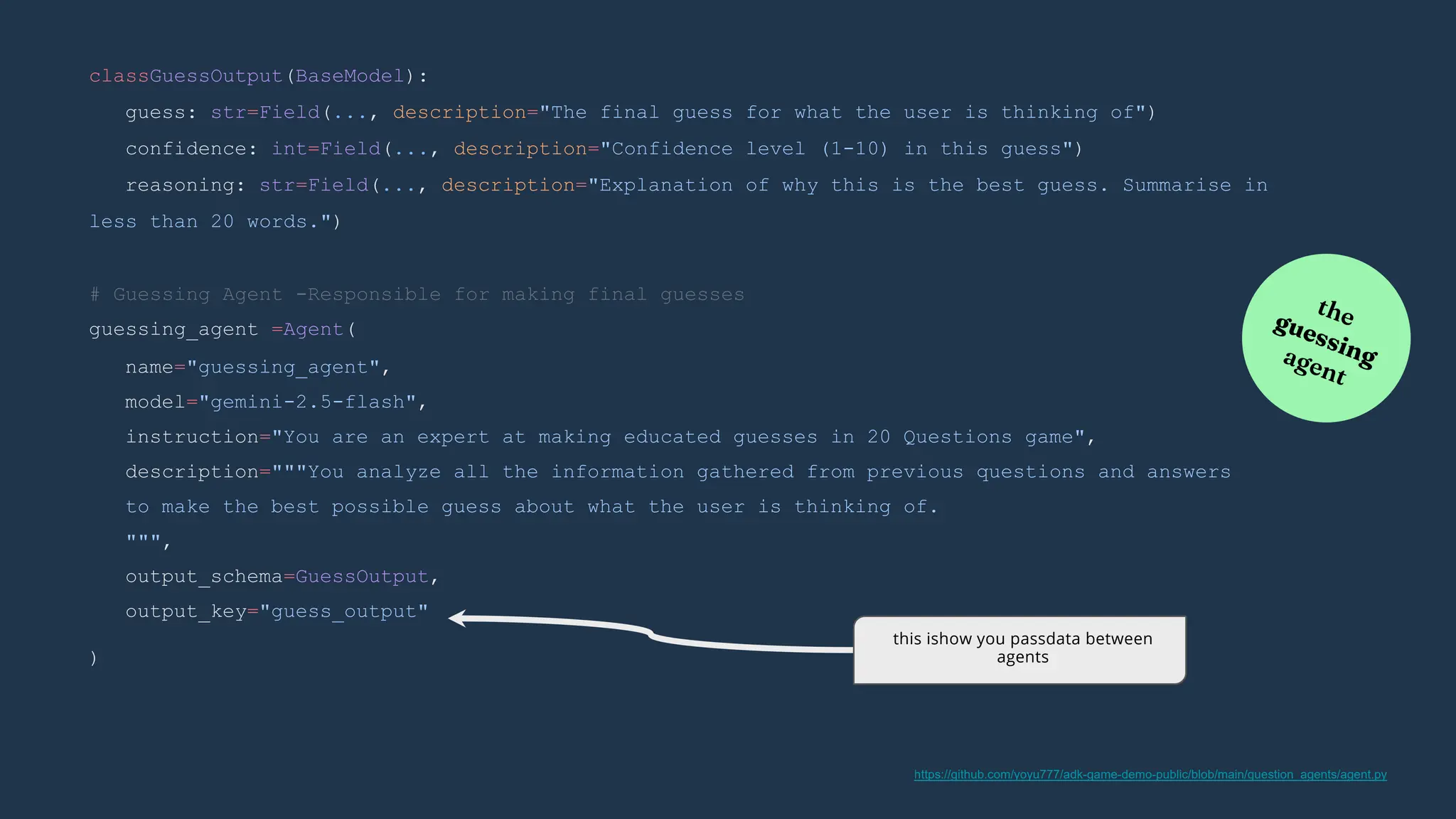
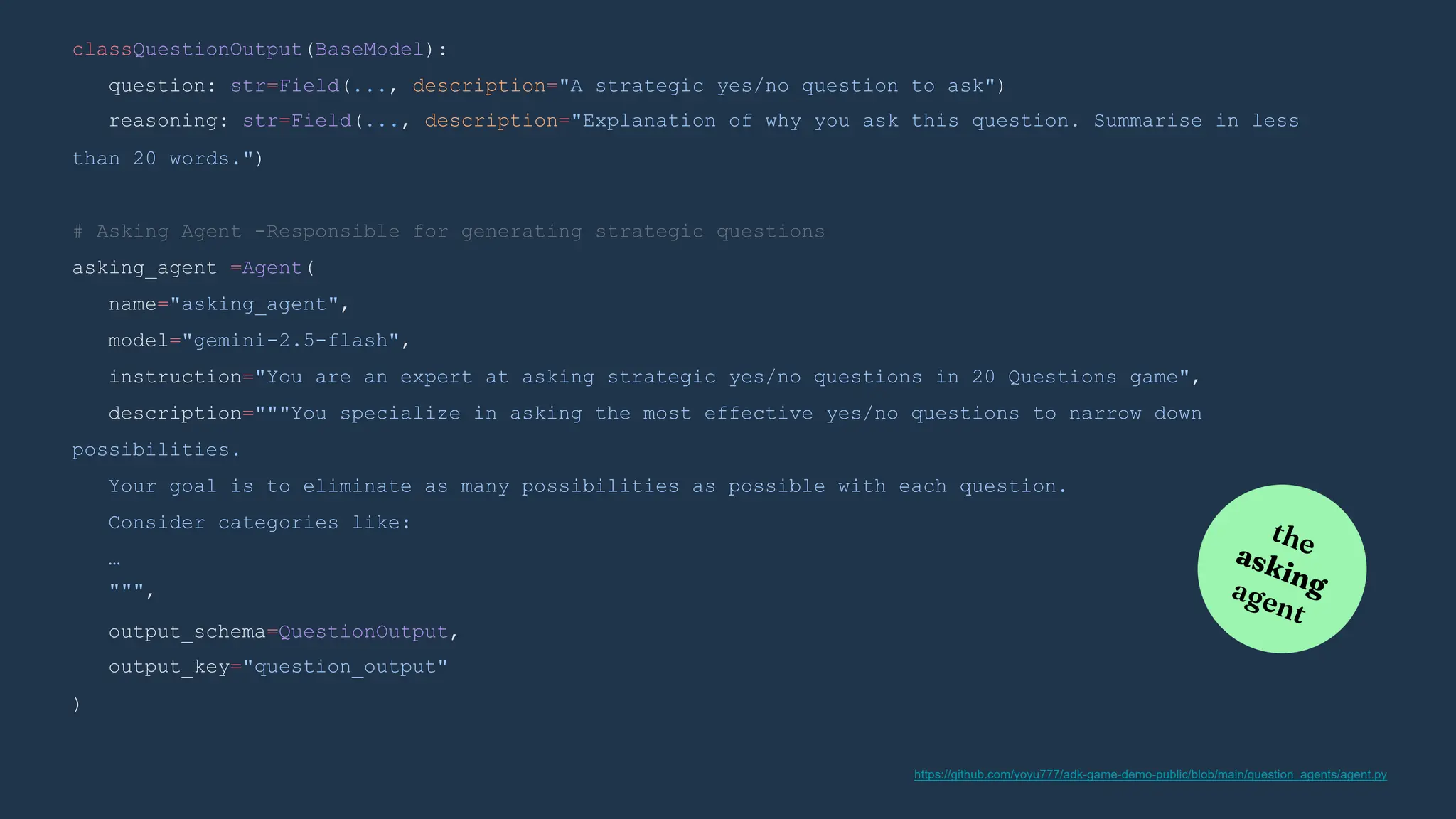

![)
(custom logic)
yield event
class RootAgent(BaseAgent):
guessing_agent:Agent
asking_agent:Agent
def __init__(self,name:str,guessing_agent:Agent,asking_agent:Agent):
async def _run_async_impl(
self,ctx: InvocationContext
)-> AsyncGenerator[Event, None]:
super().__init__(
name=name,
guessing_agent=guessing_agent,
asking_agent=asking_agent,
sub_agents=[guessing_agent,asking_agent]
generating a series of events
overriding implementation
extending BaseAgent class
https://github.com/yoyu777/adk-game-demo-public/blob/main/question_agents/agent.py](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ilovepdfmerged3-251125193517-47d6289e/75/DevFest-Baku-2025-Speaker-Presentations-Software-AI-Workshop-tracks-291-2048.jpg)