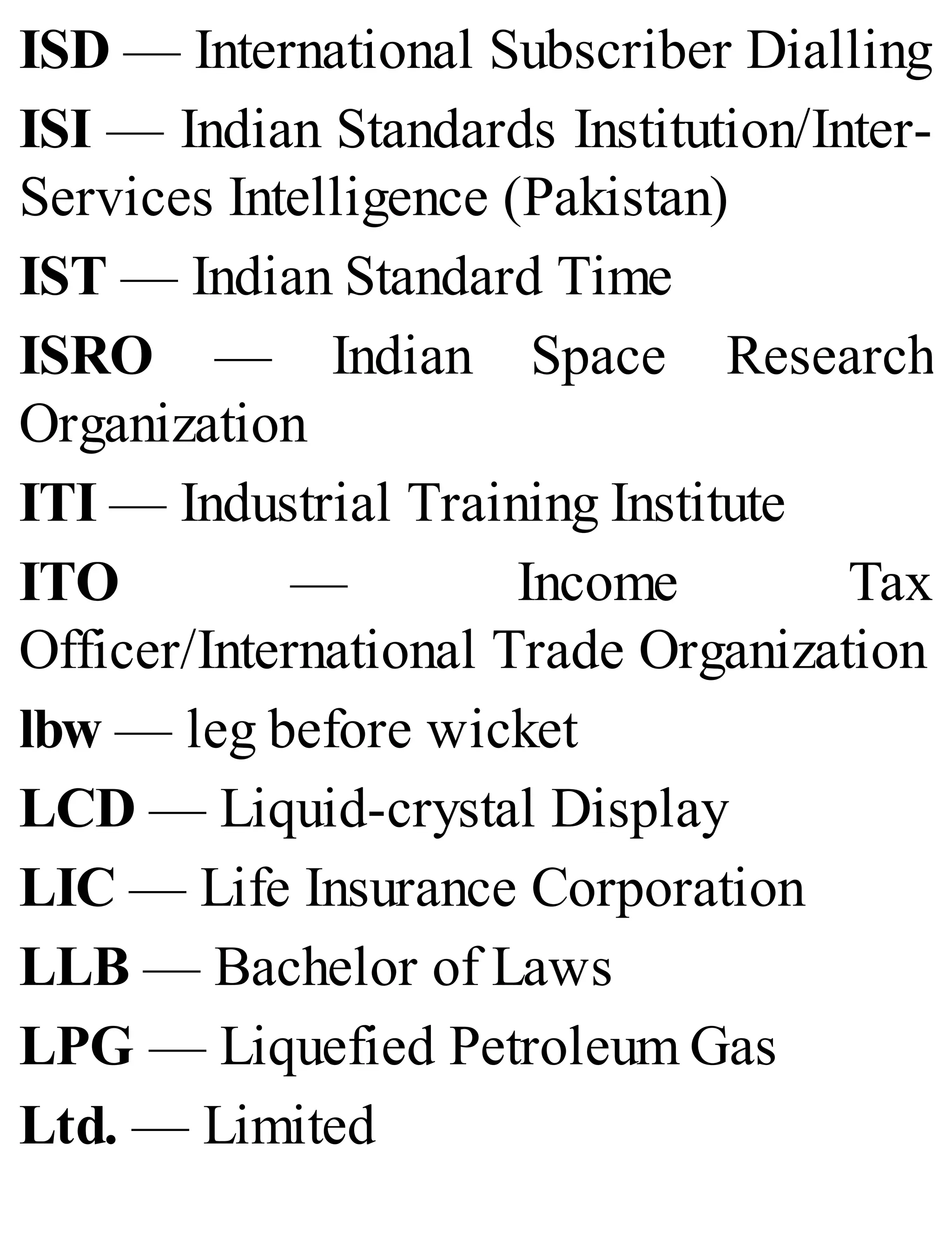
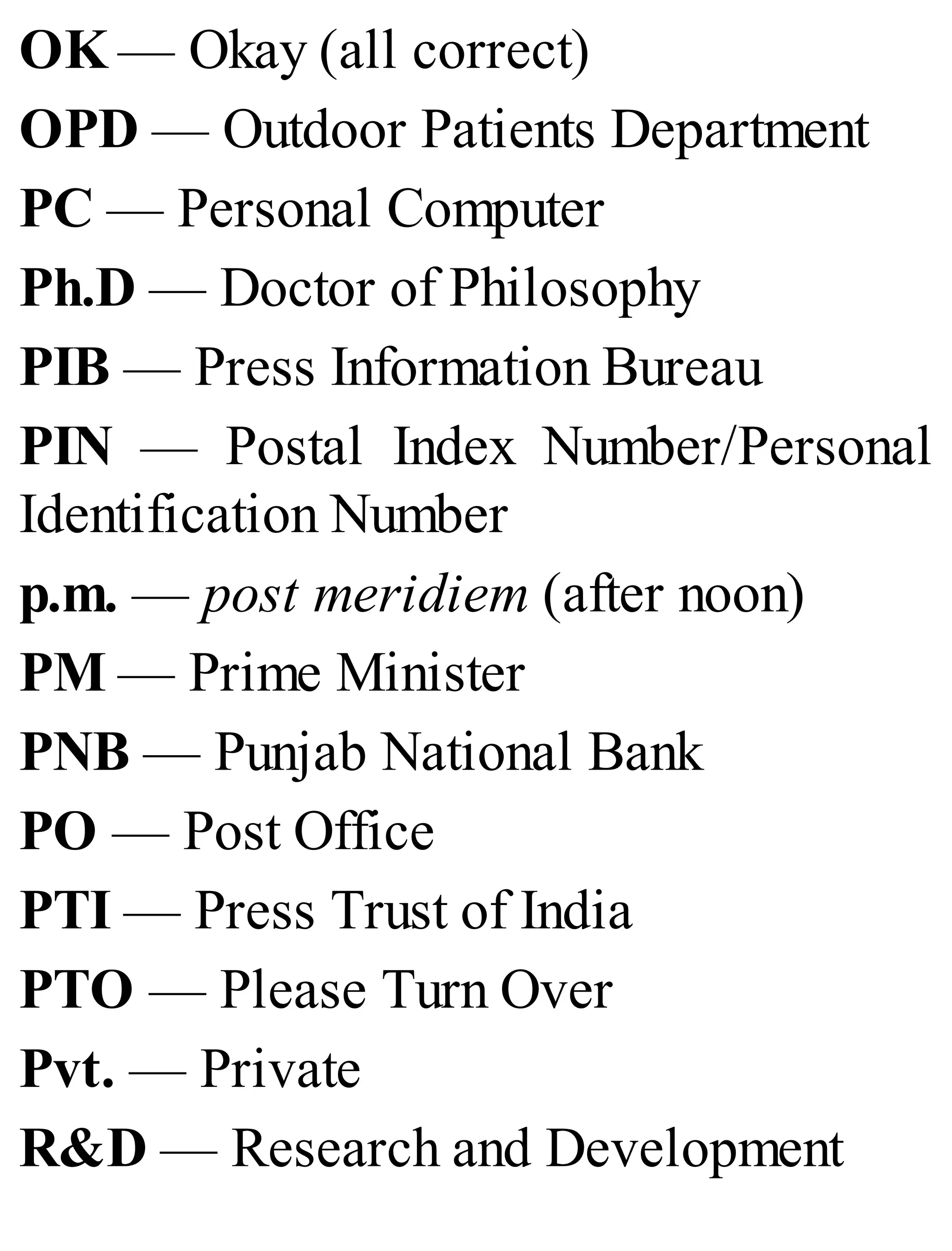
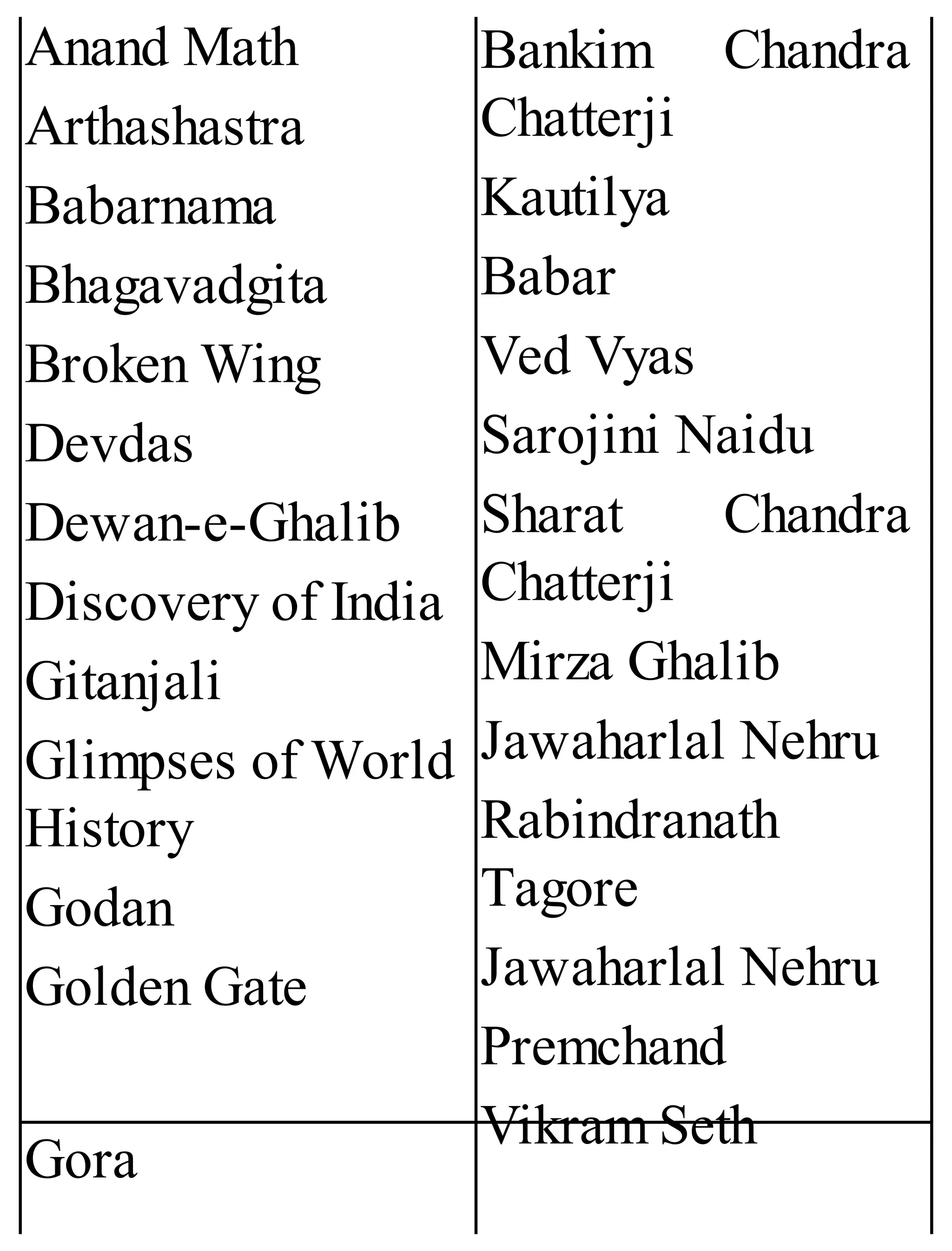
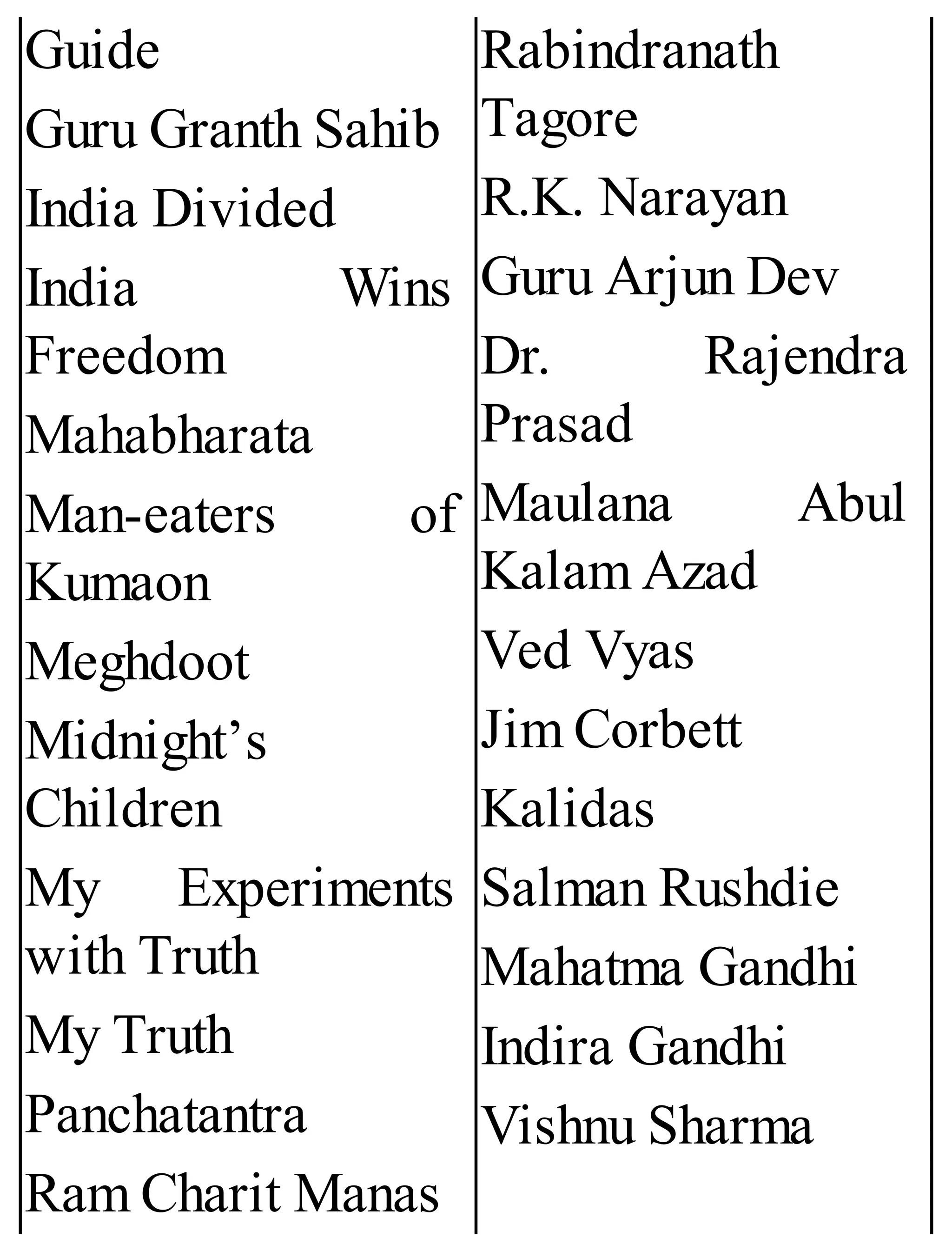
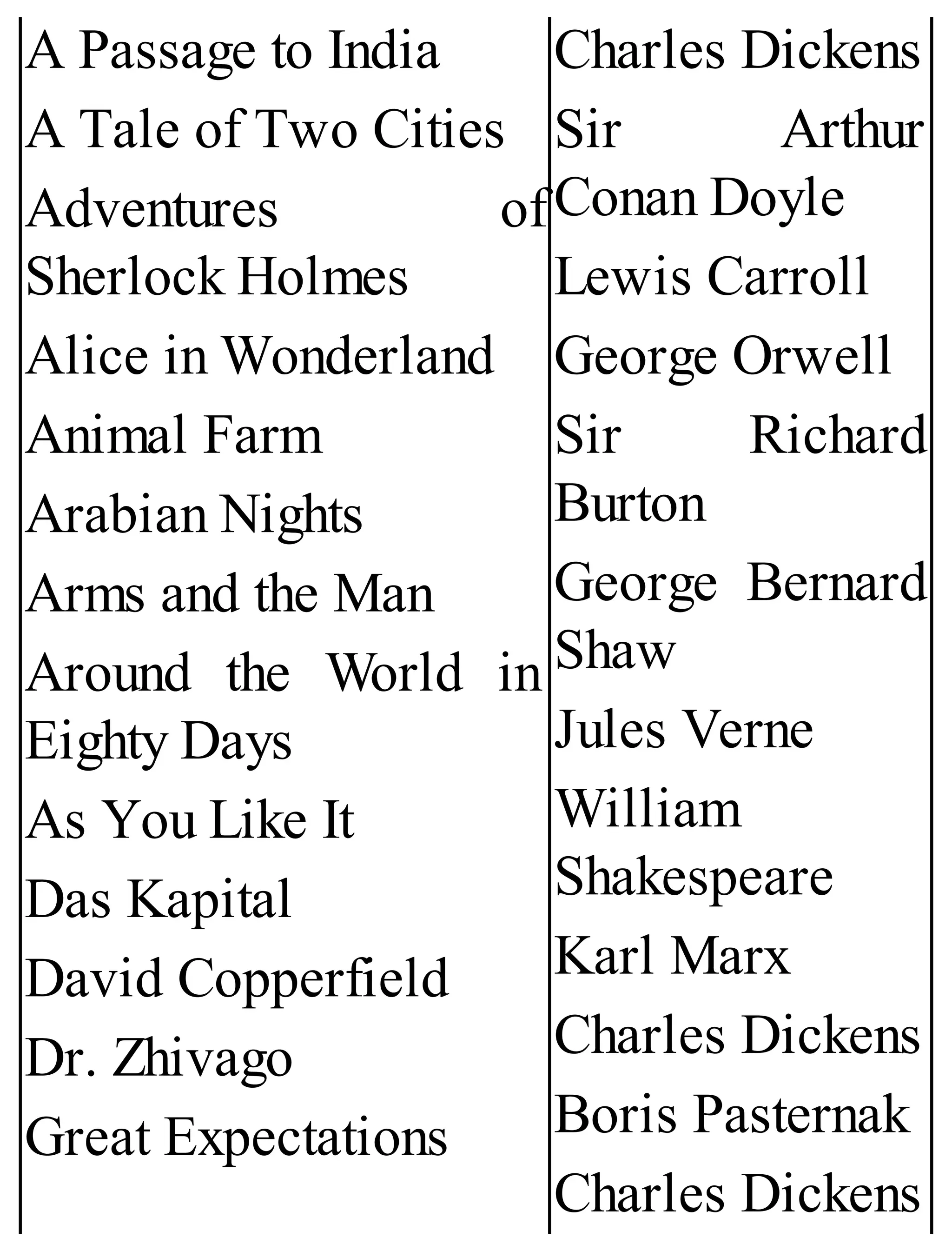
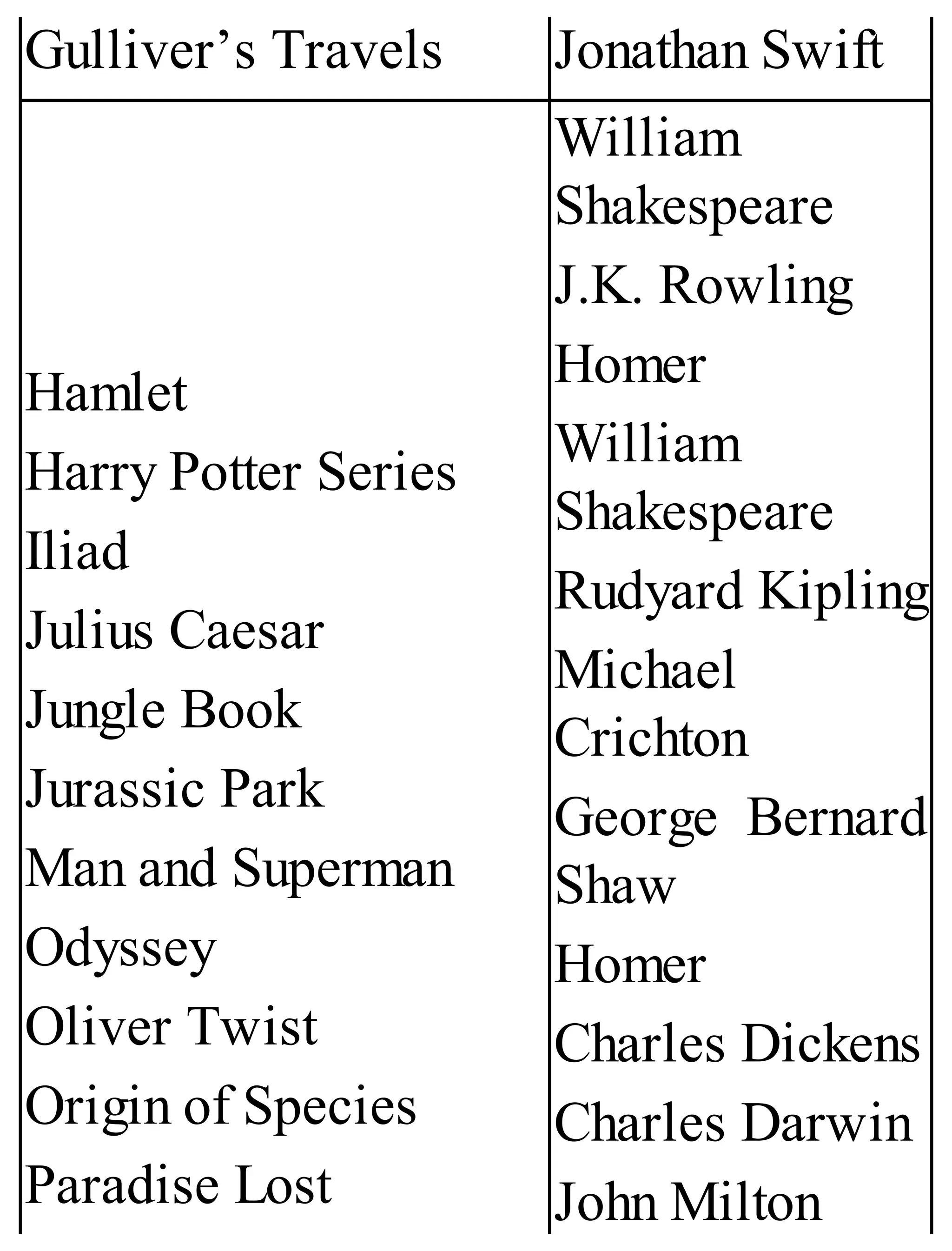
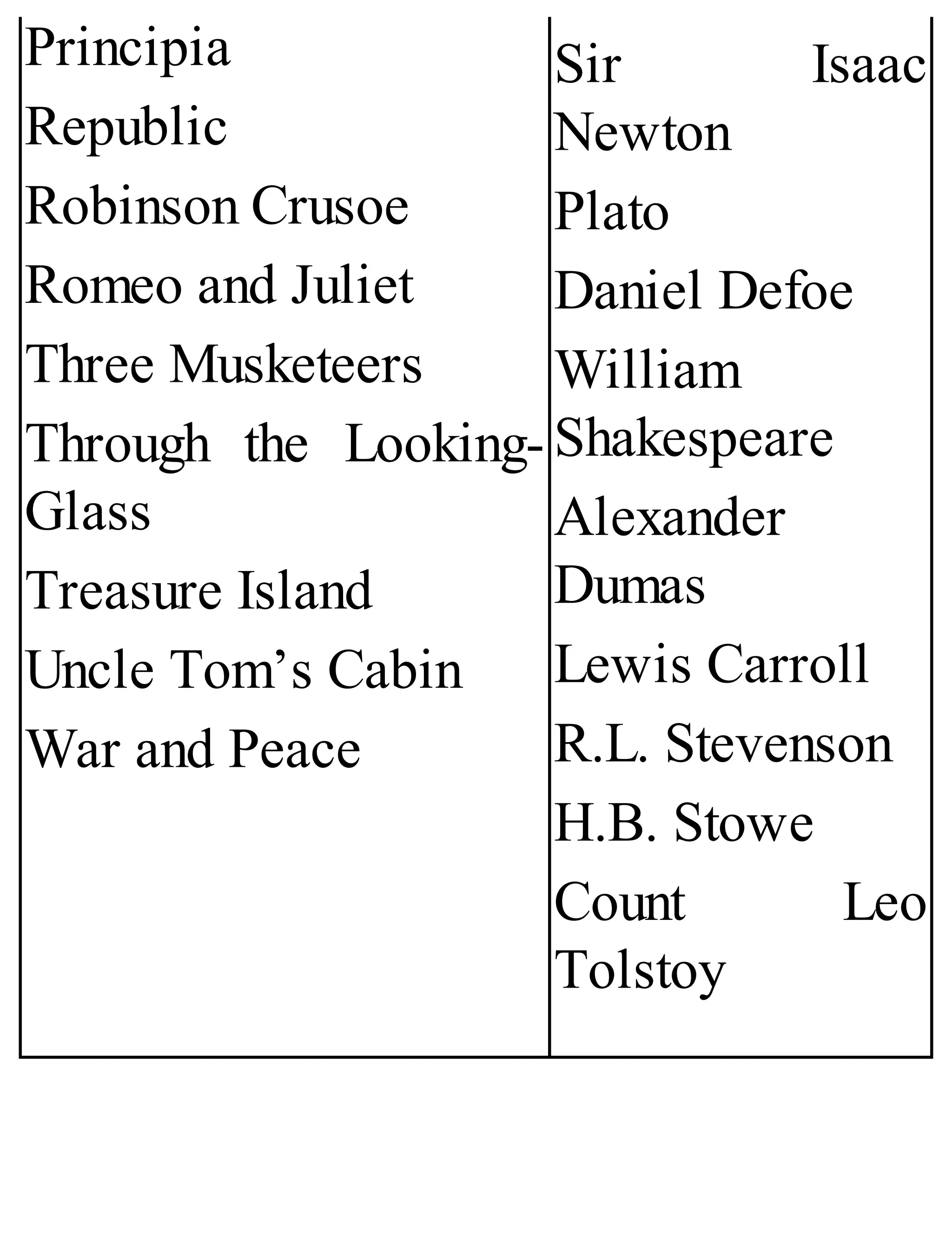
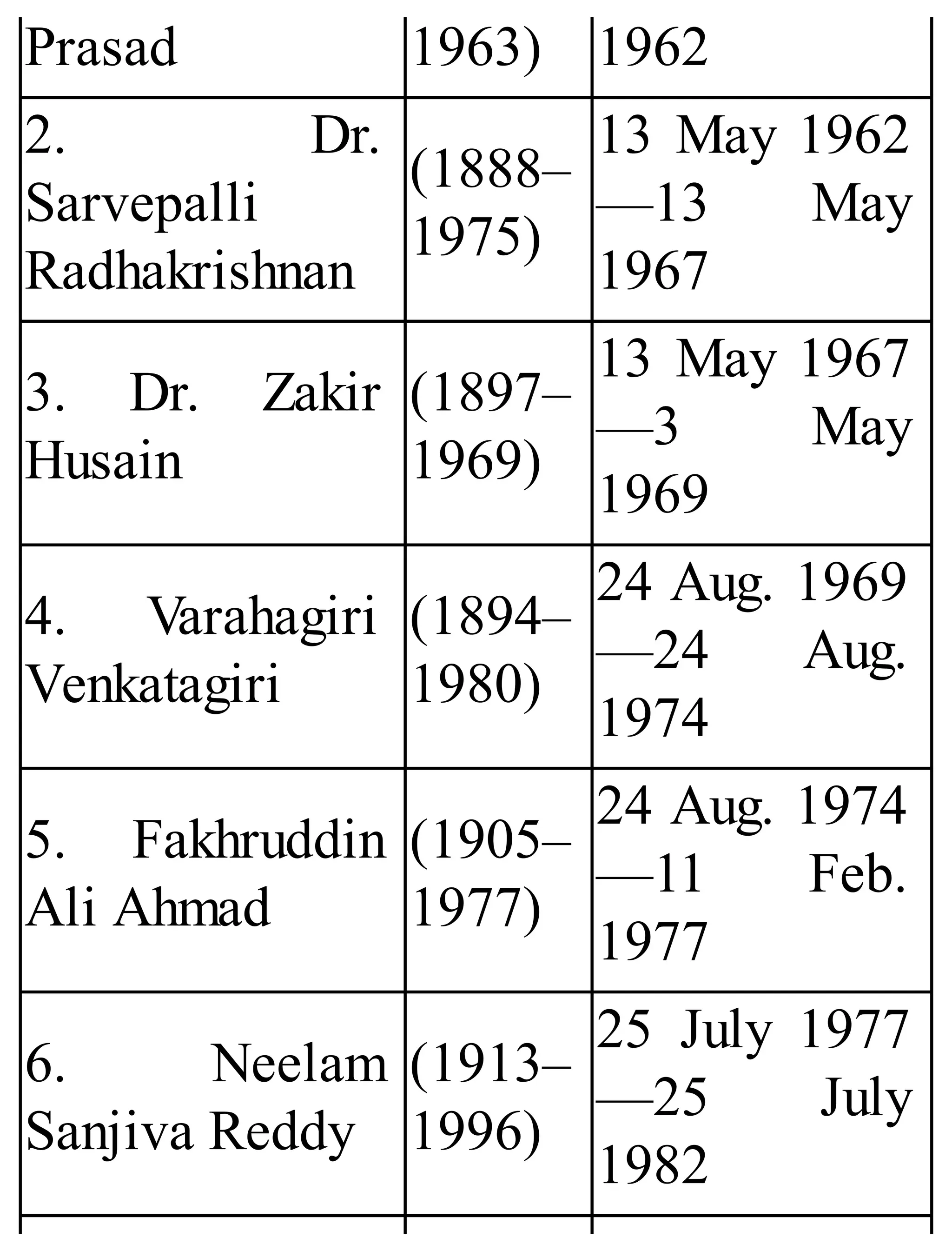
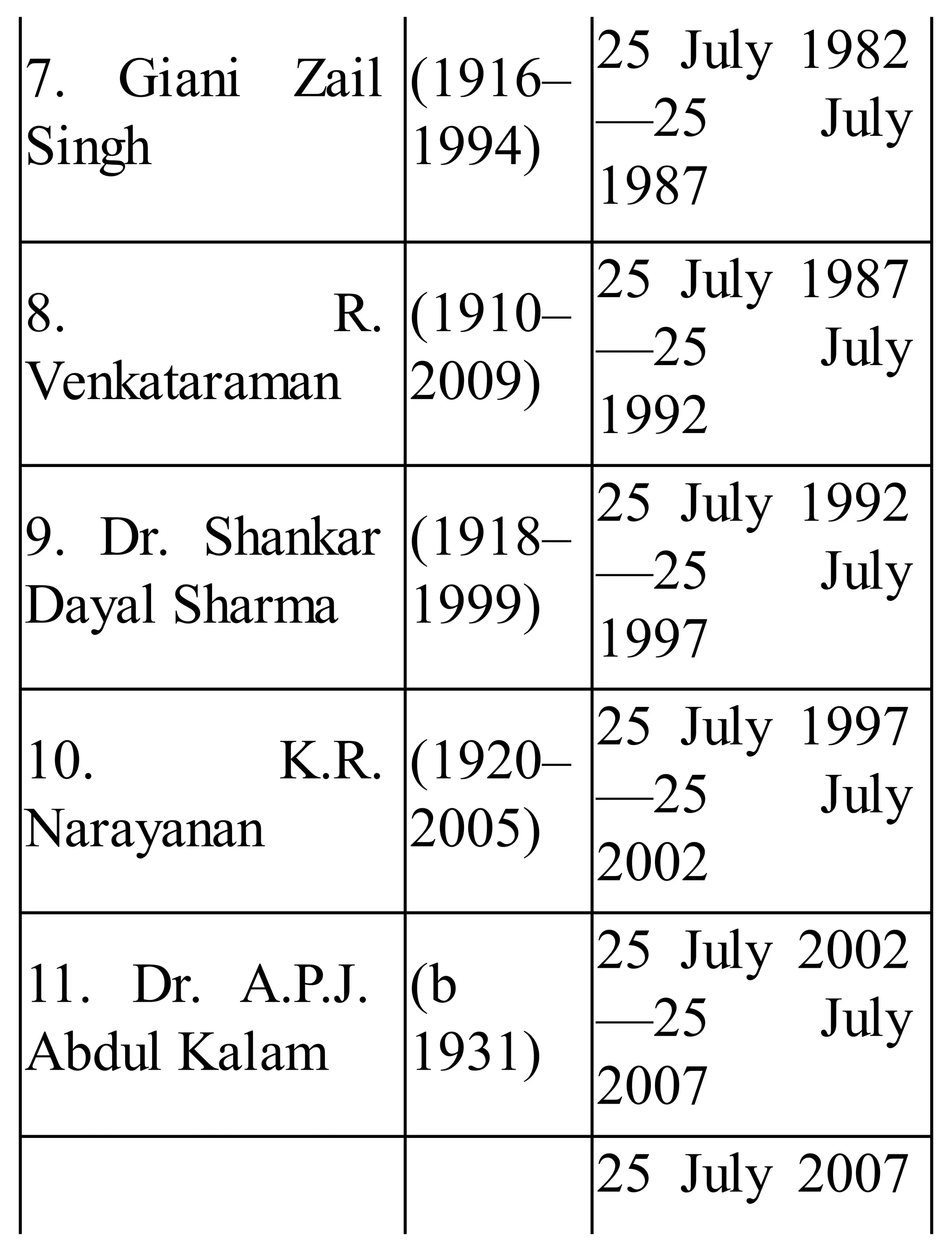
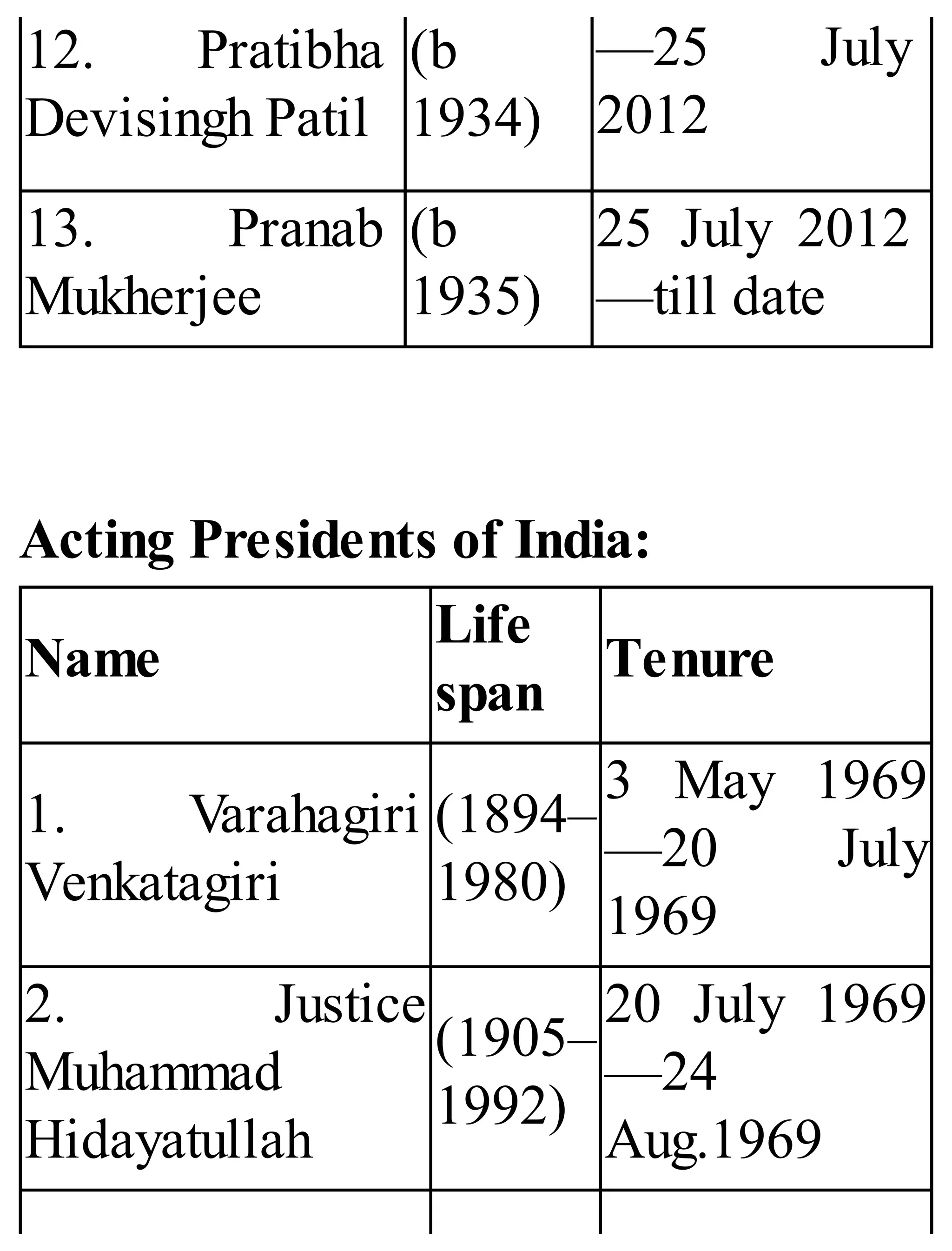
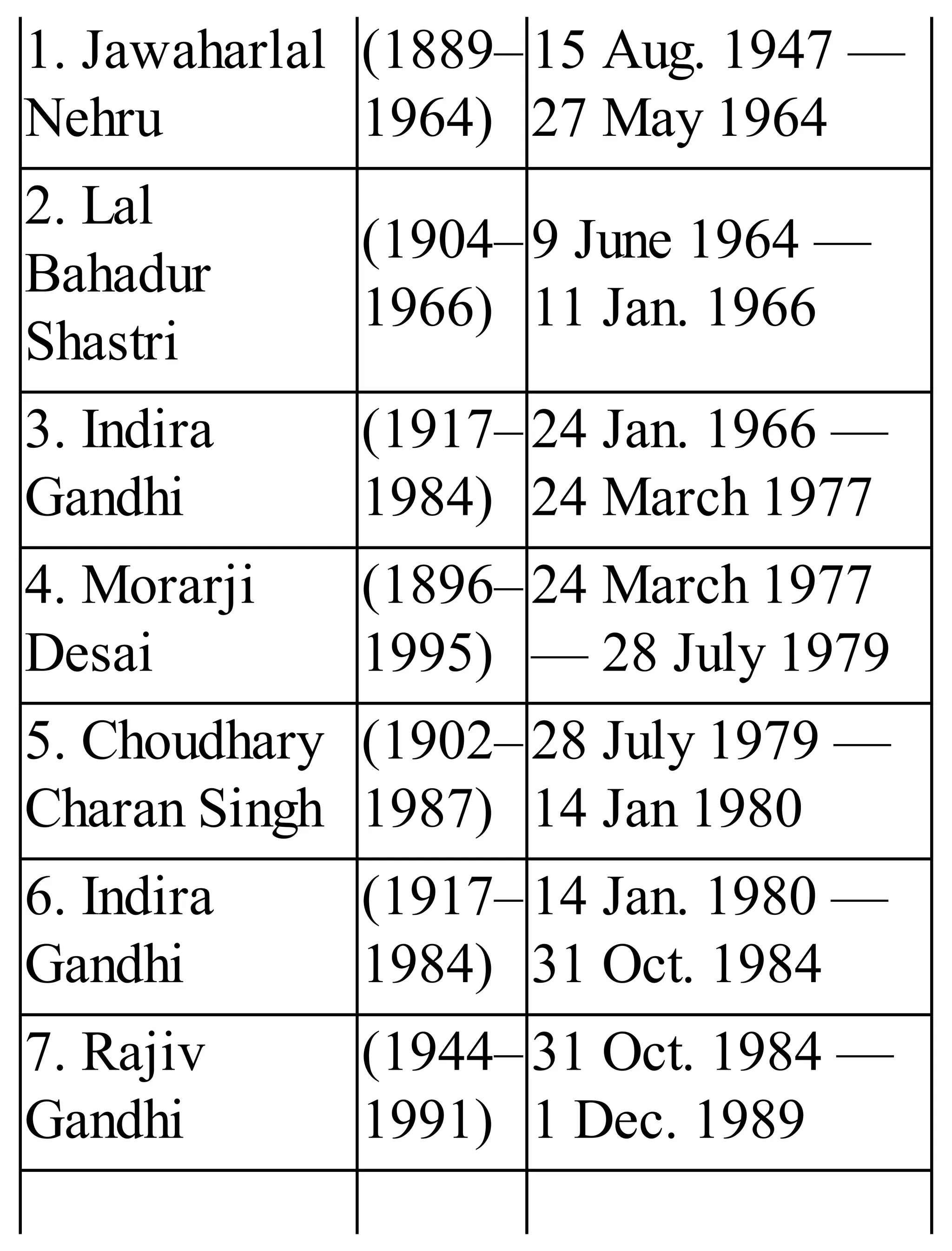
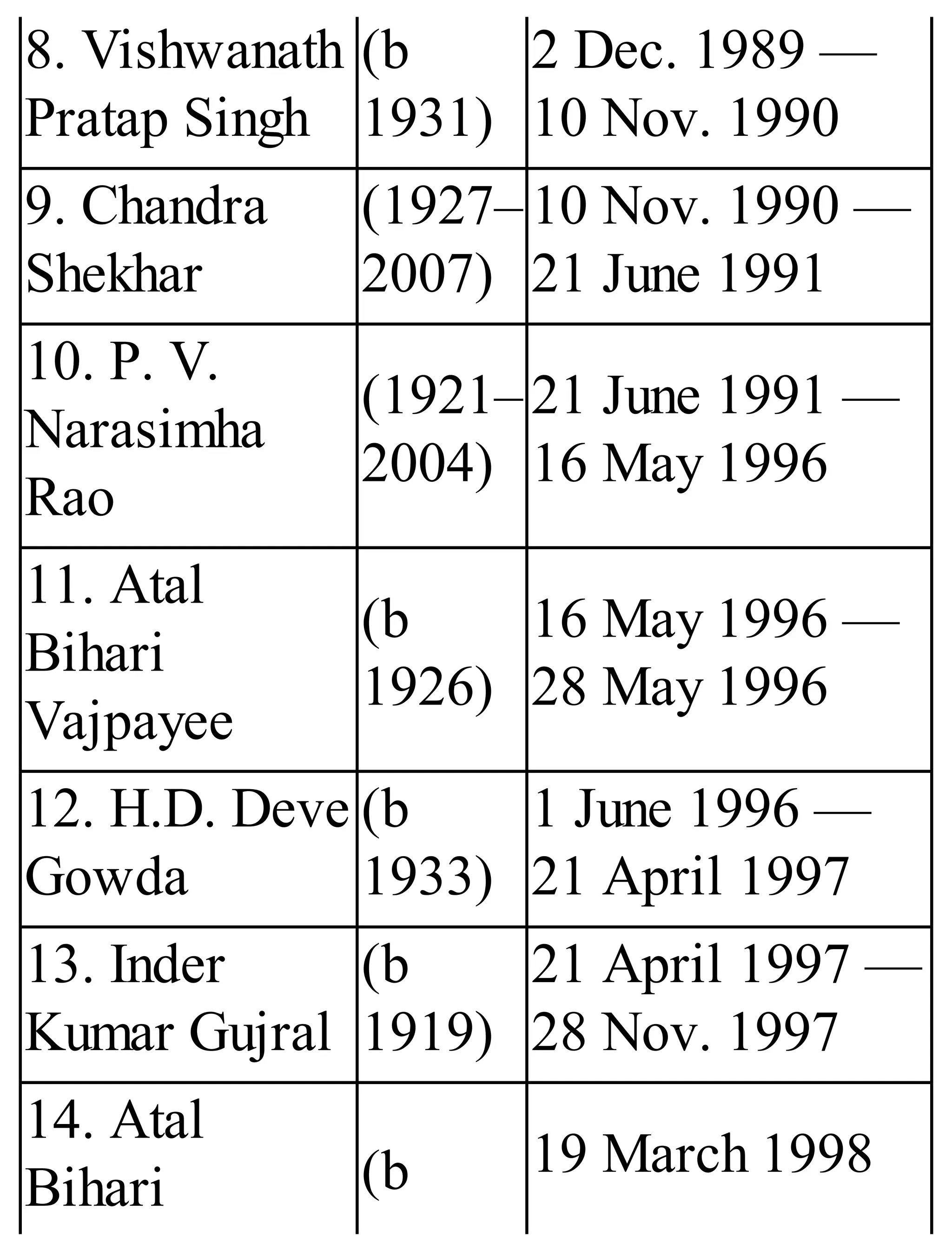
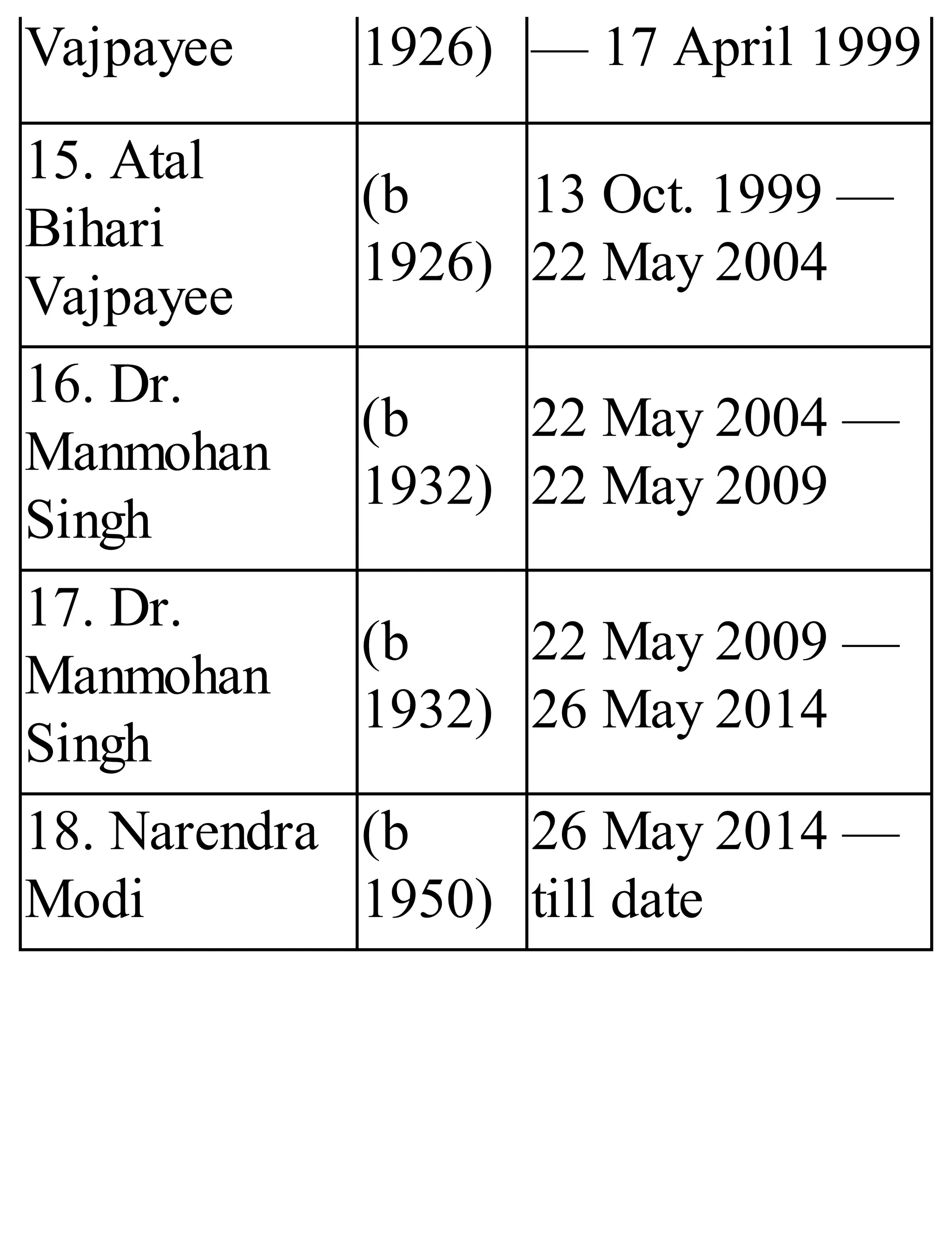
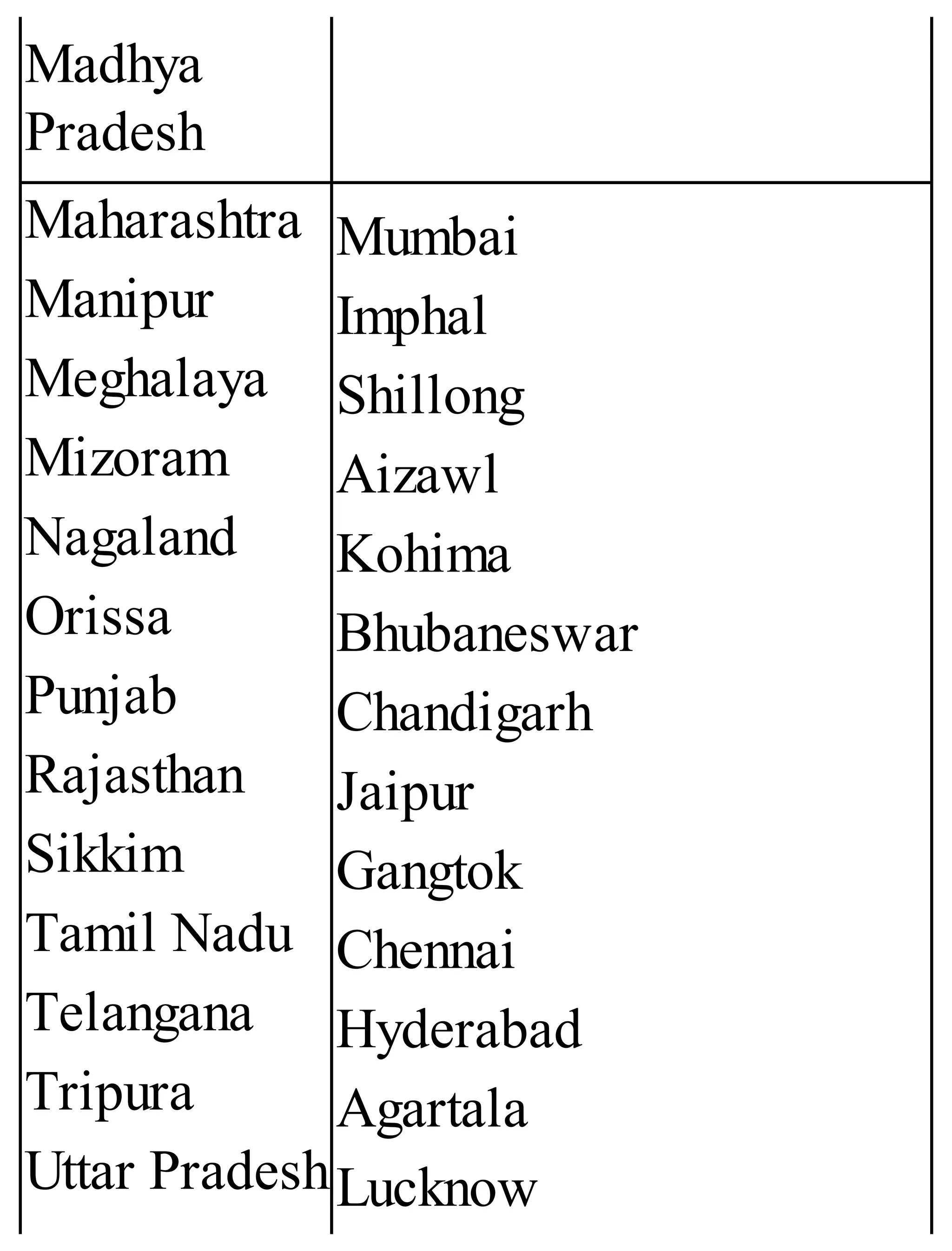
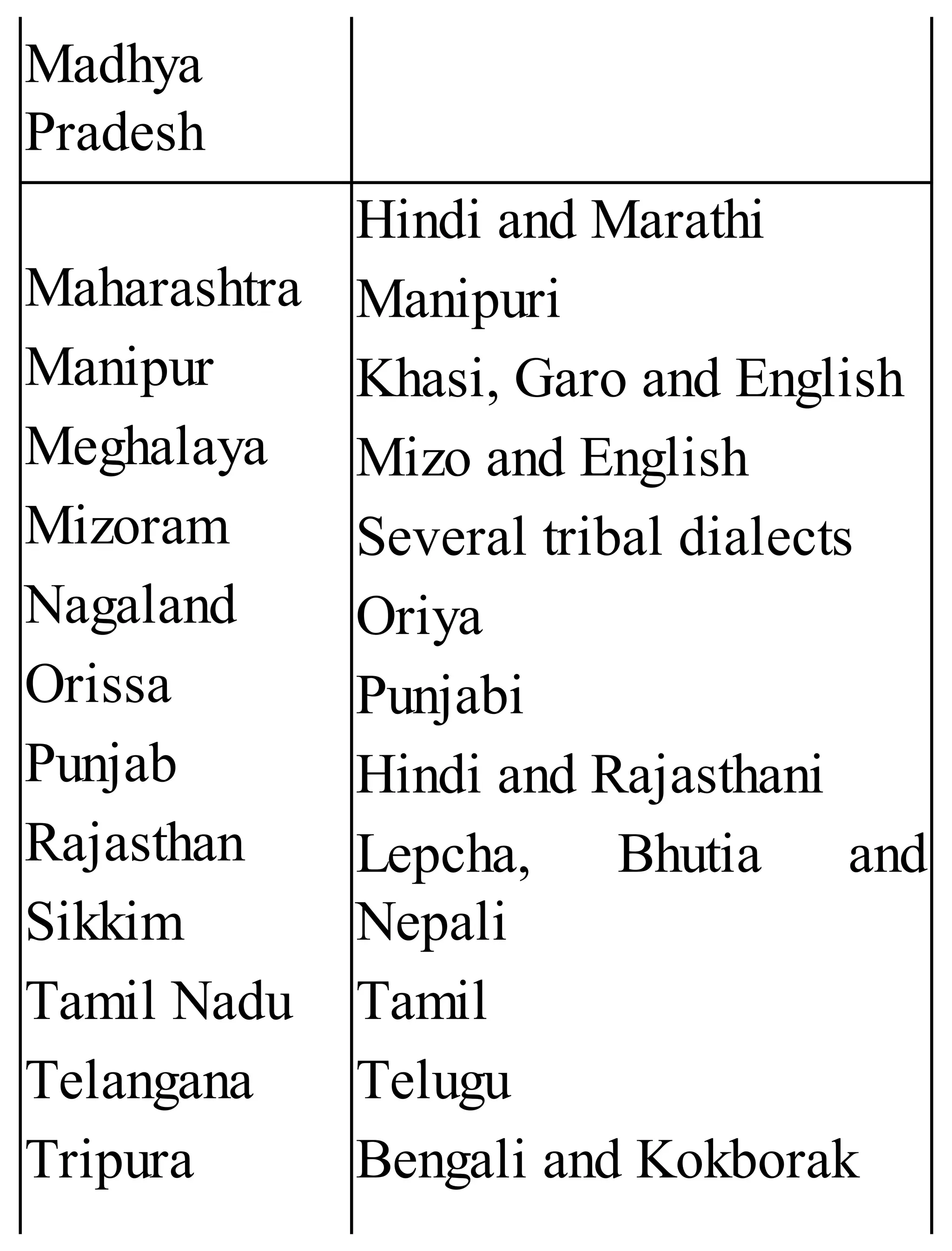
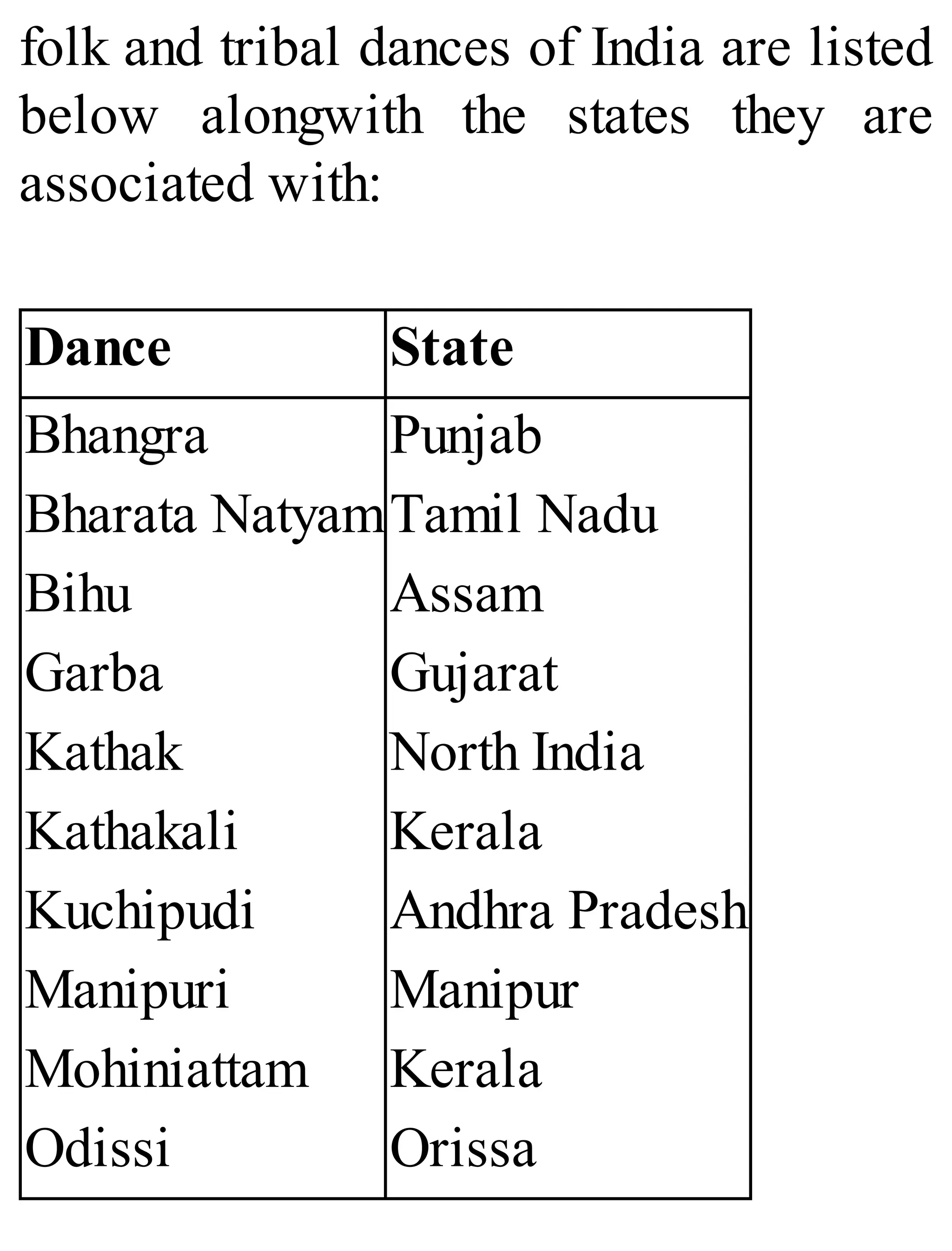
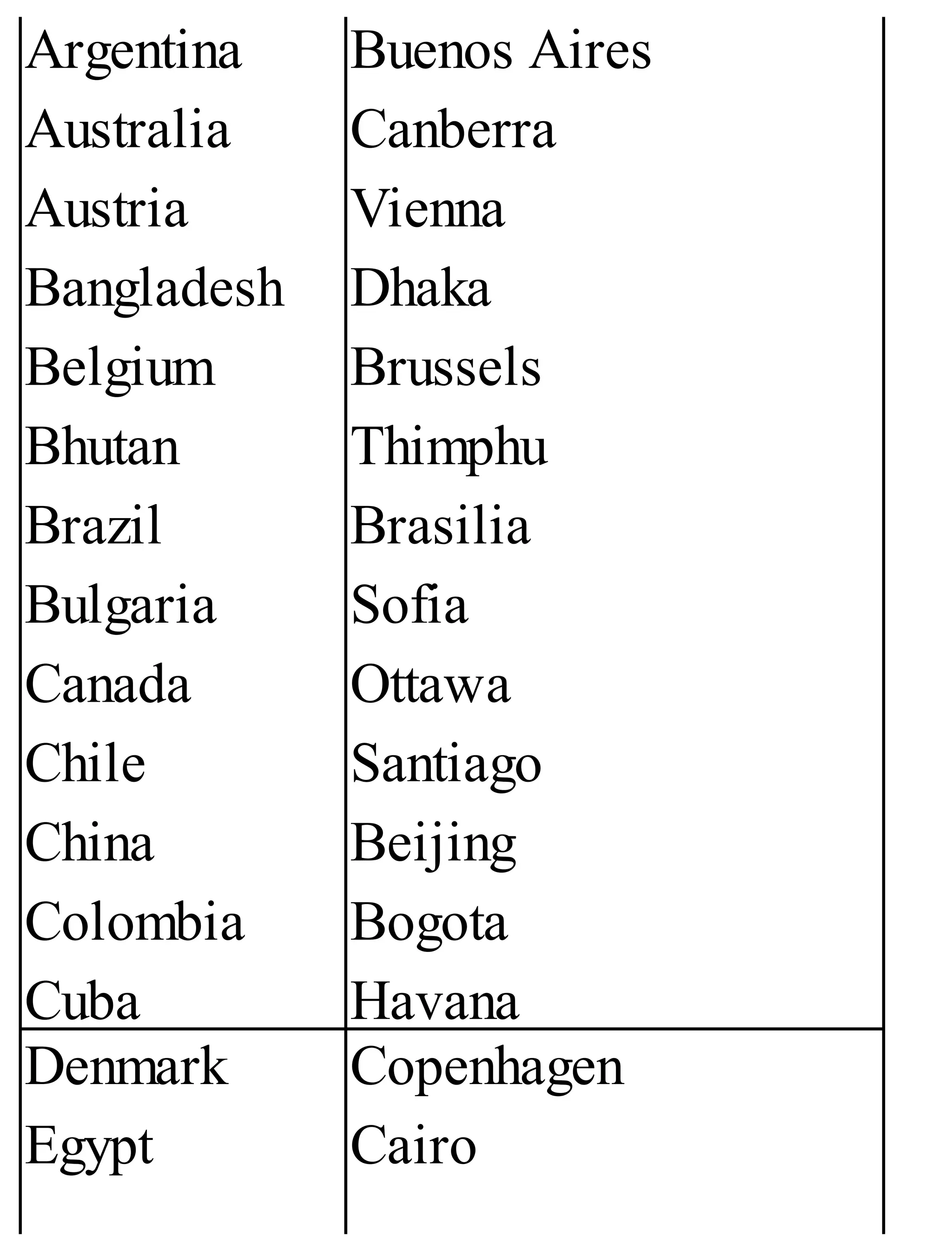
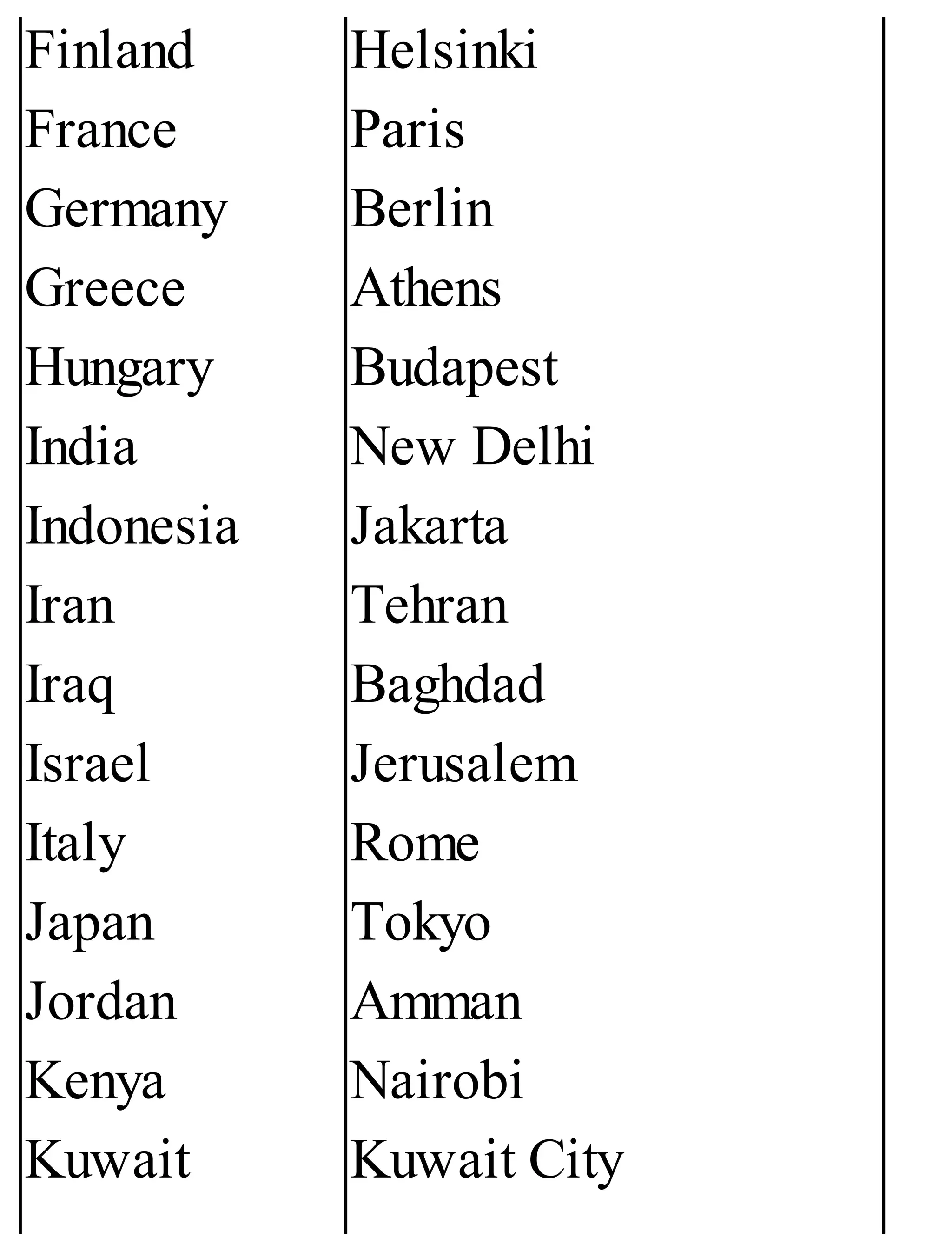
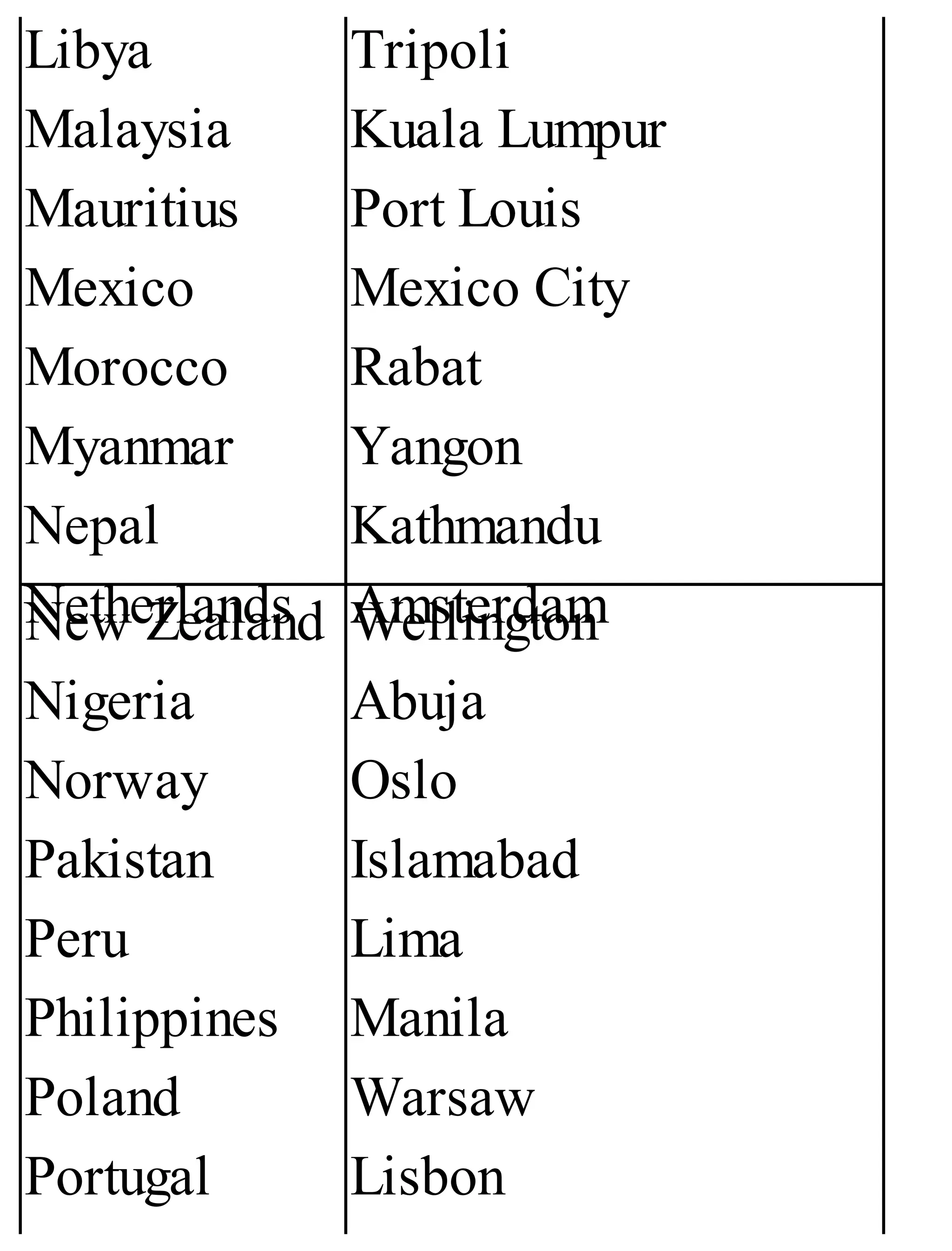
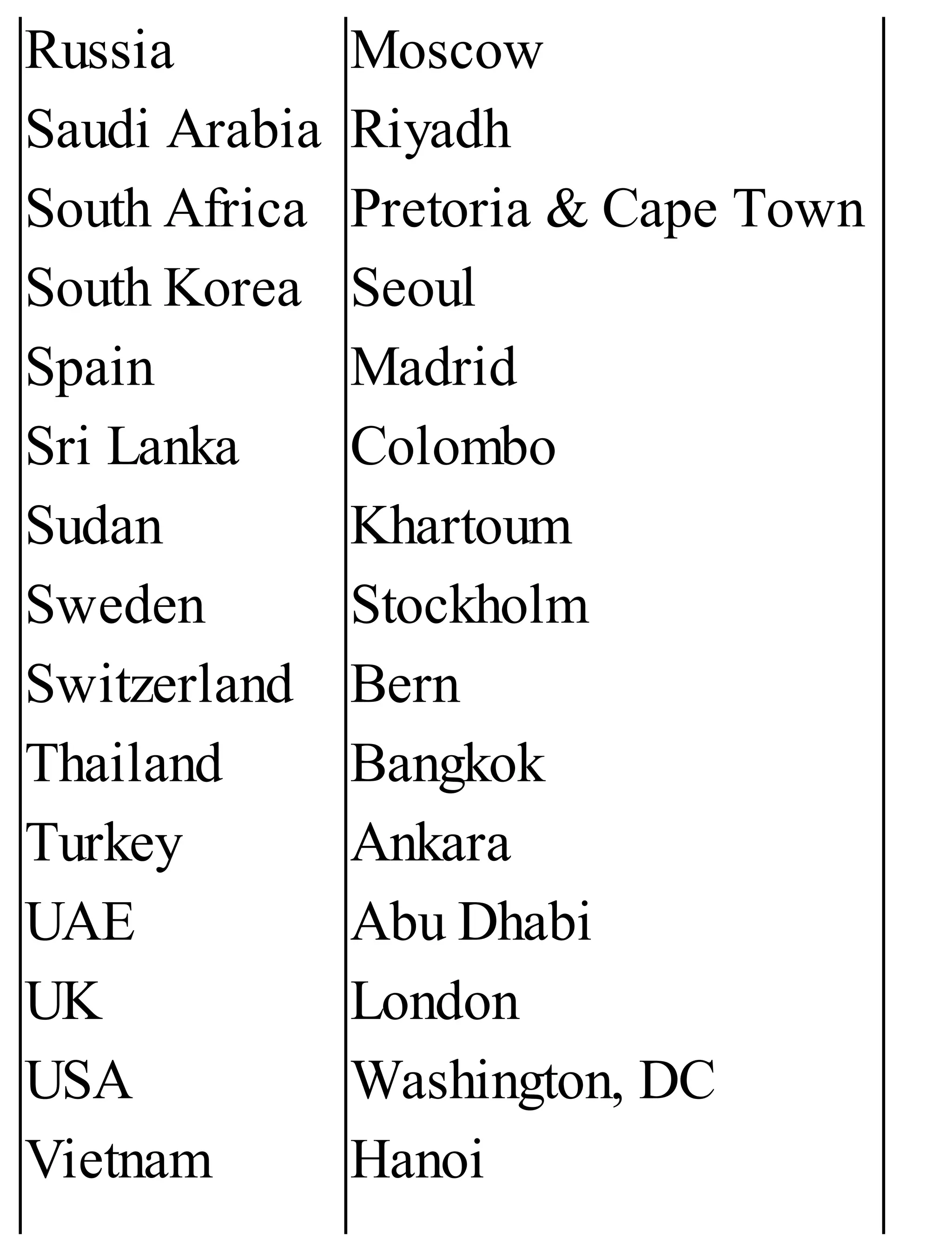
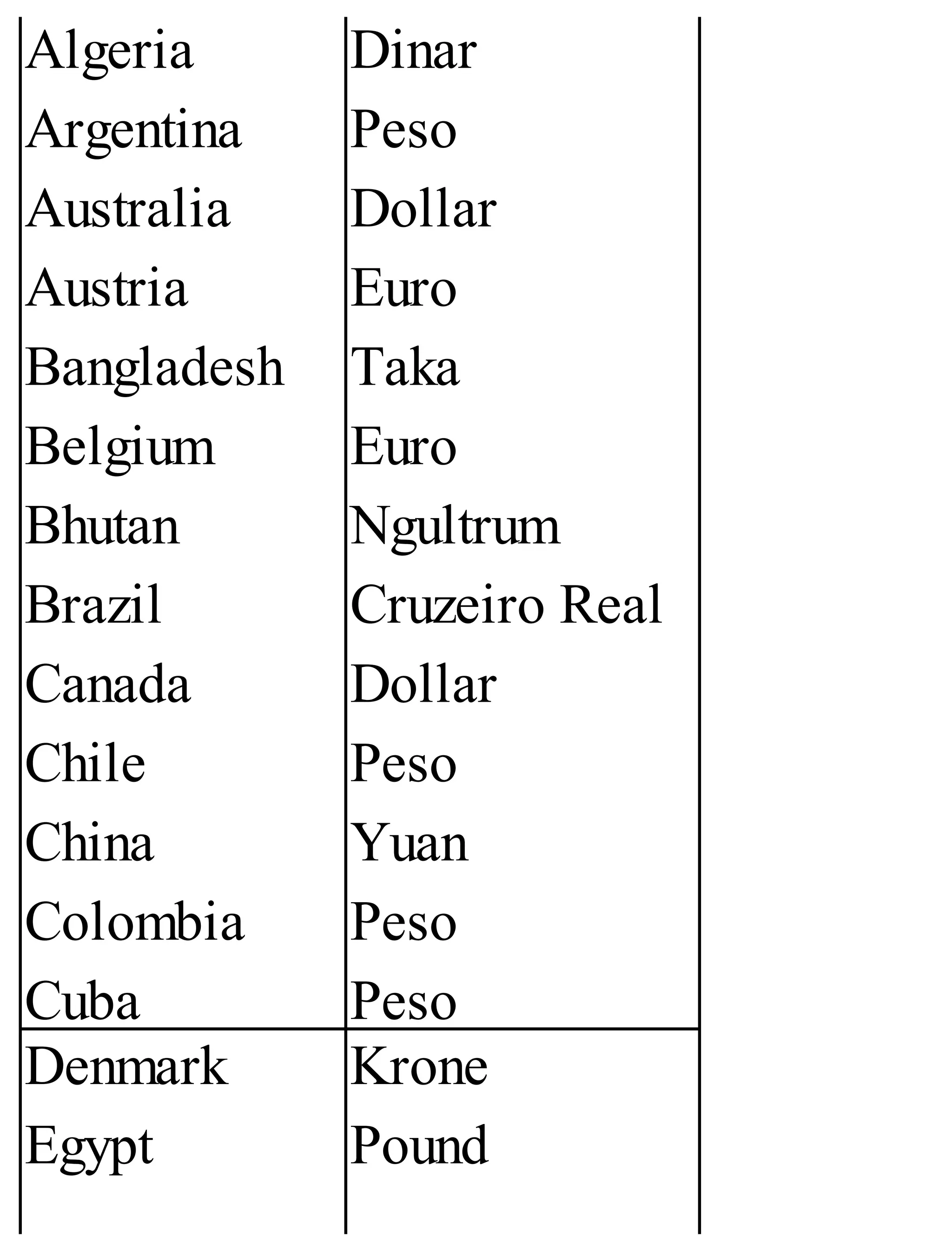
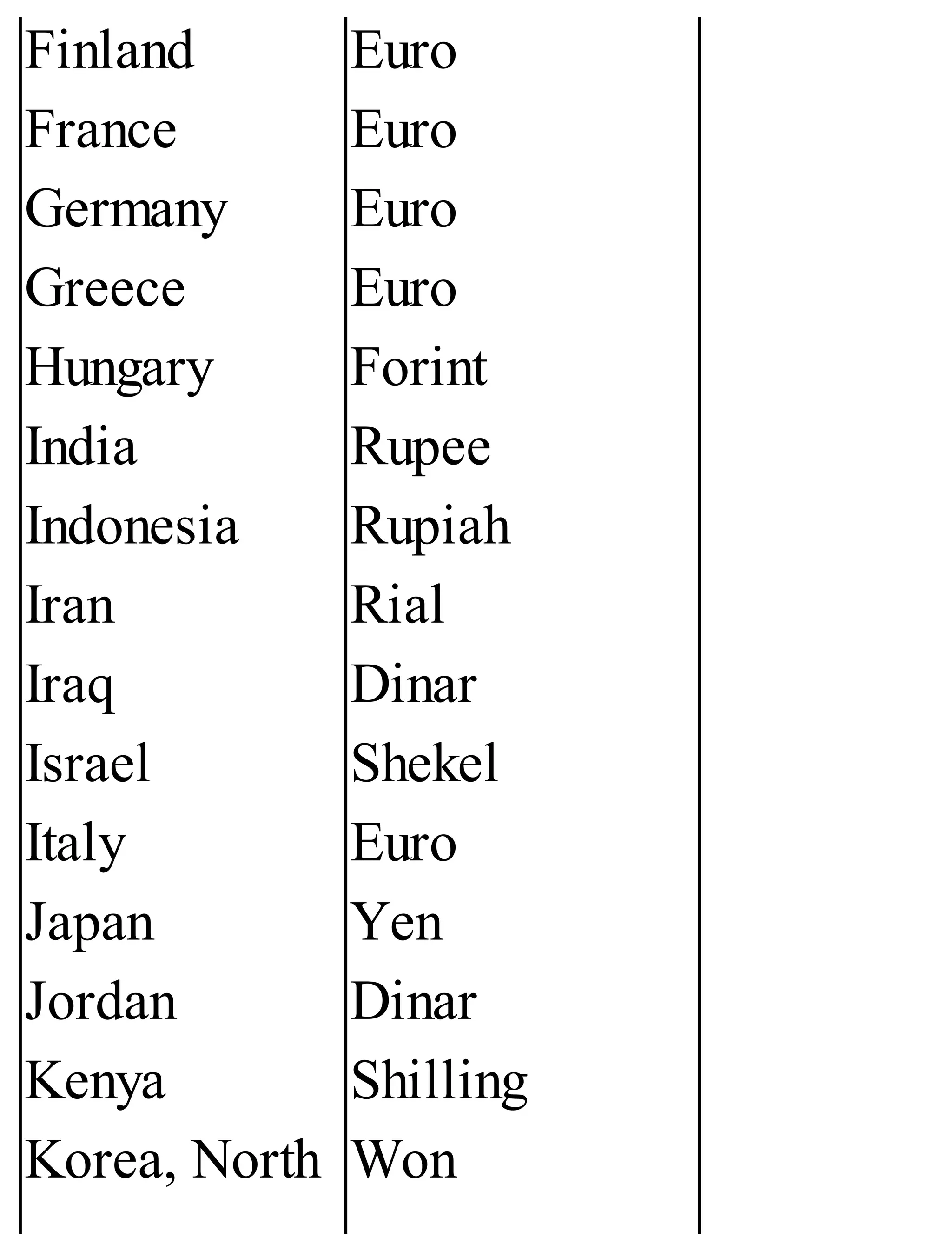
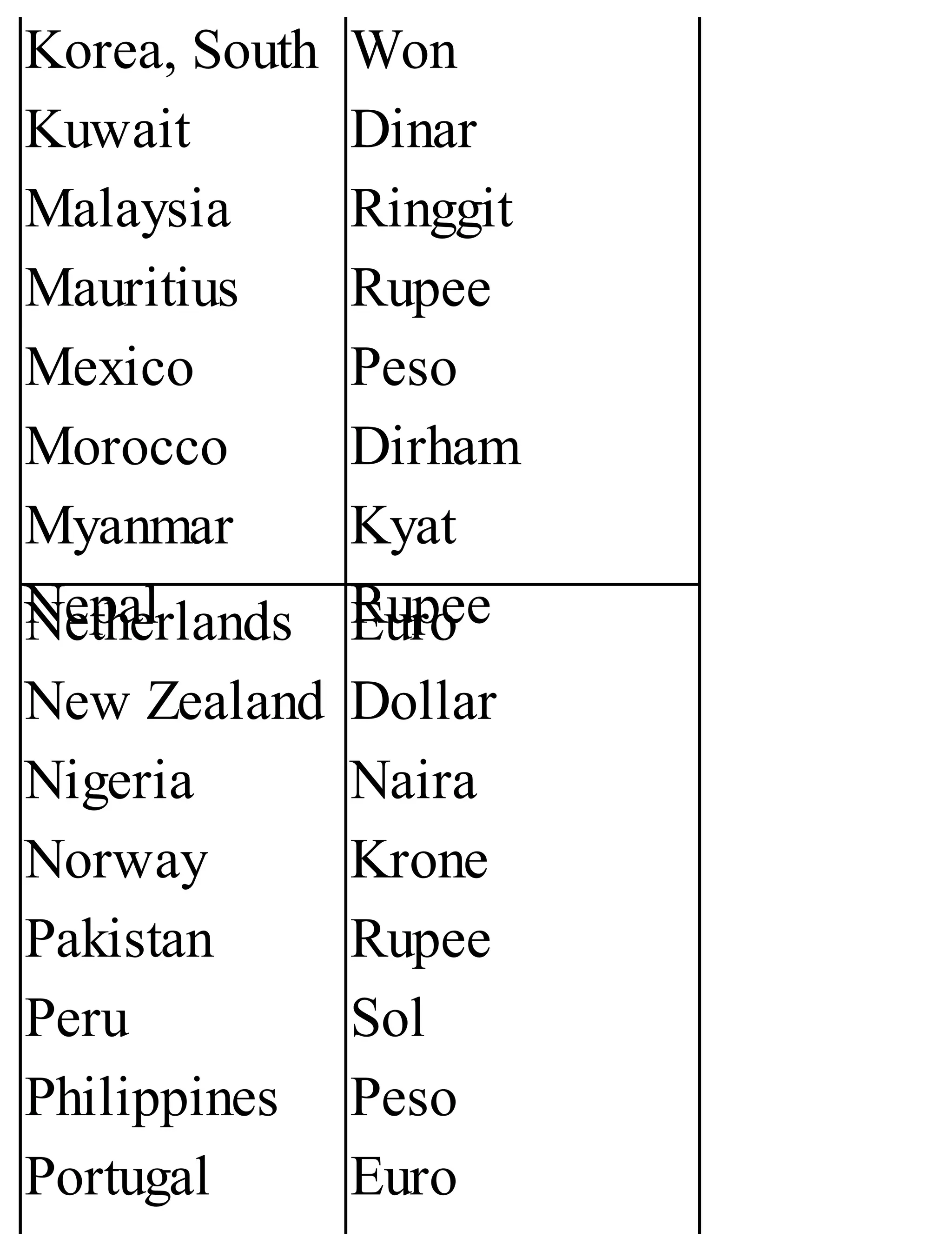
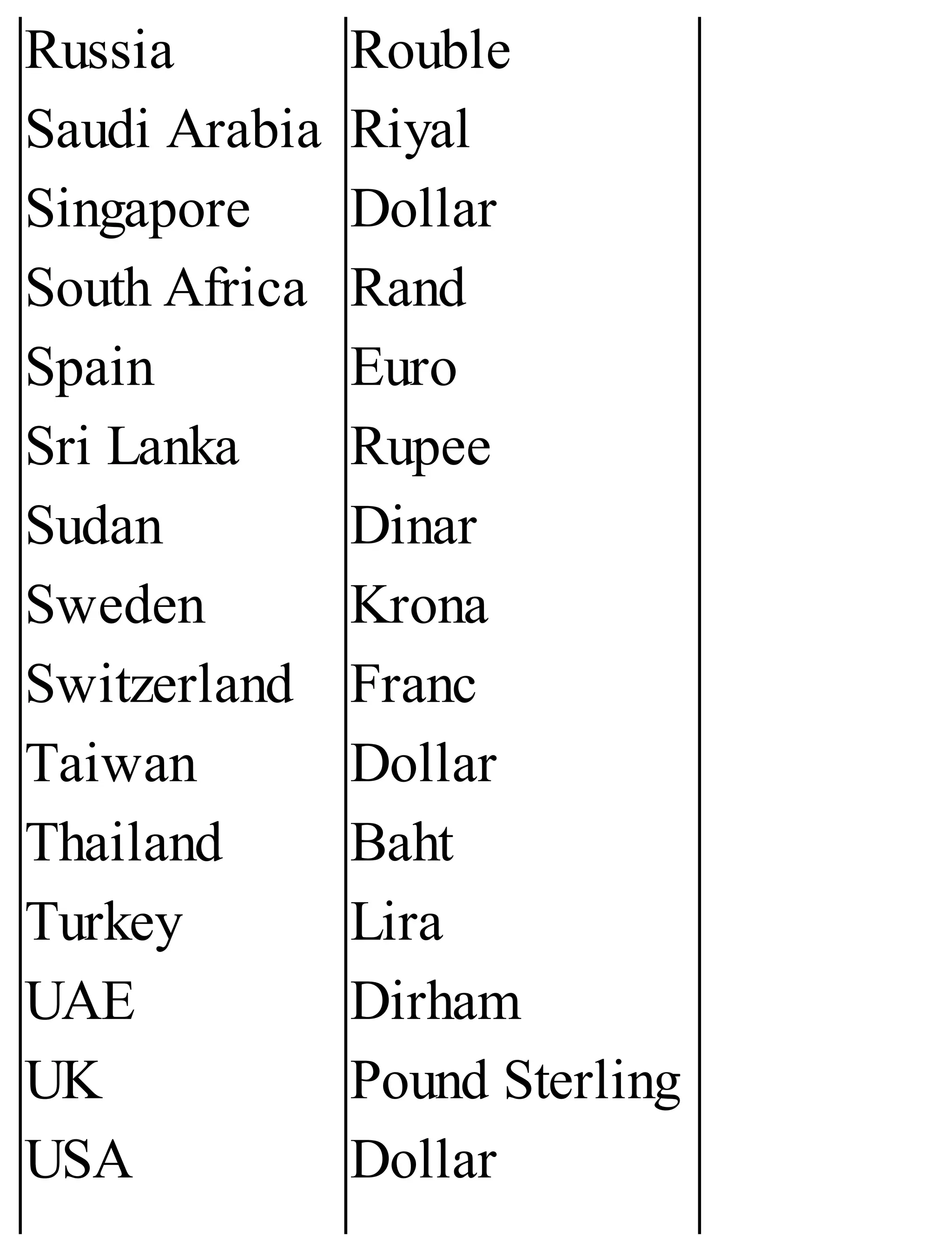
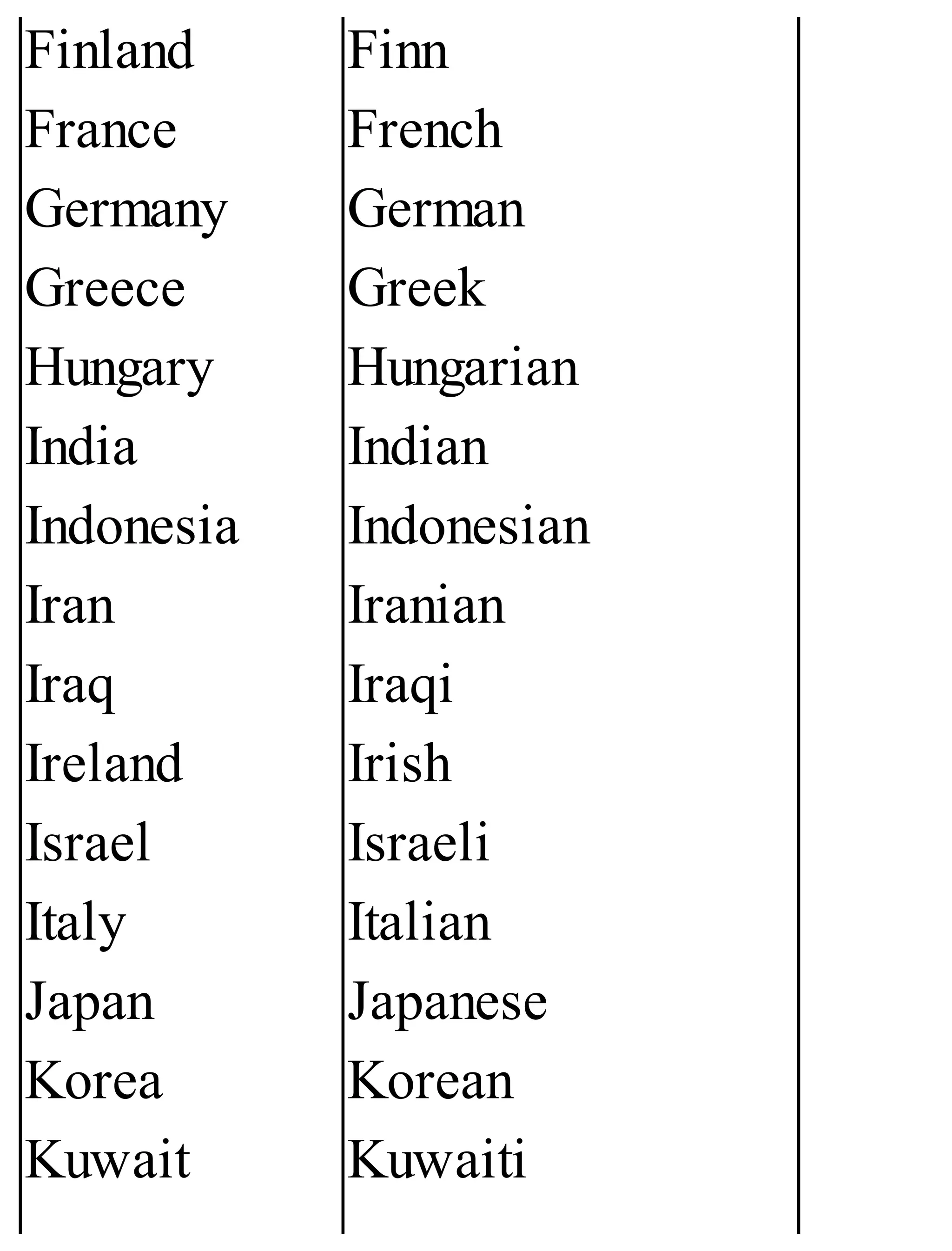
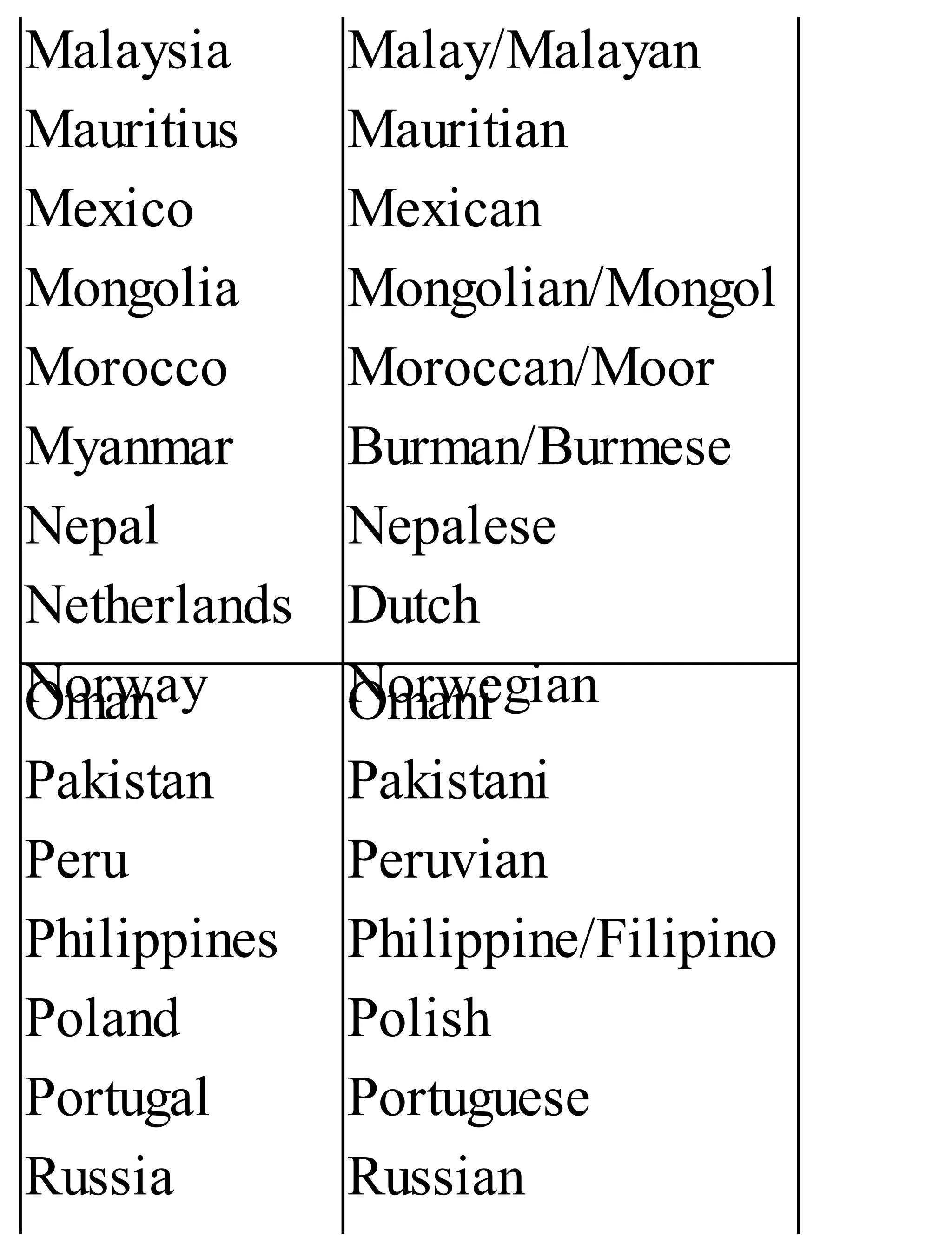
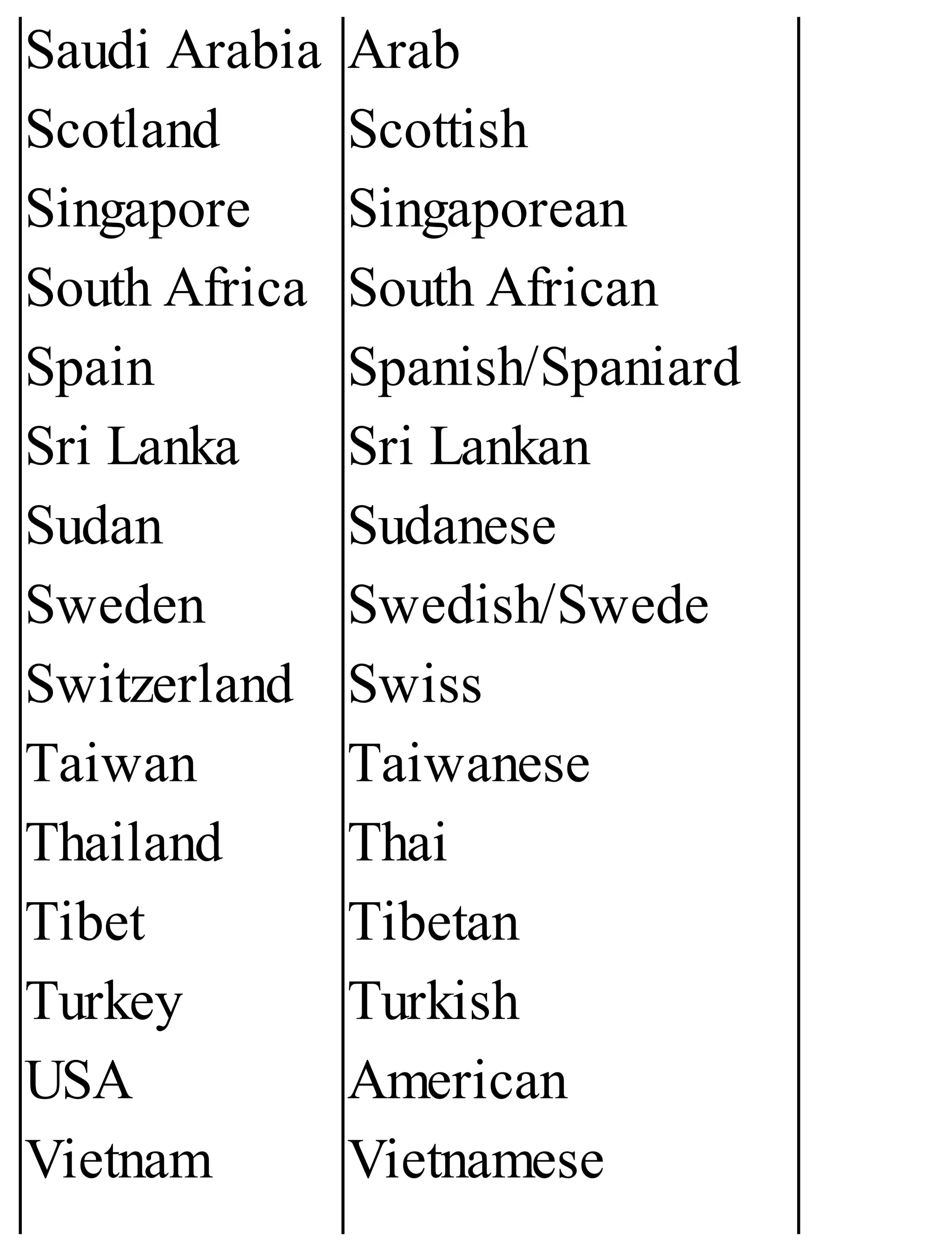
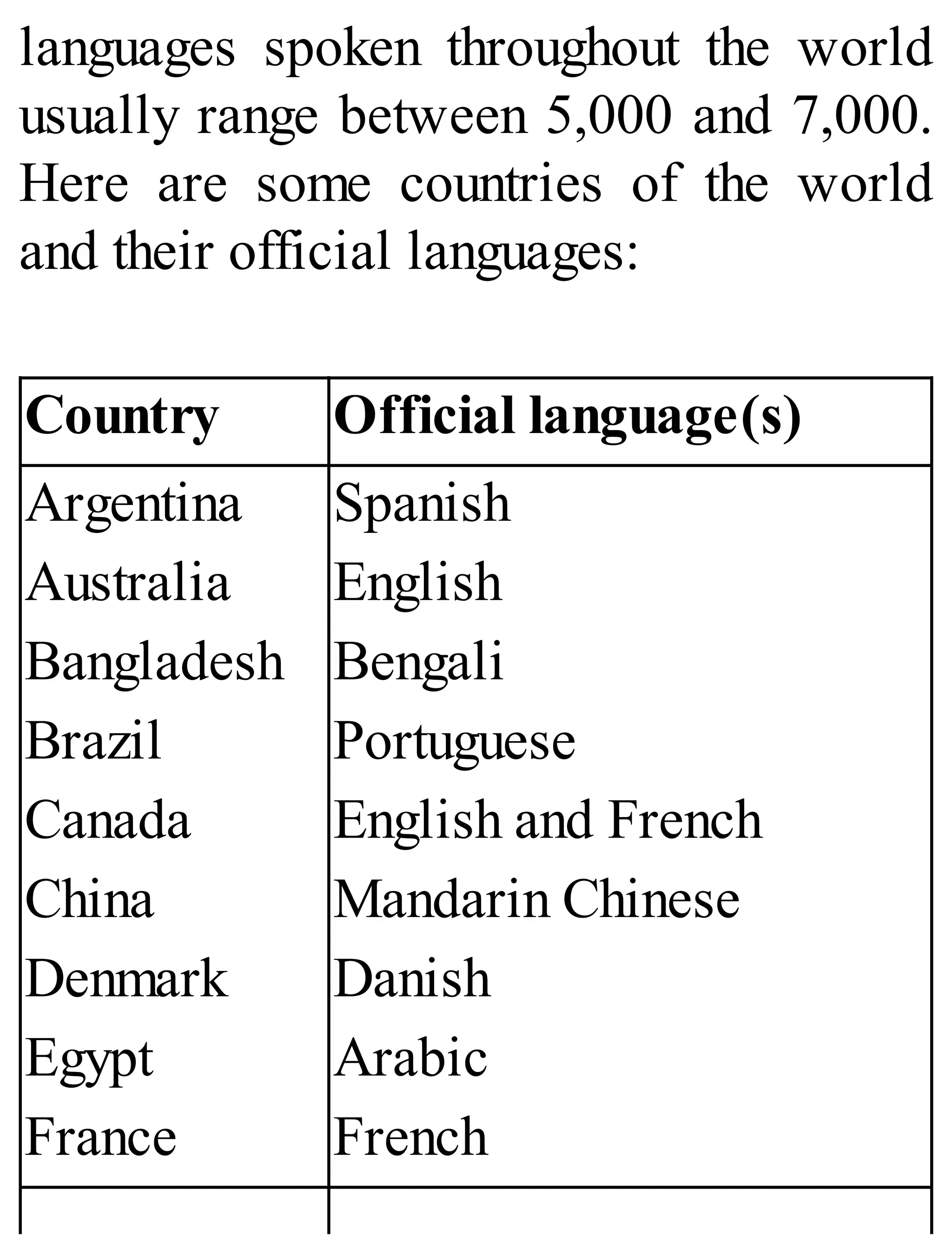
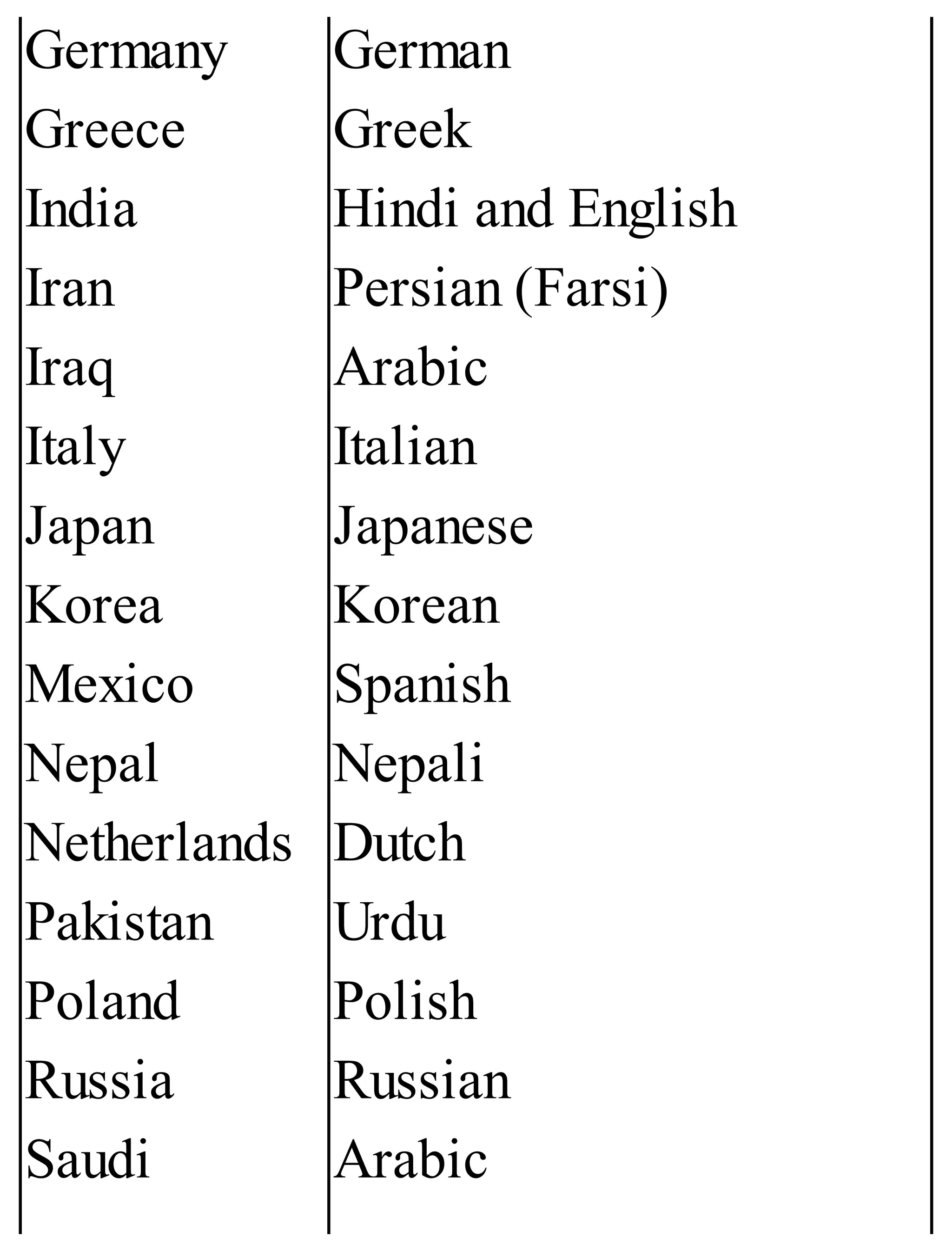
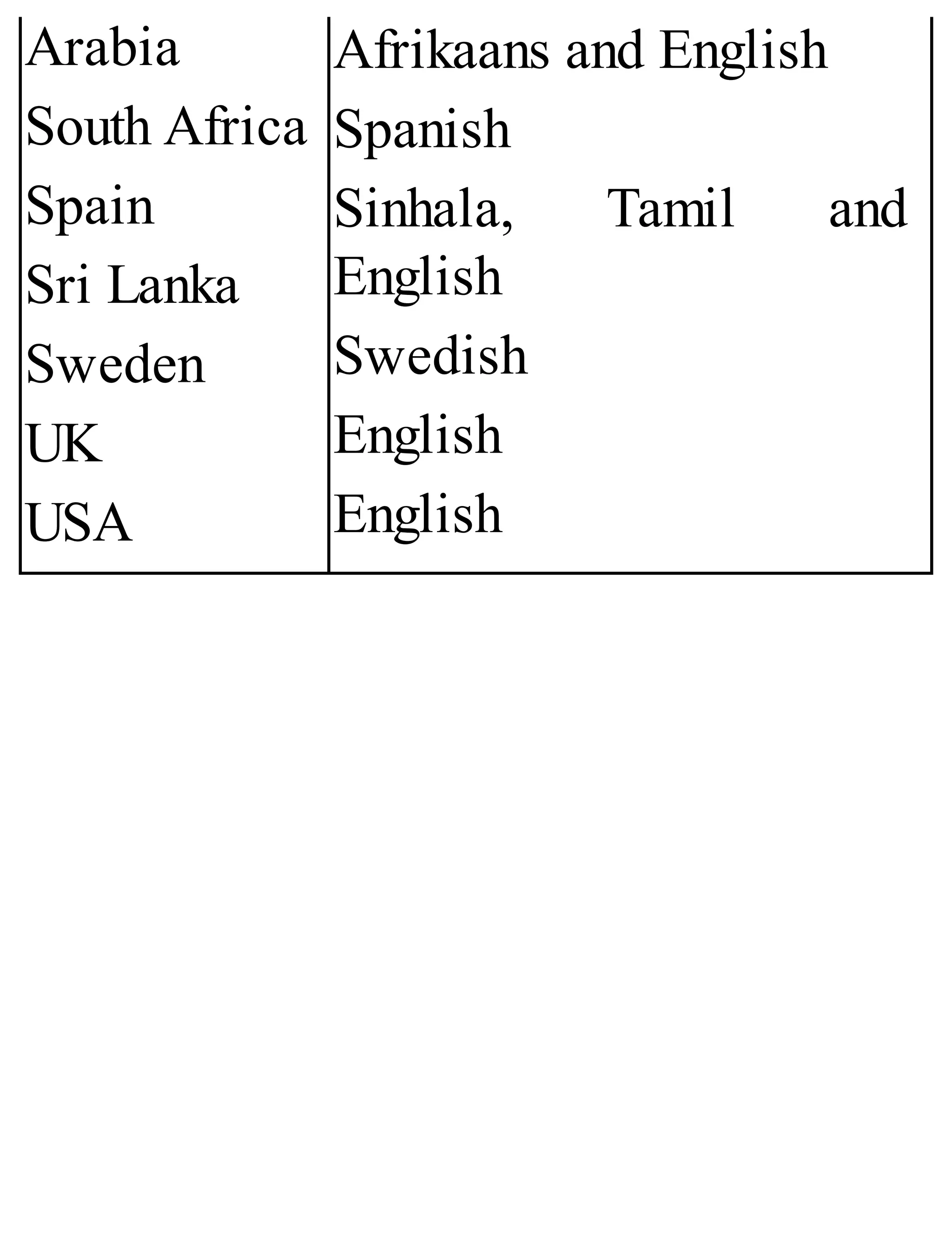
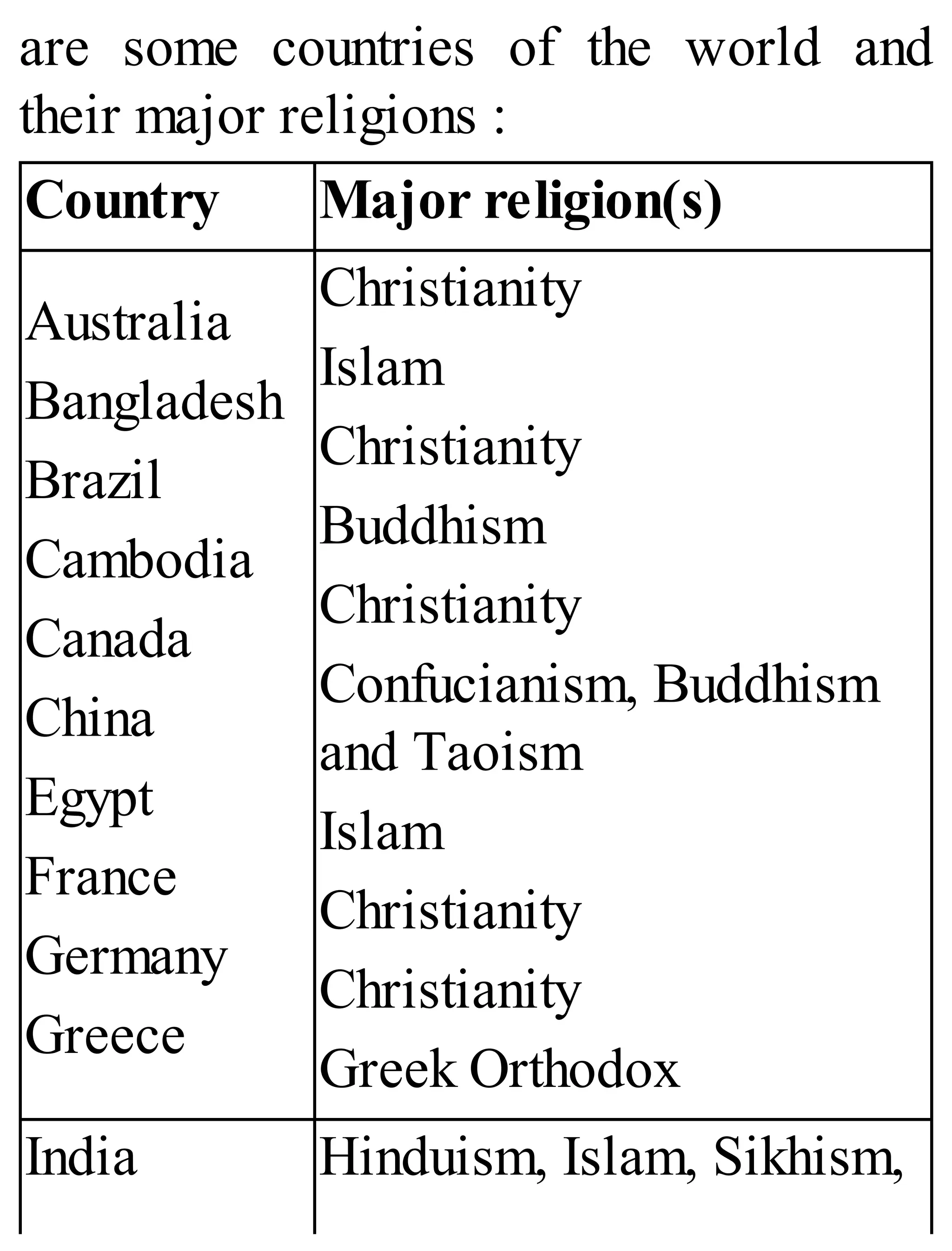
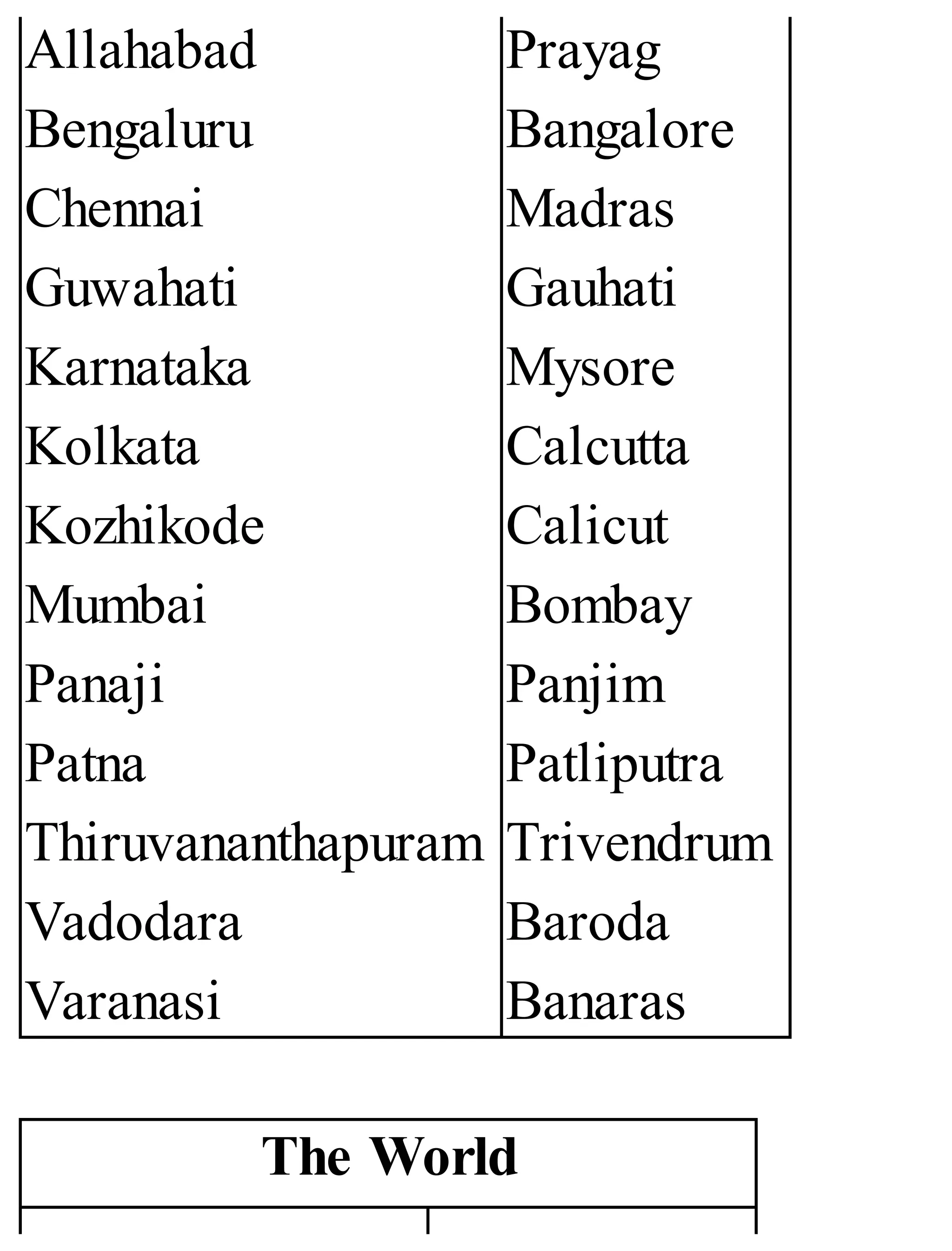
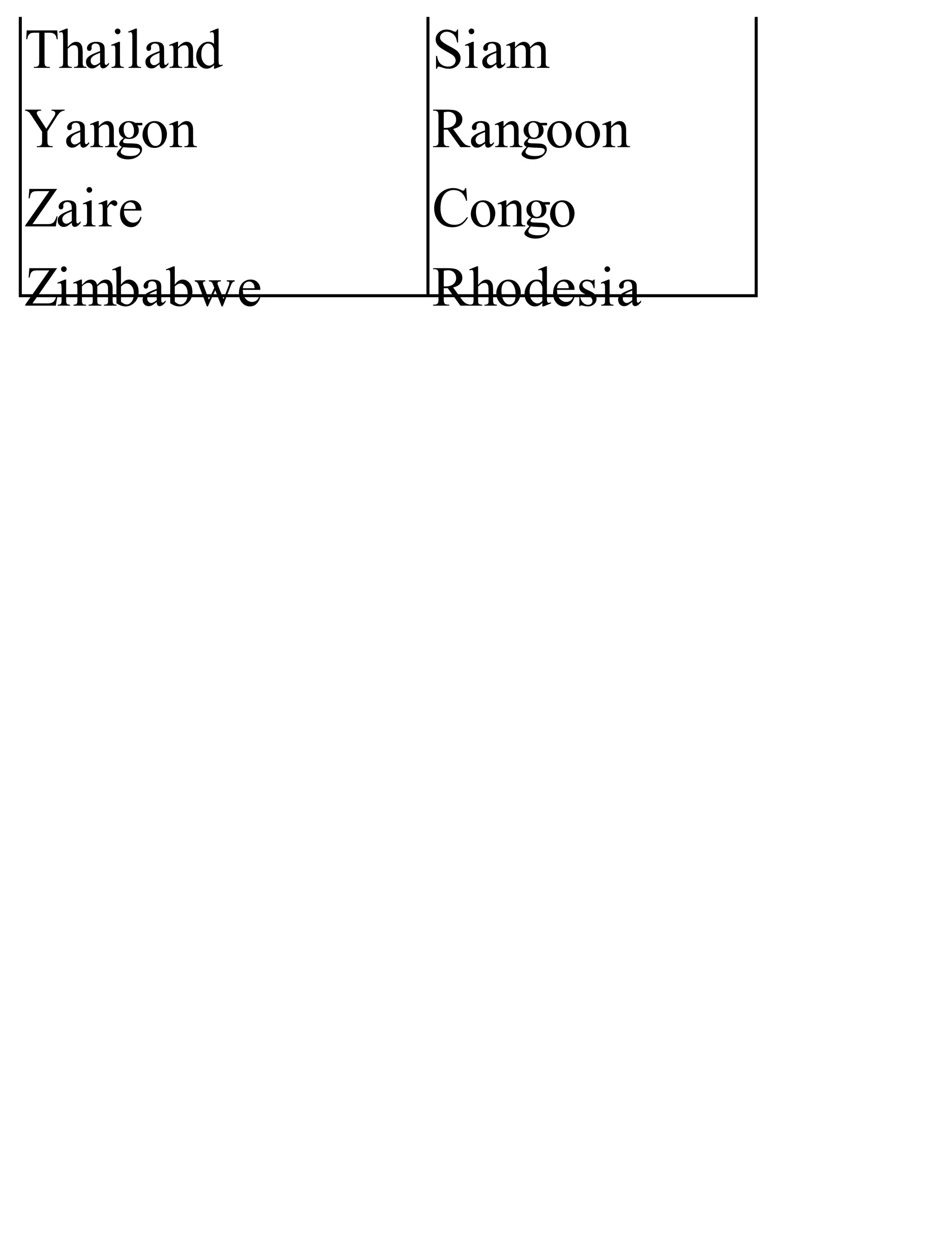
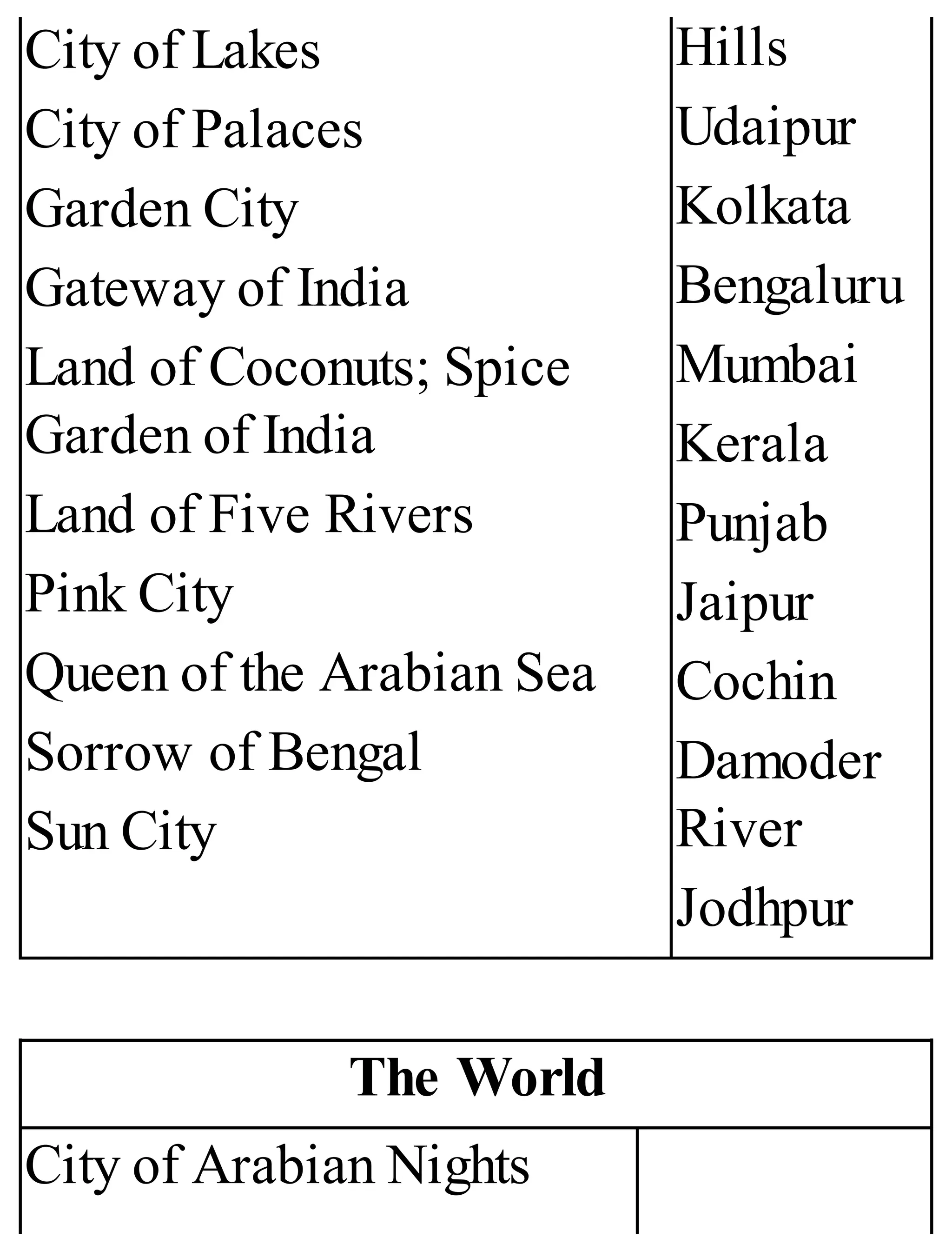
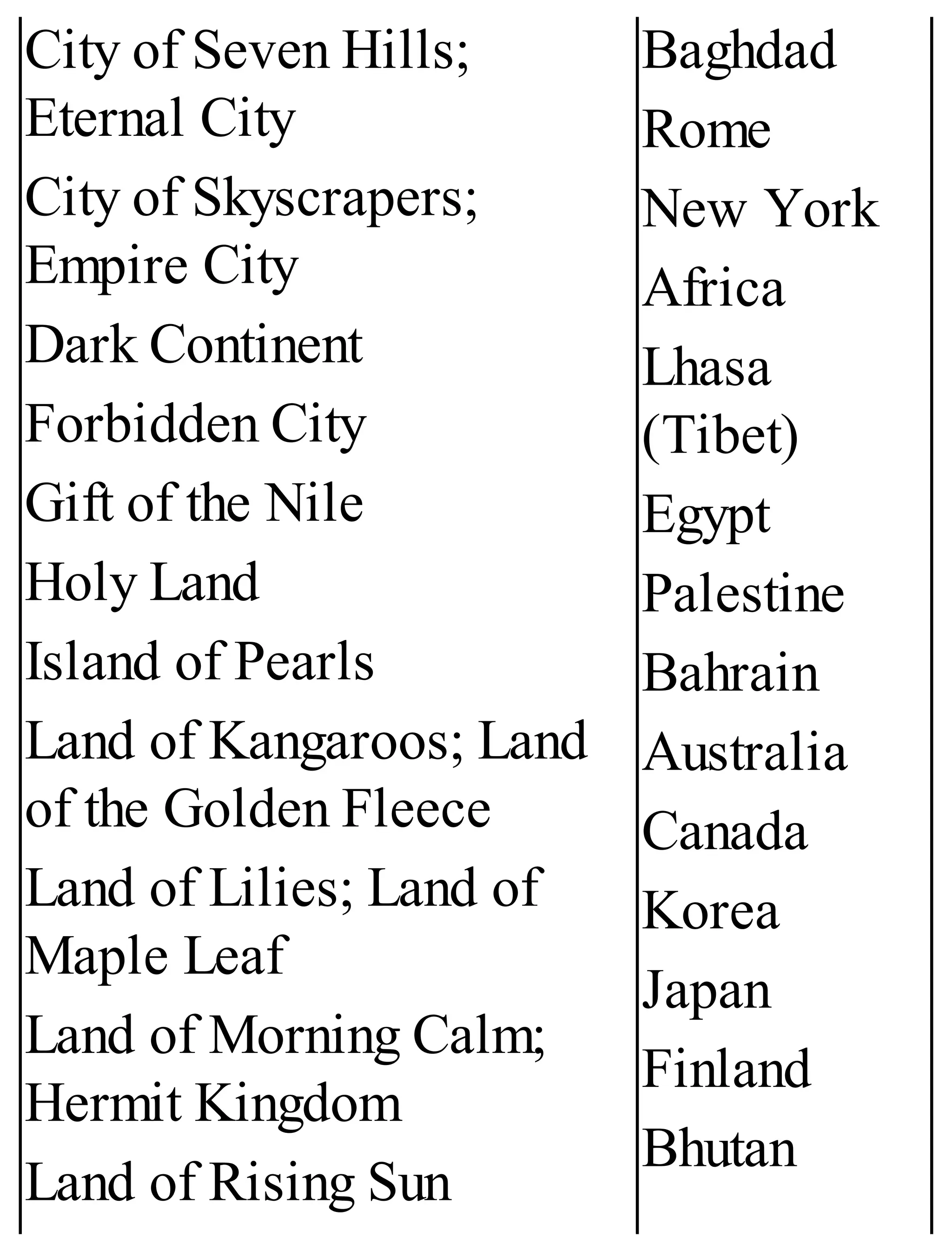
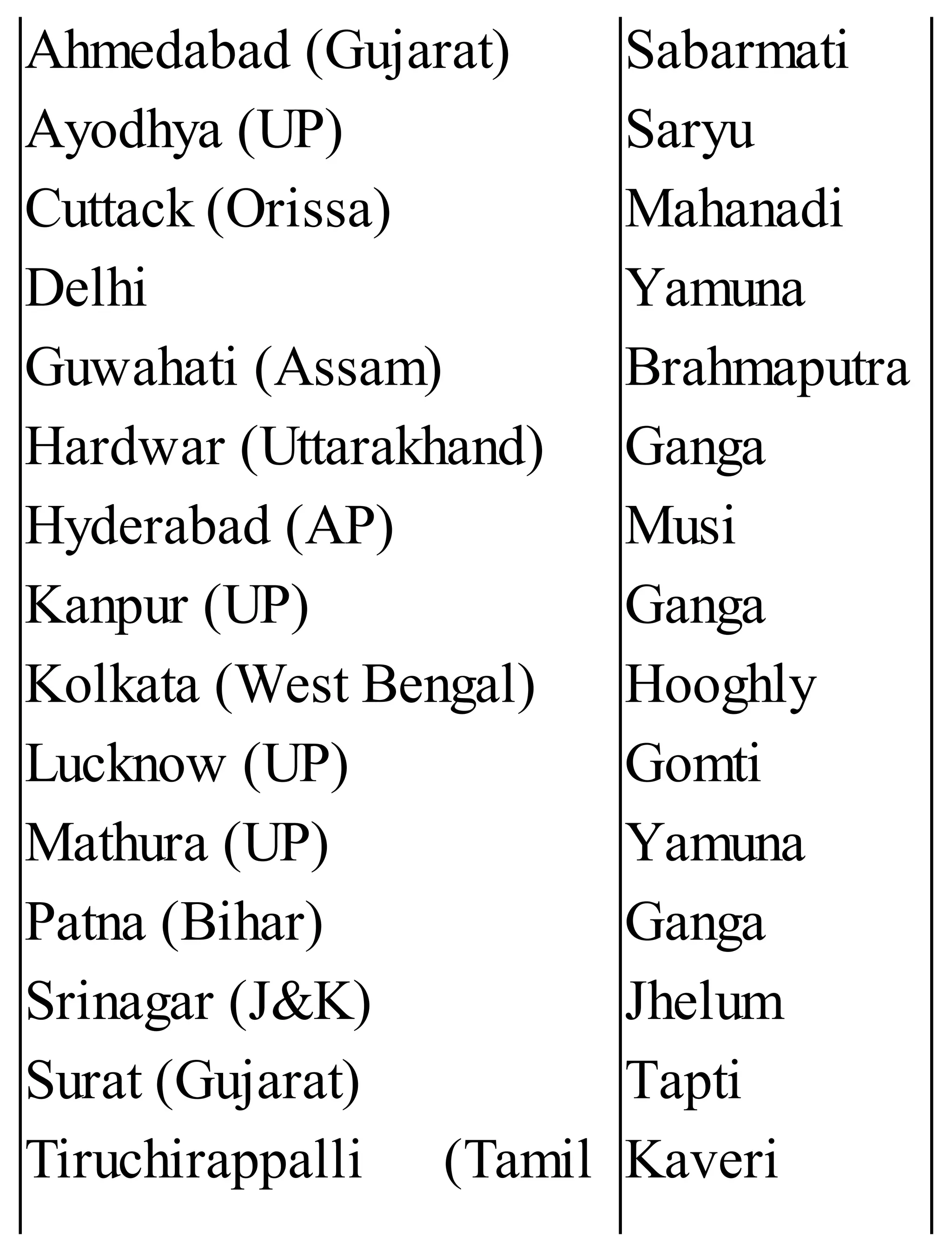
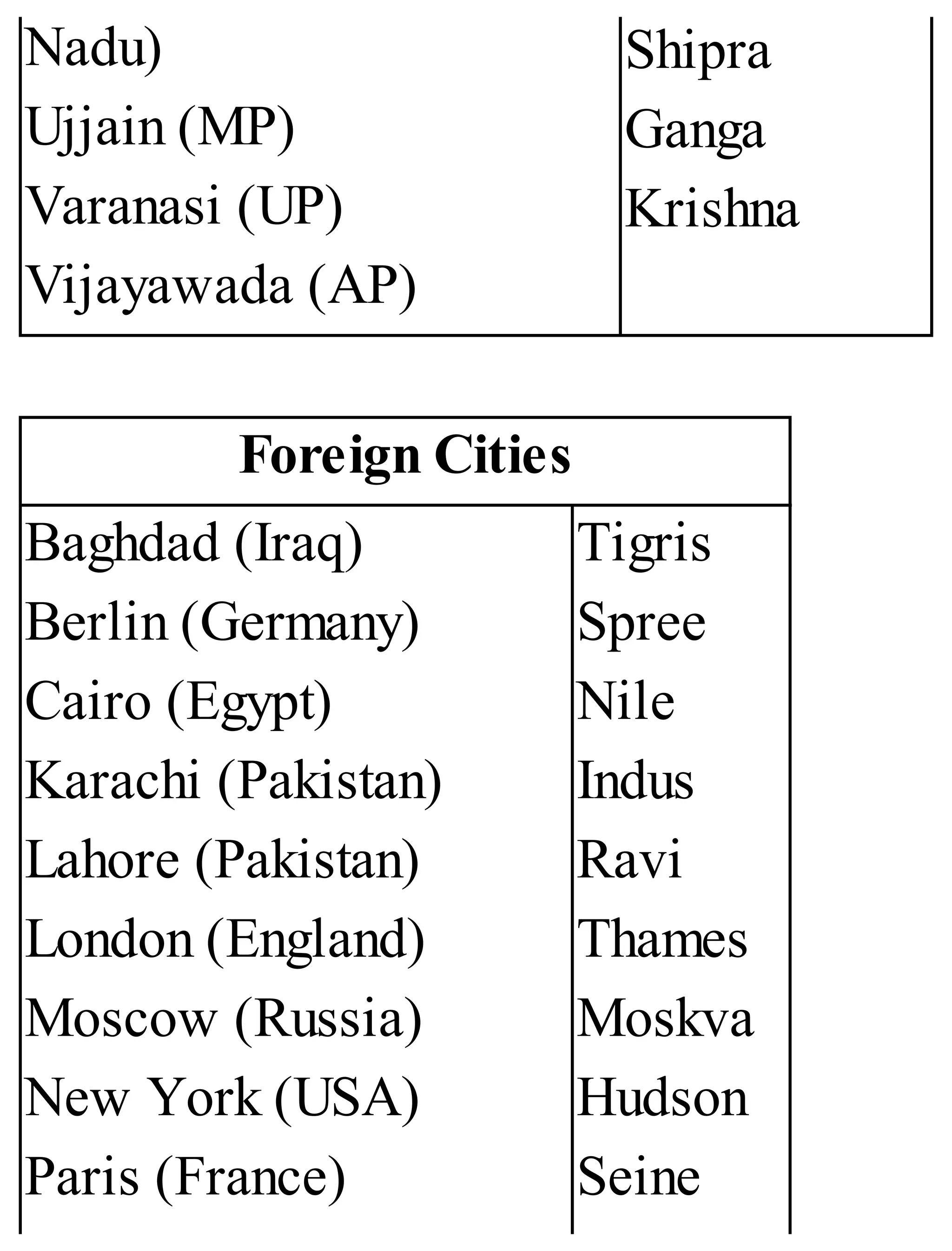
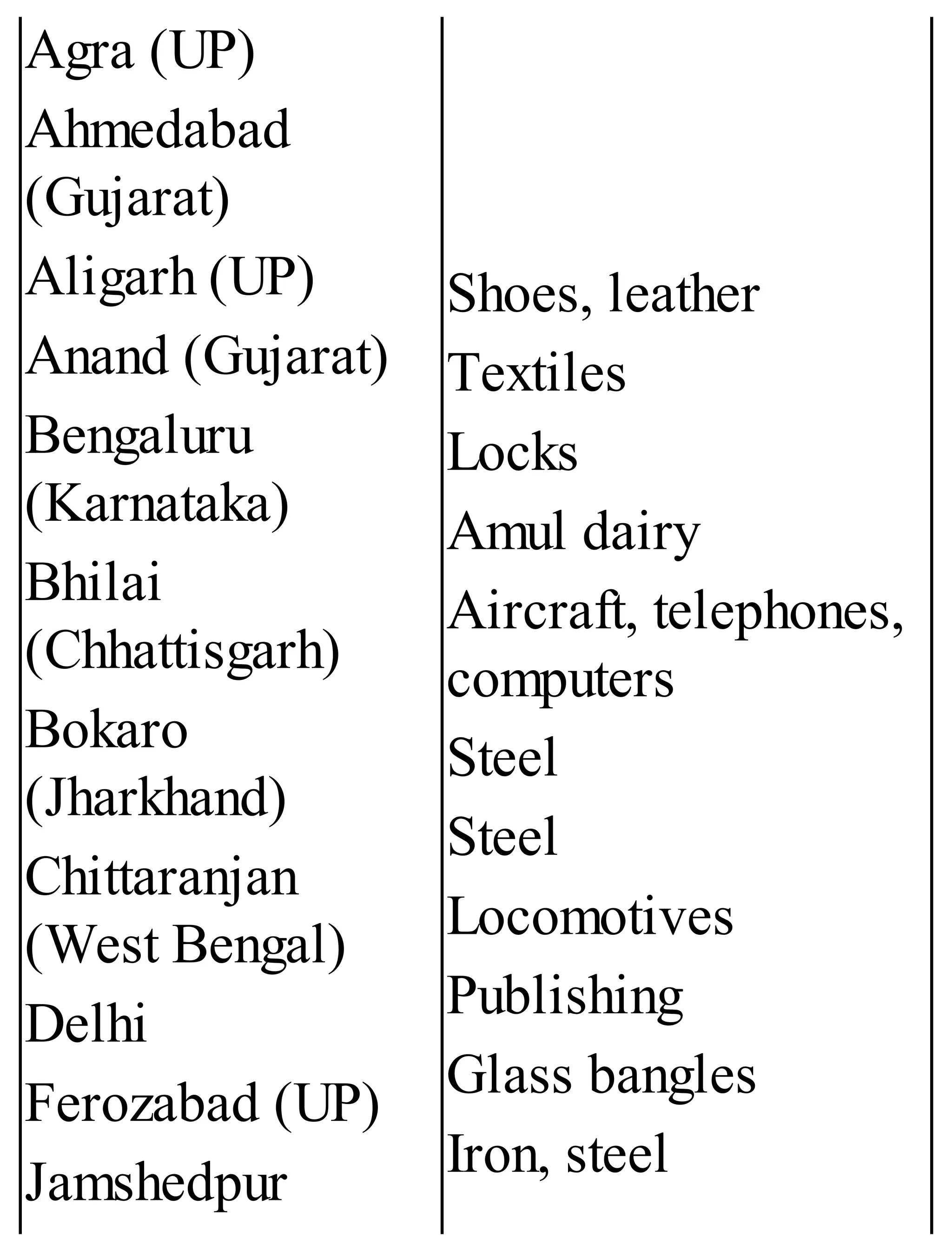
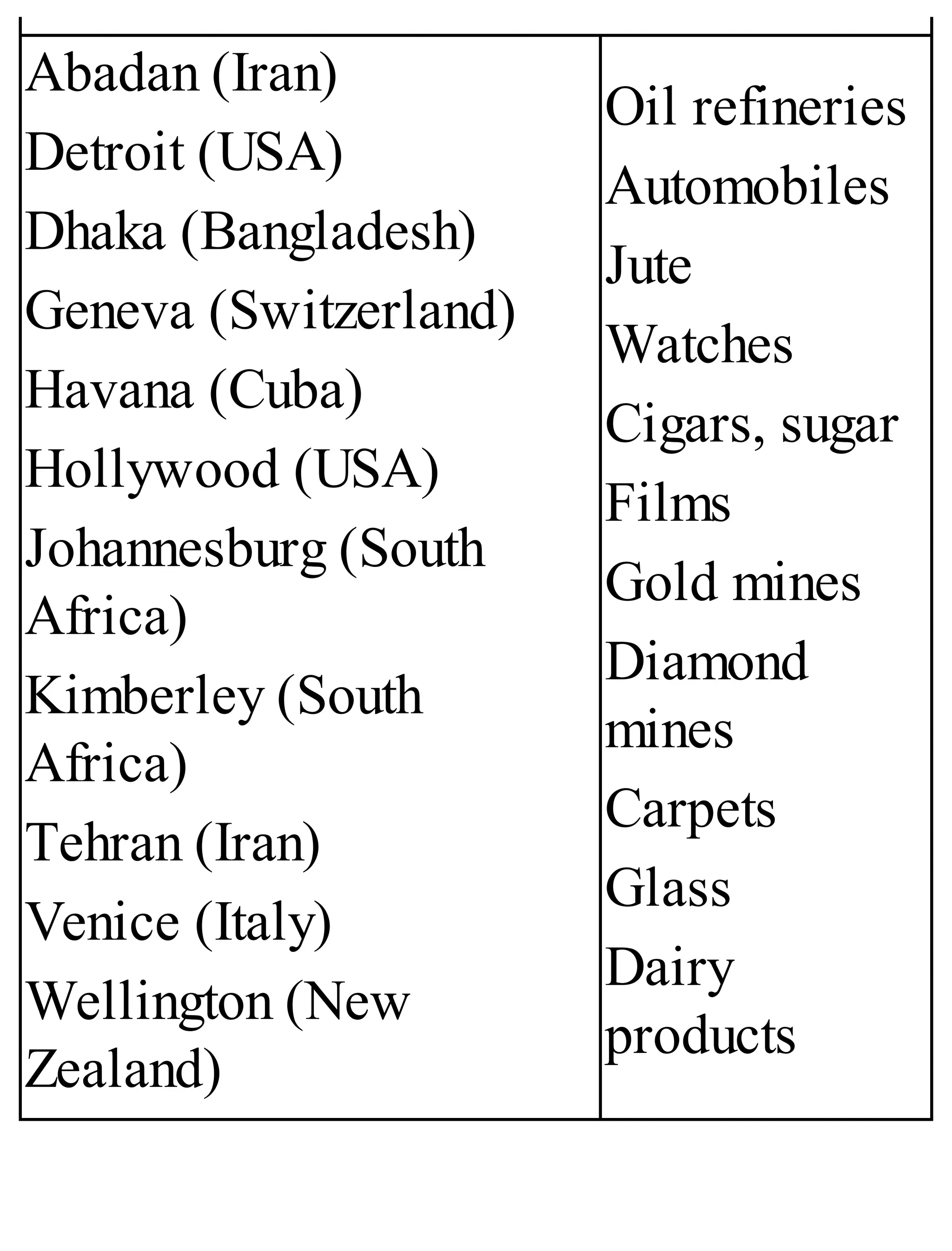
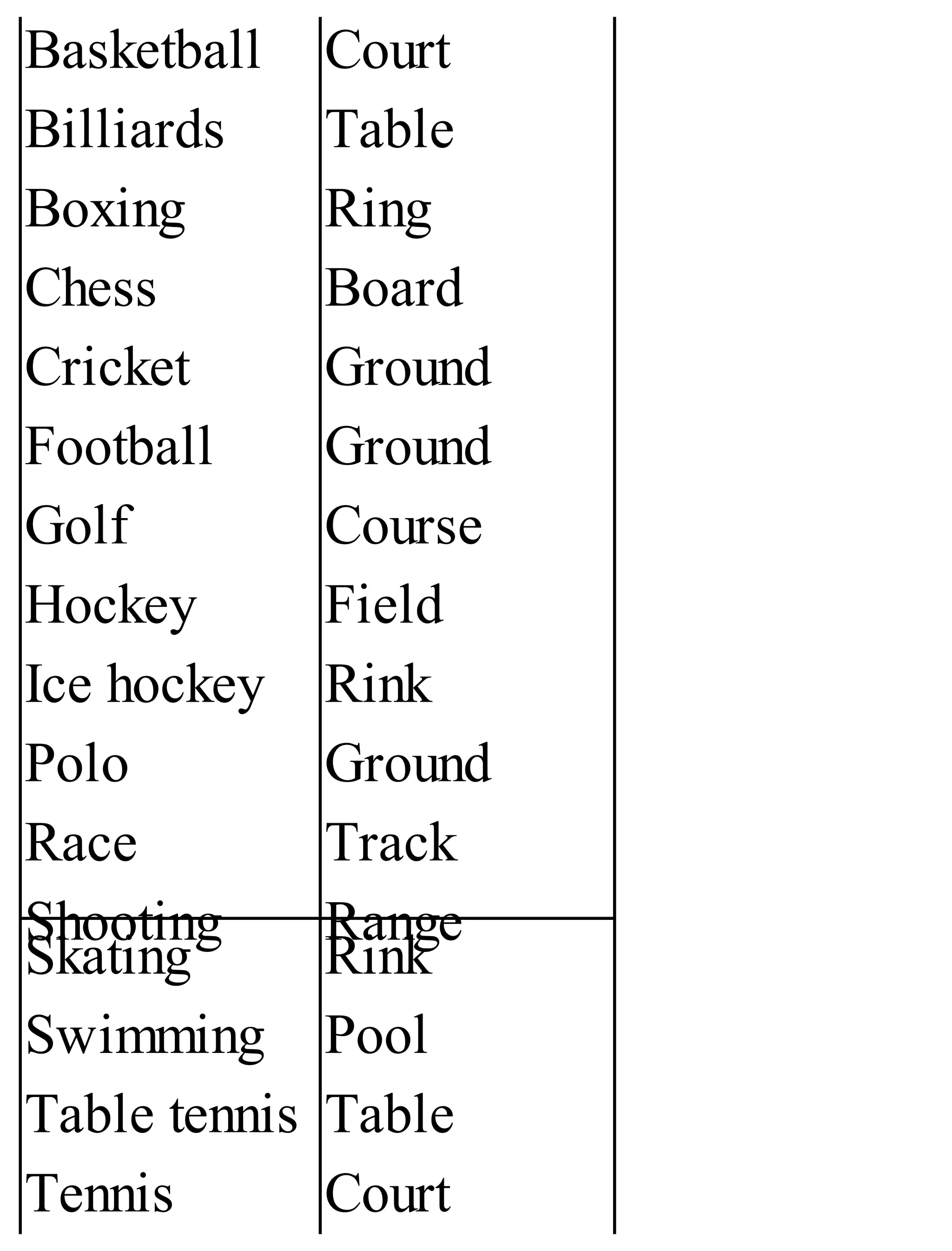
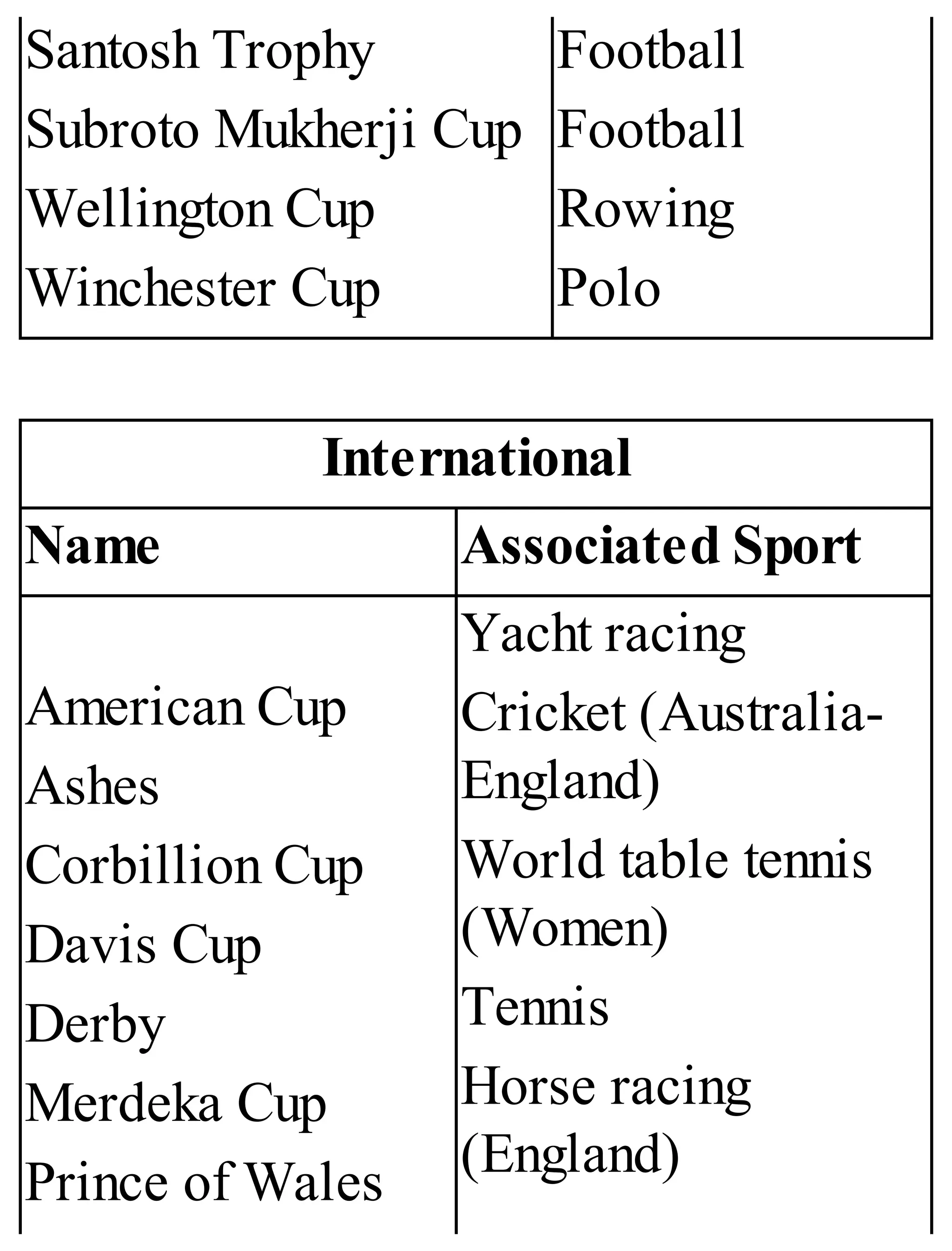
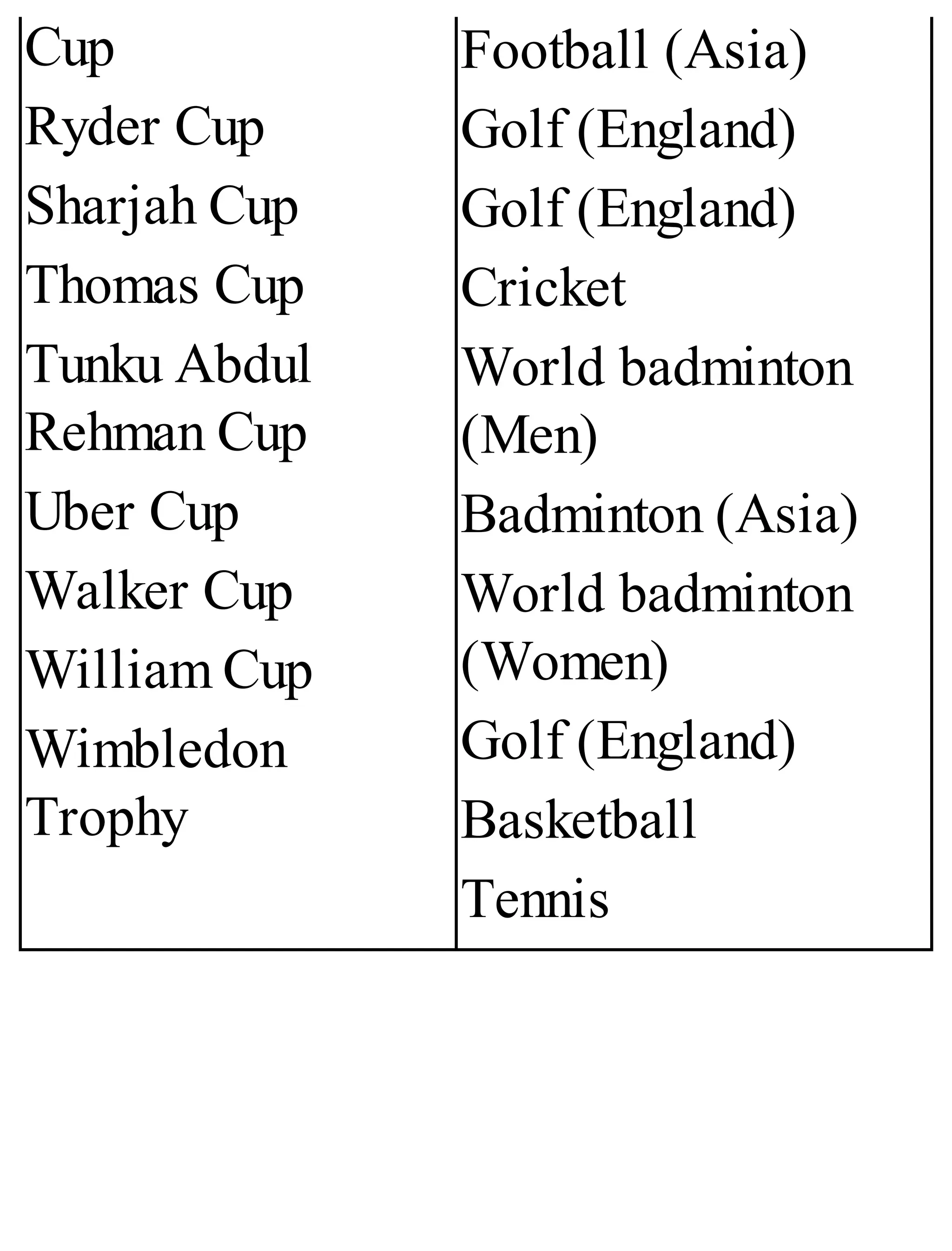
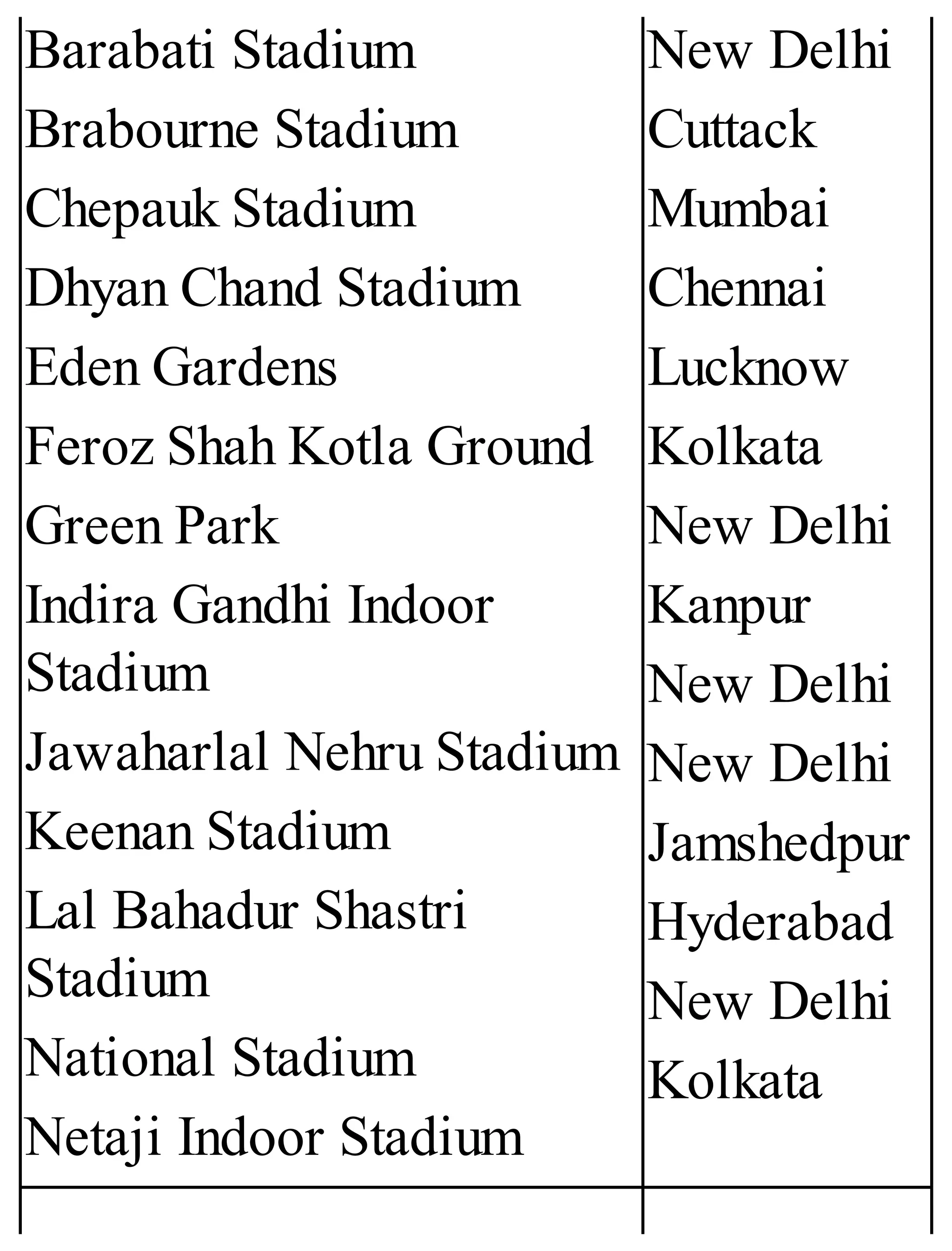
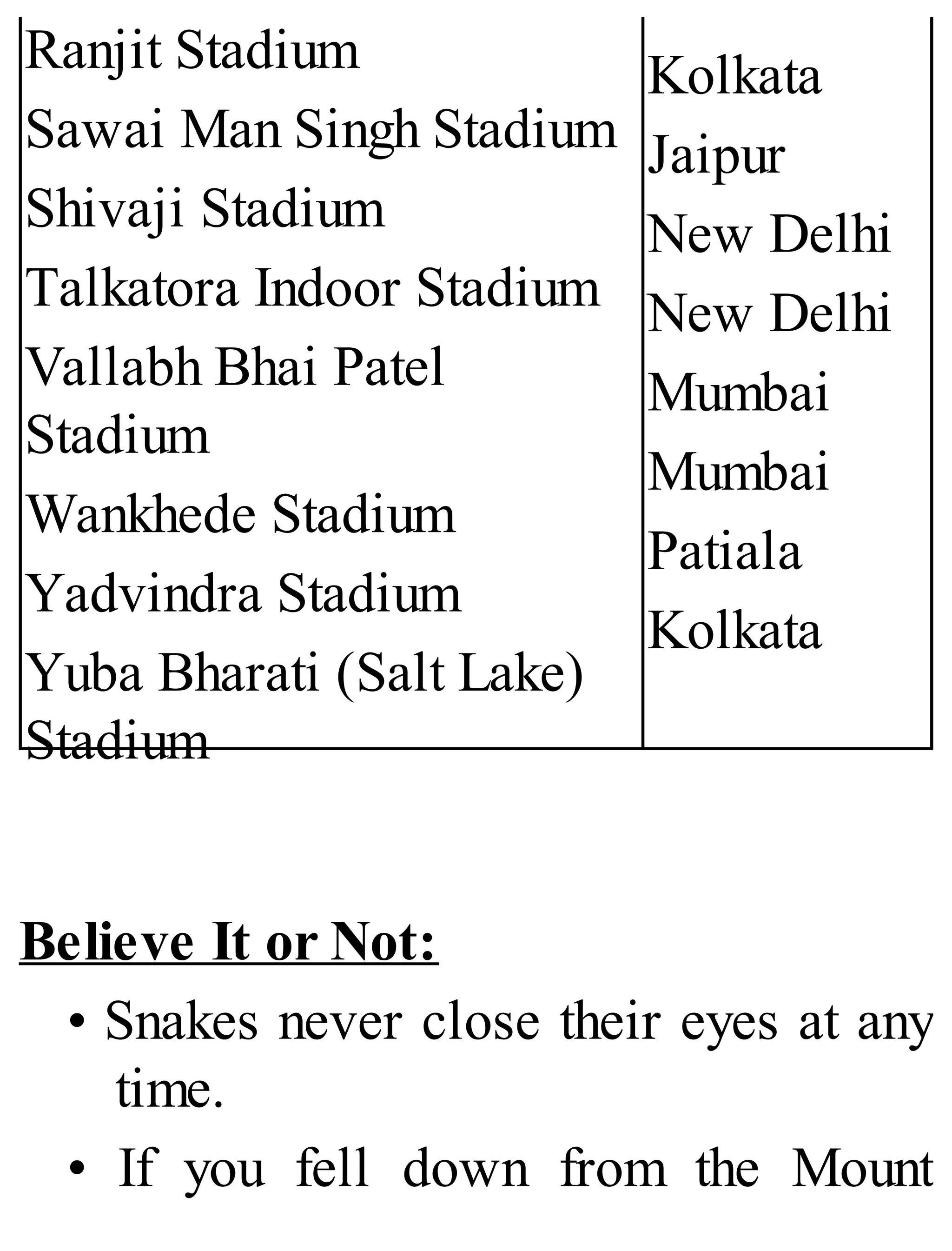
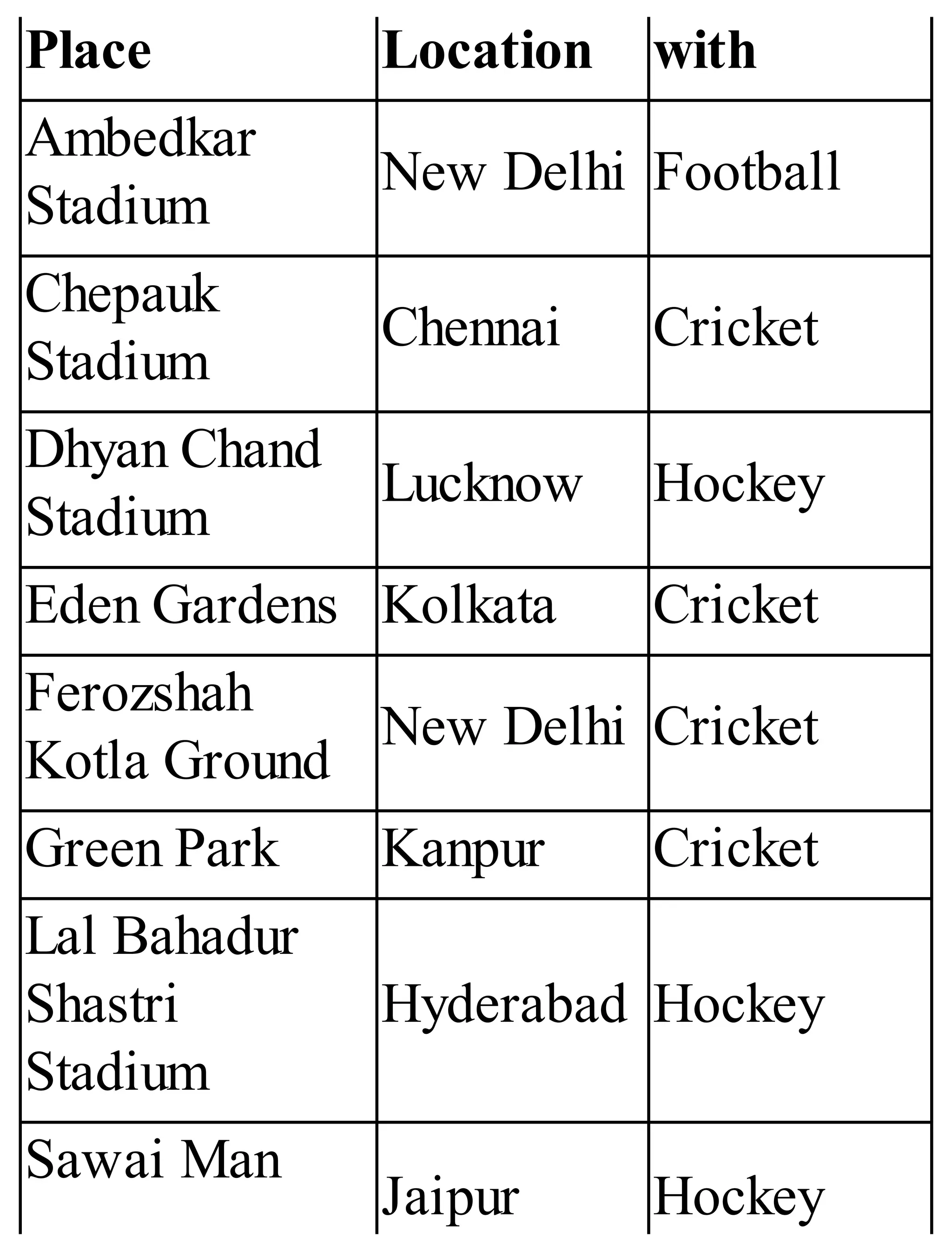
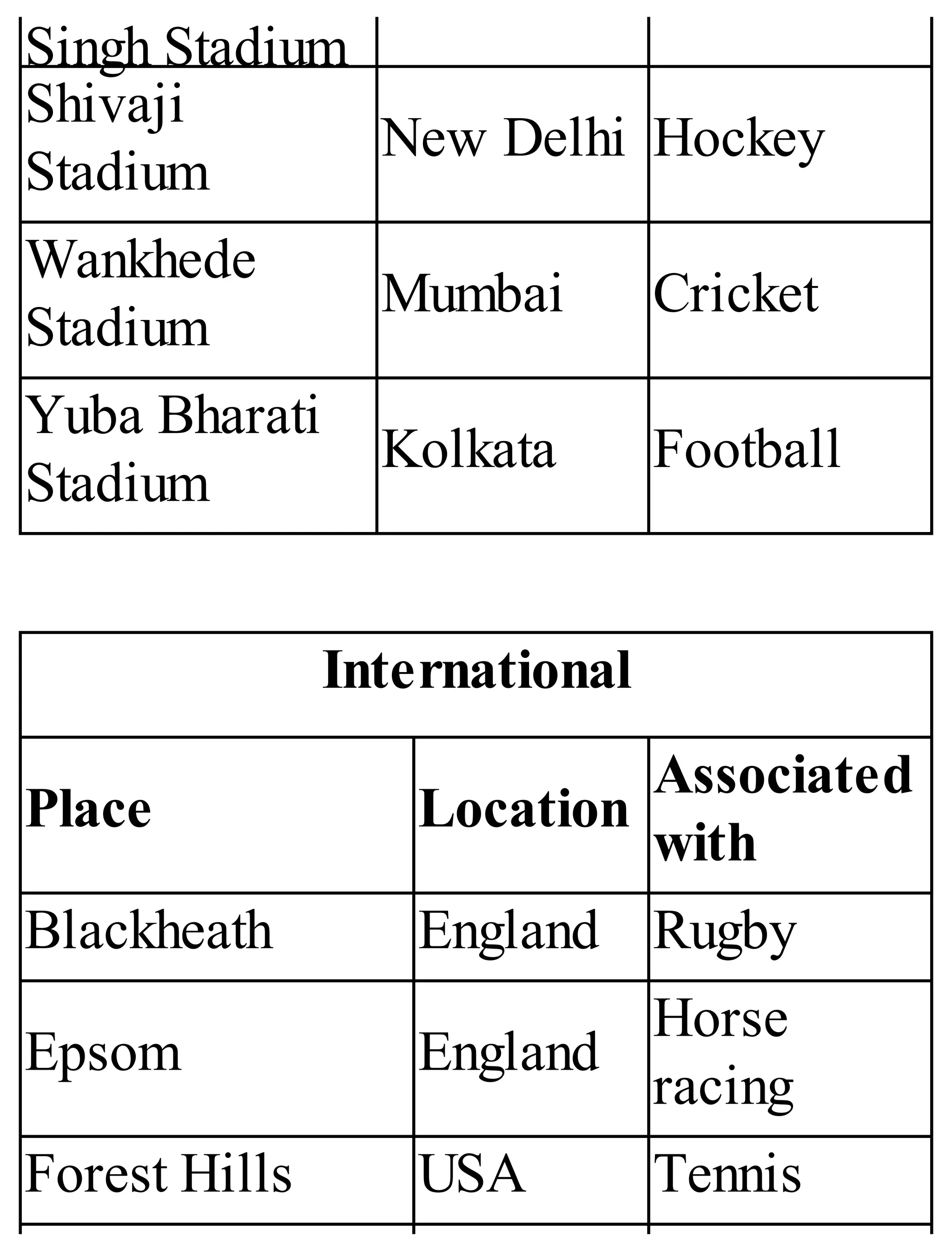
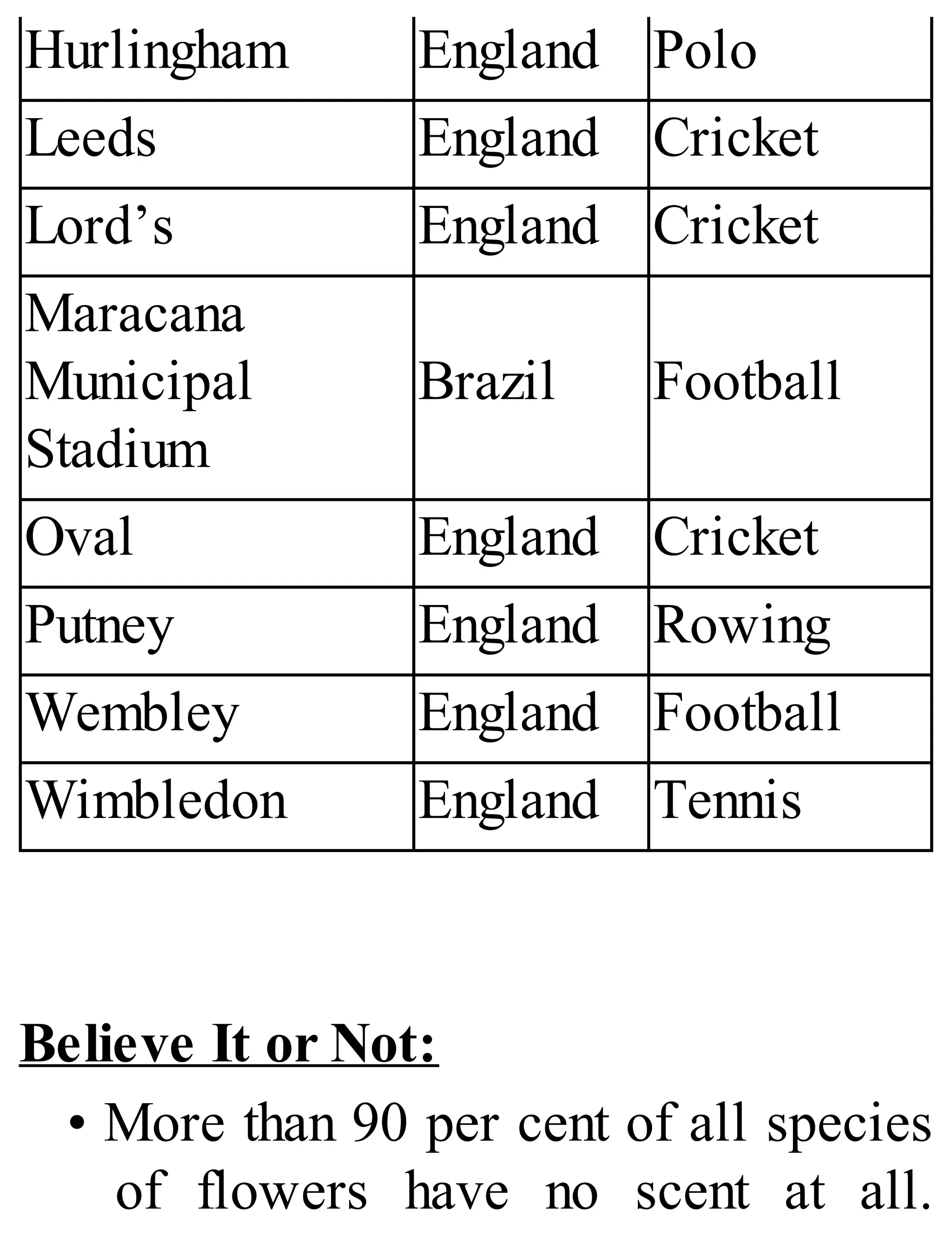
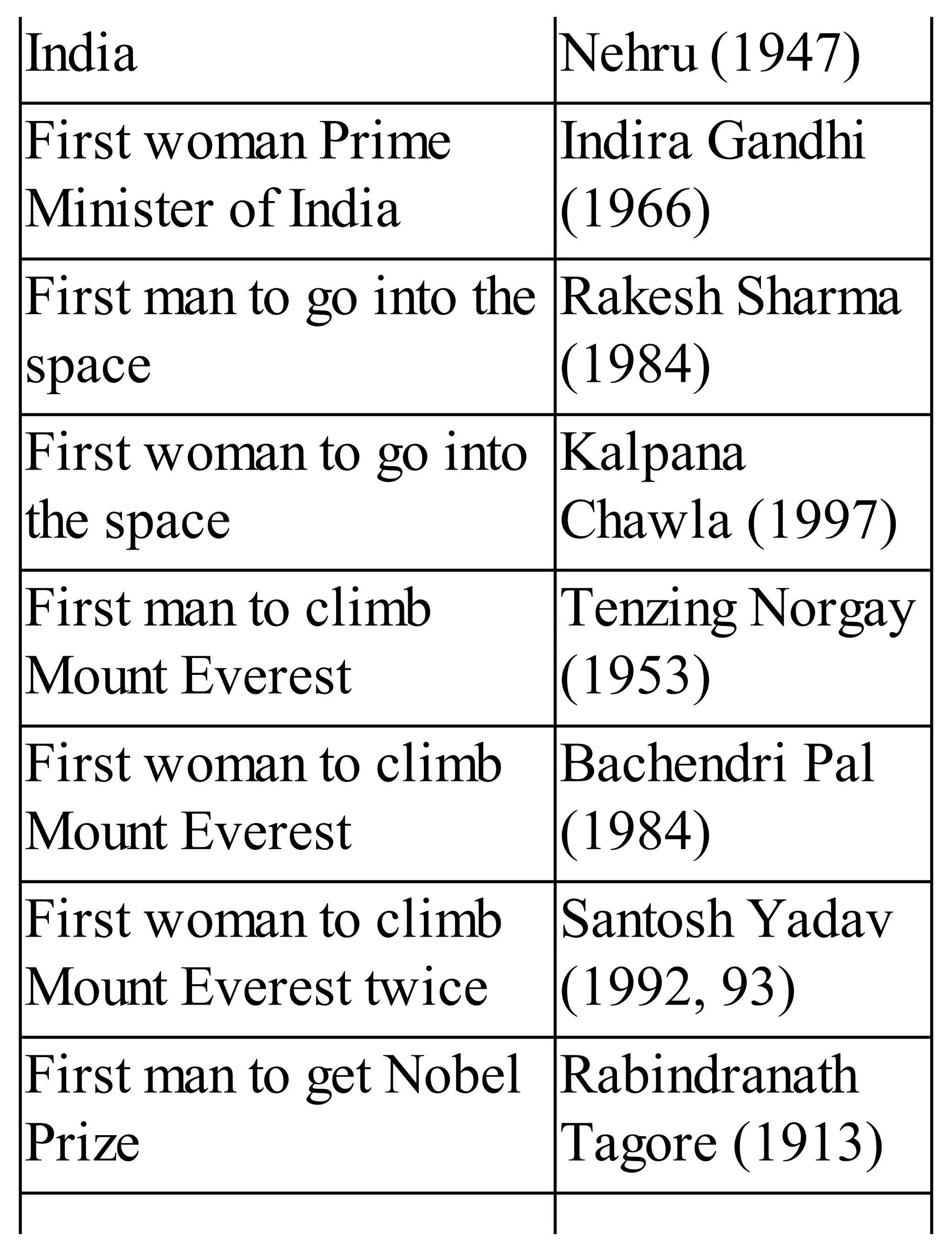
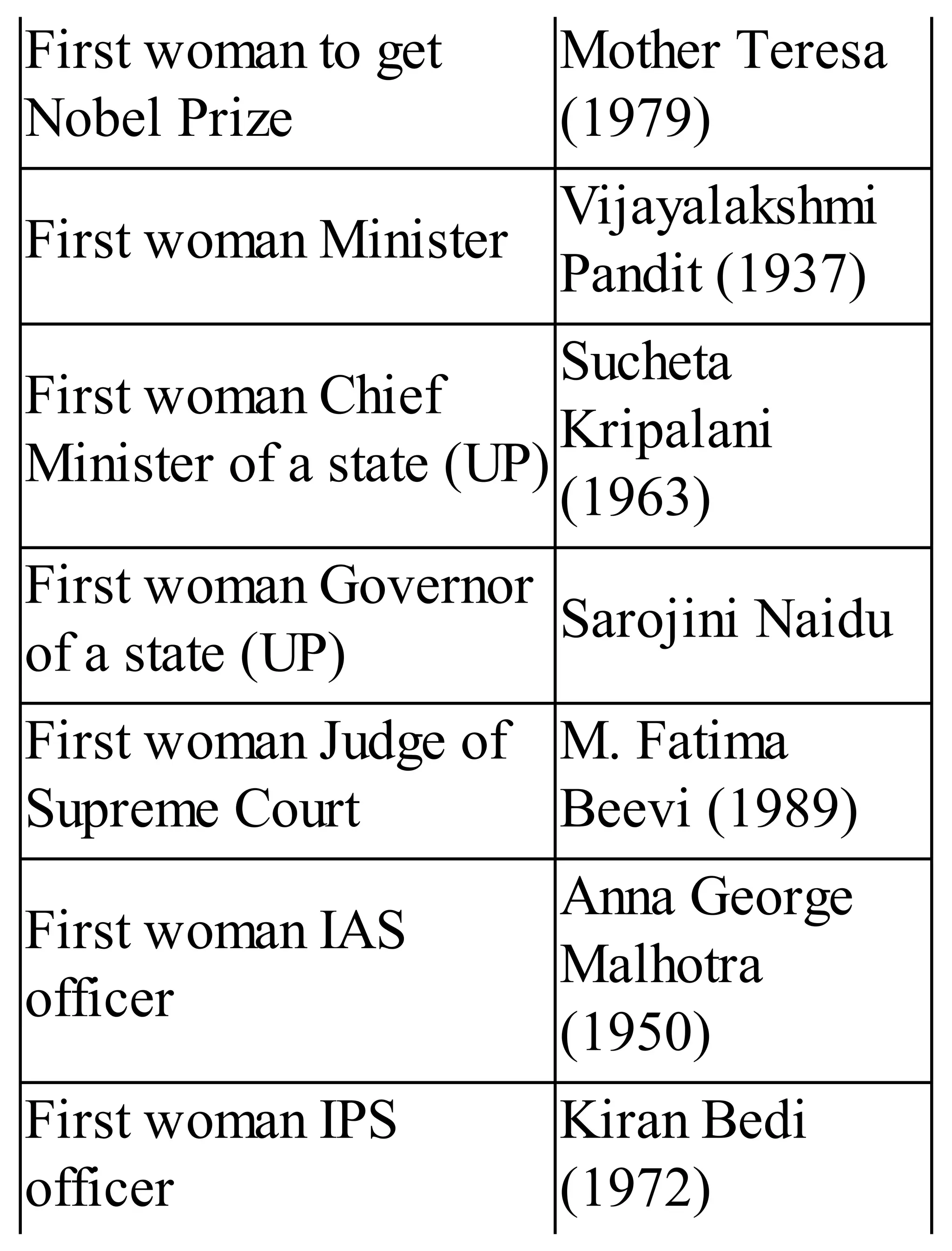
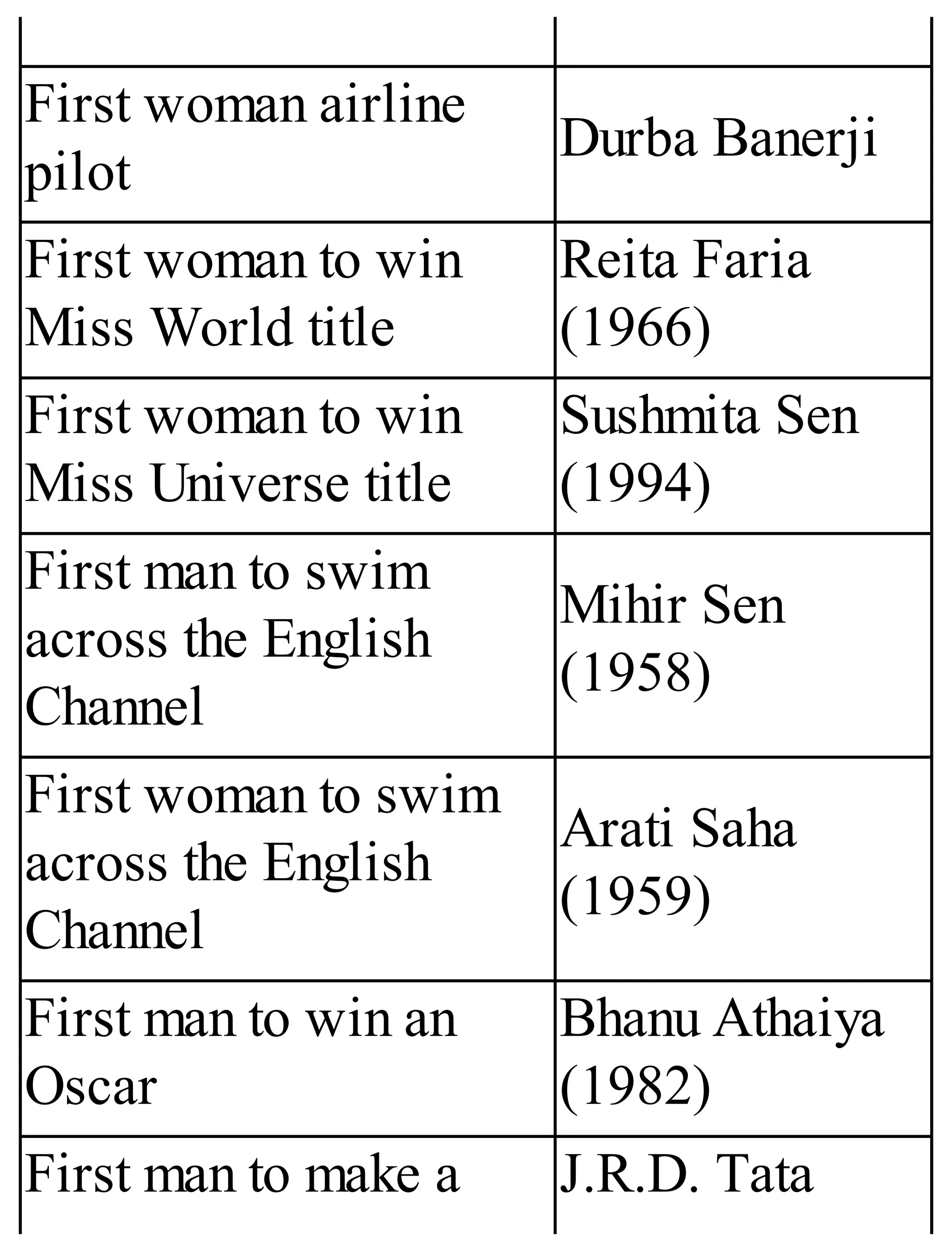
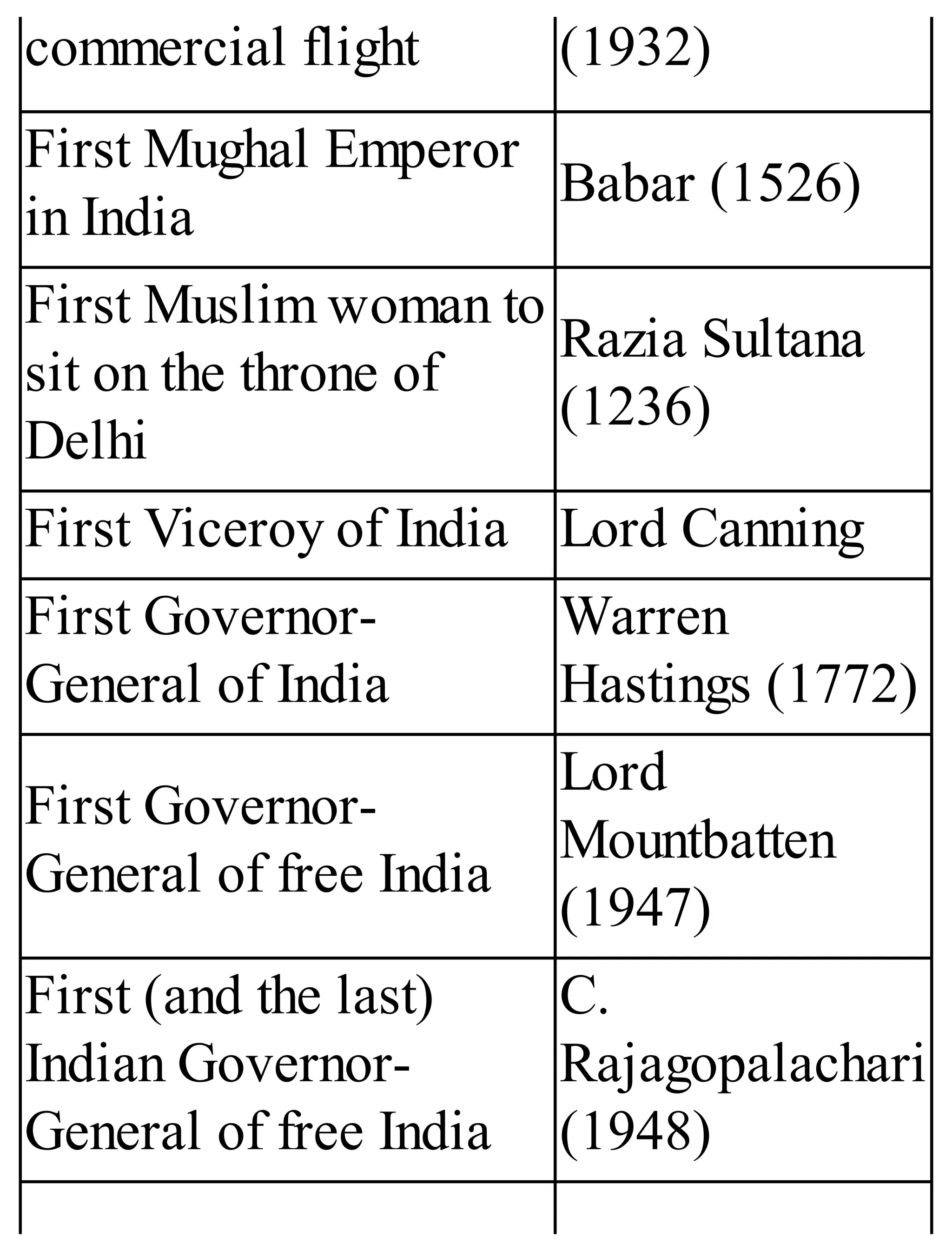
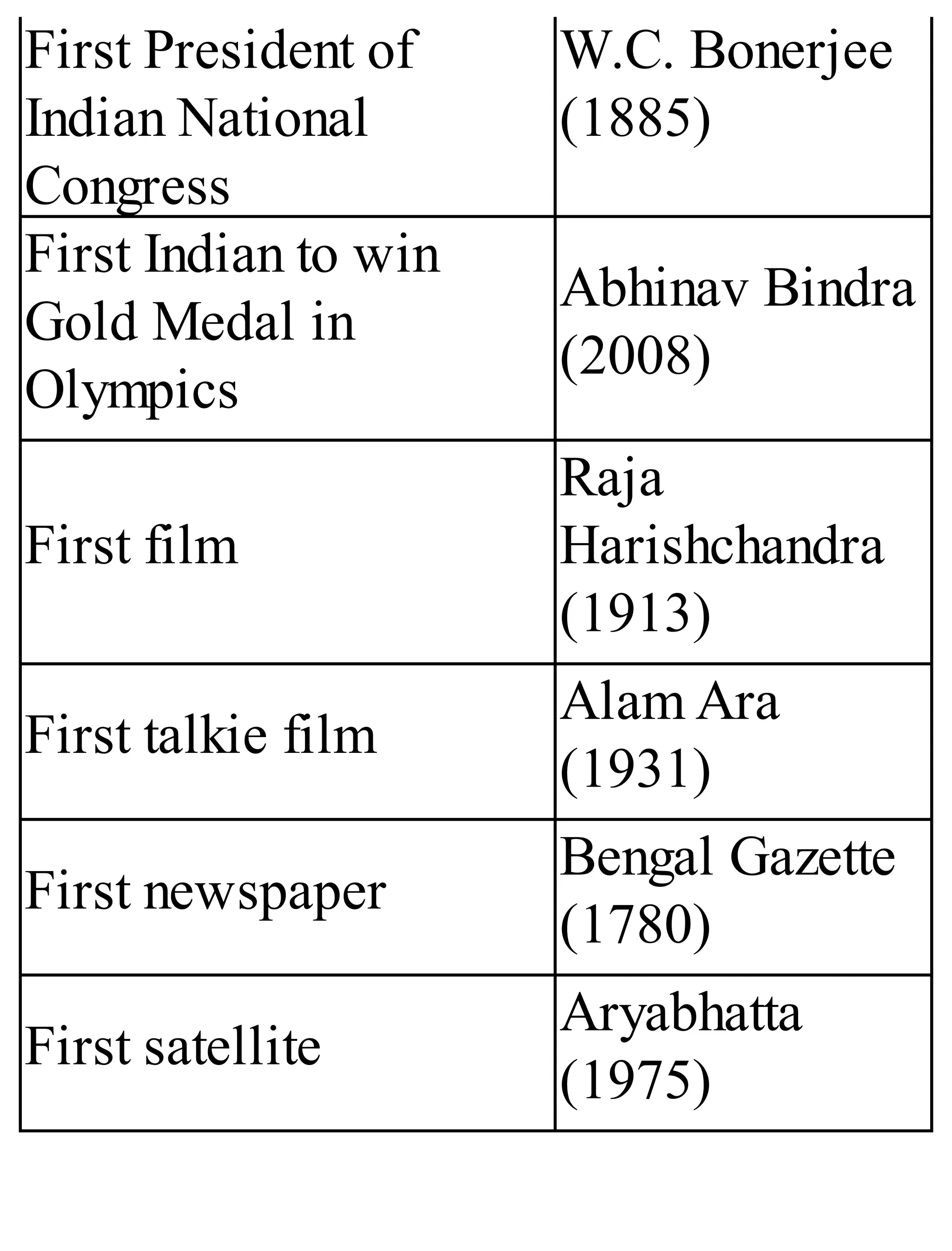
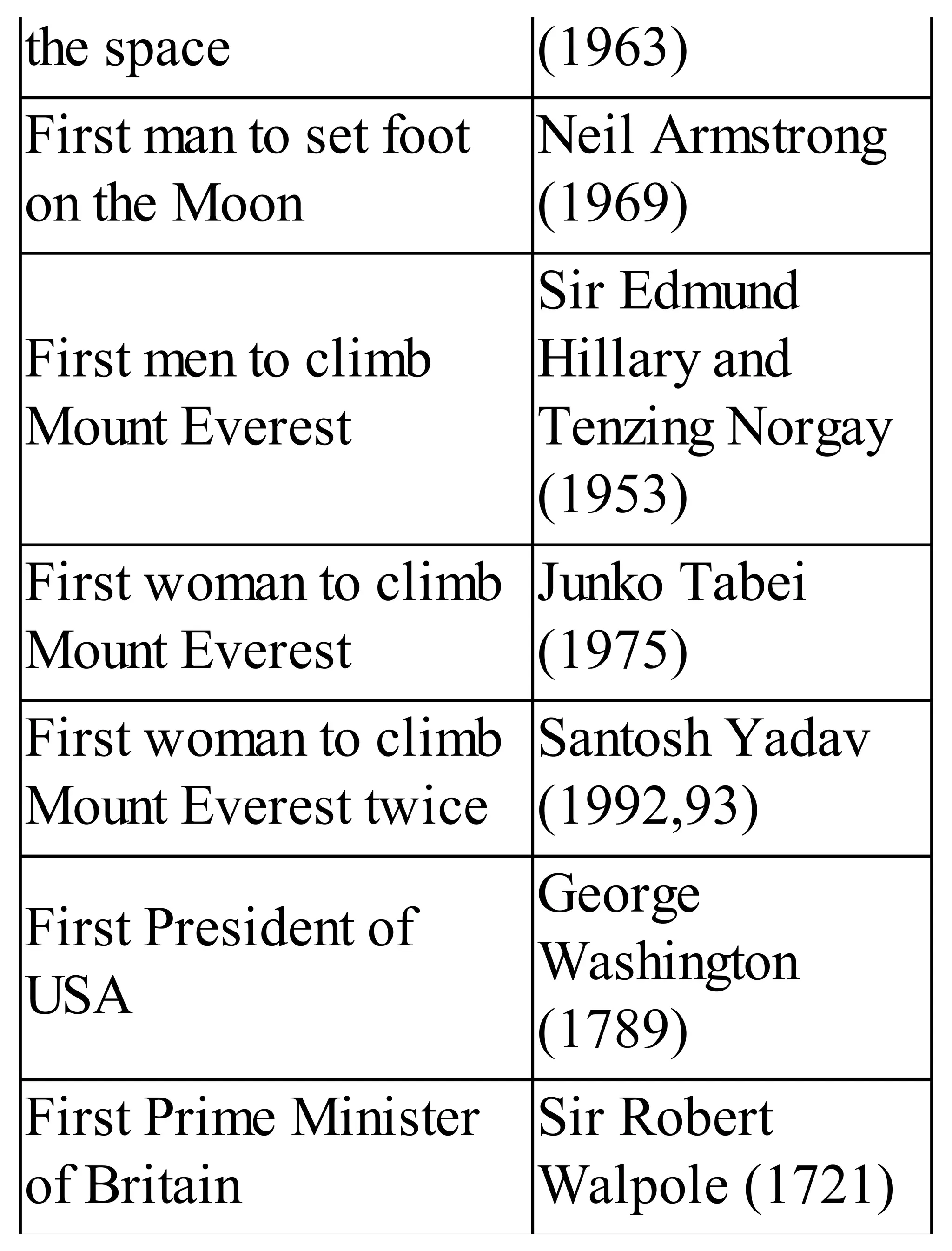
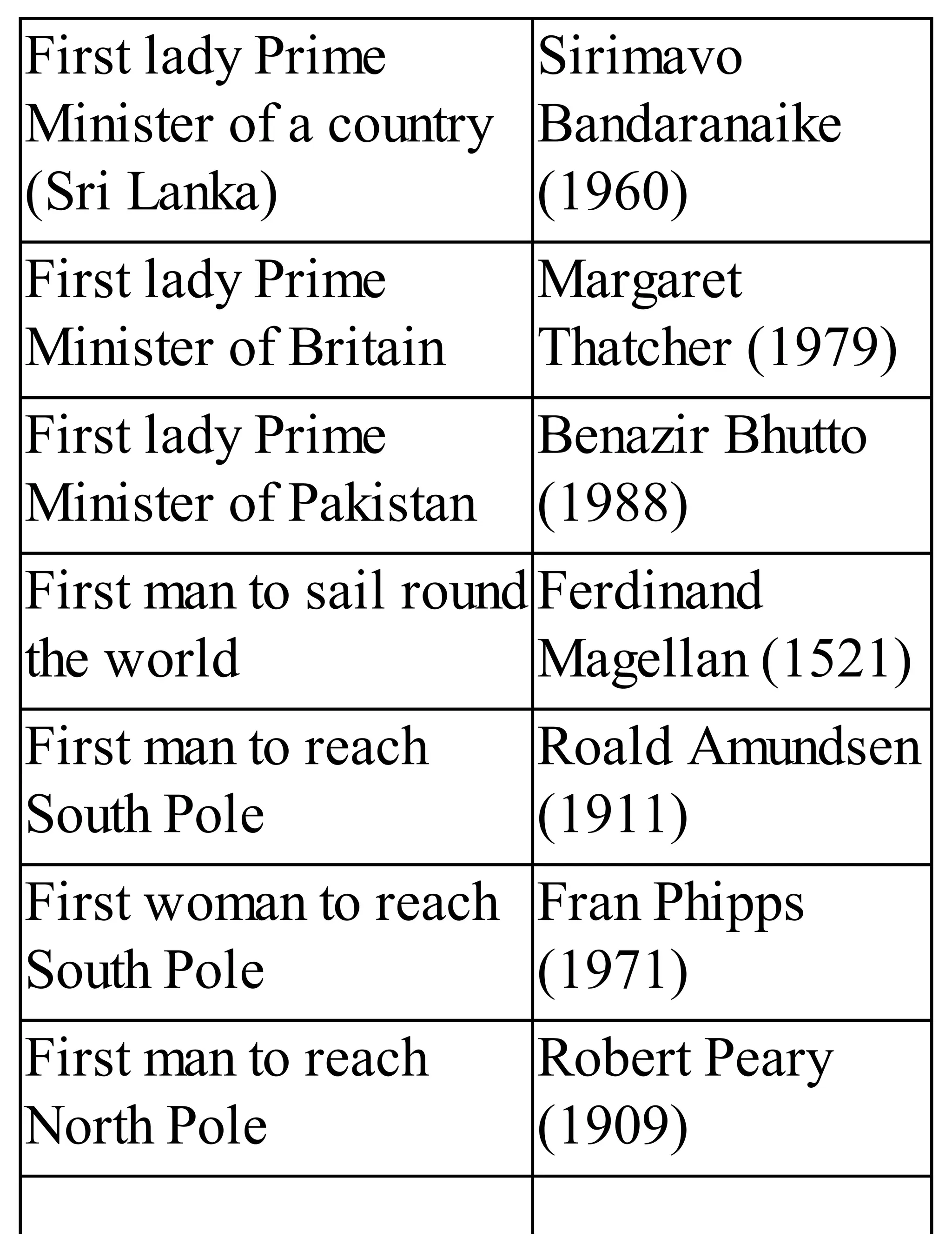
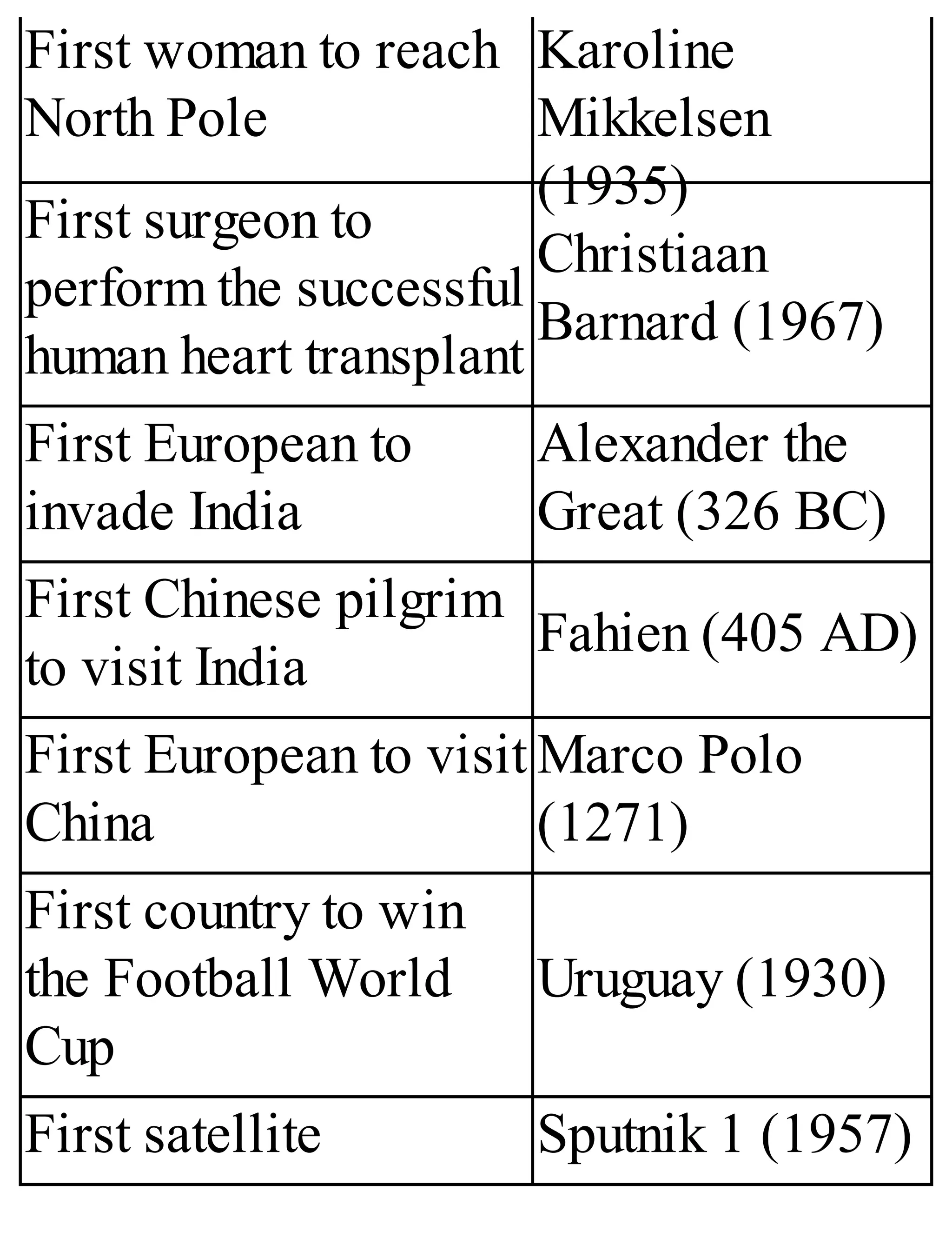
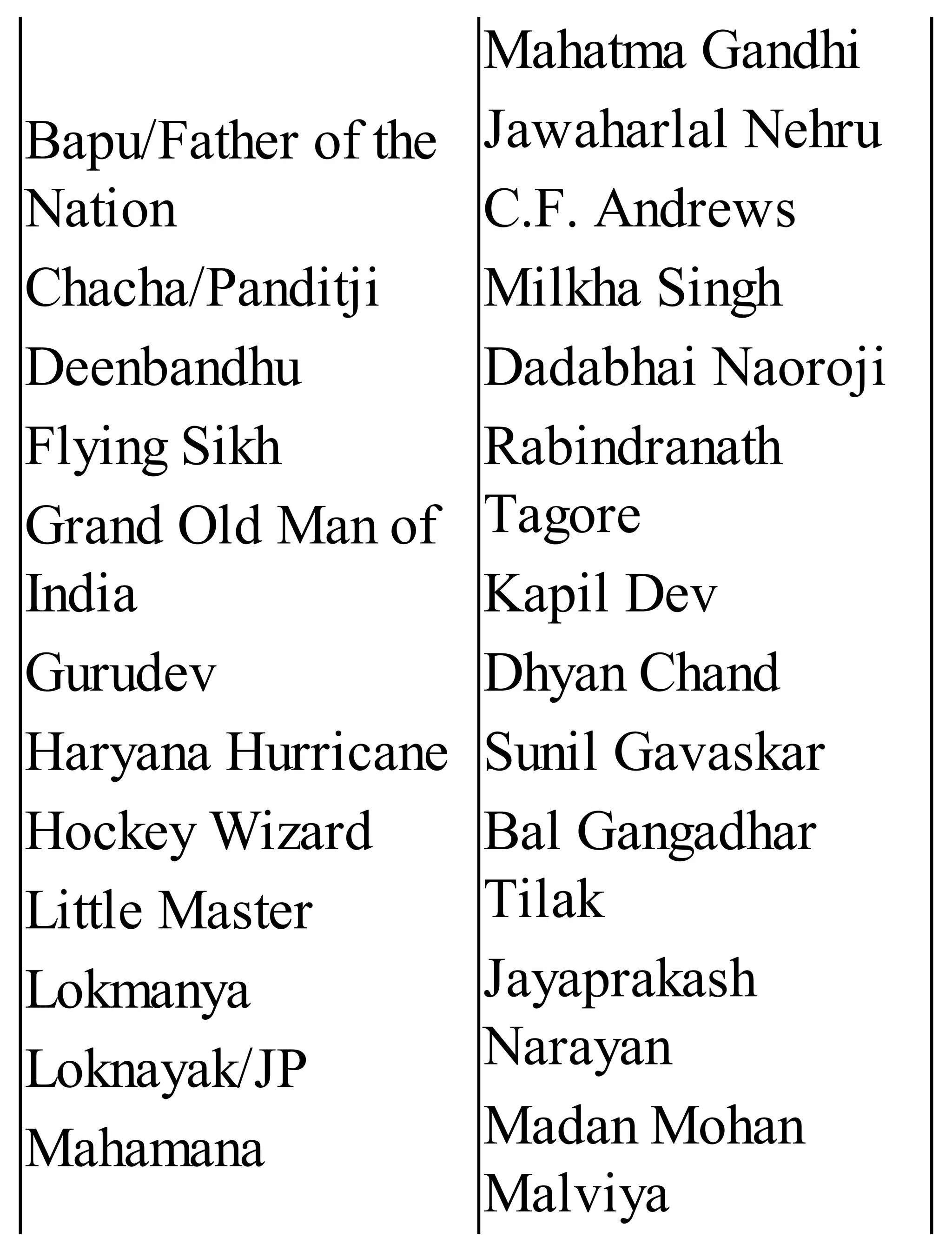
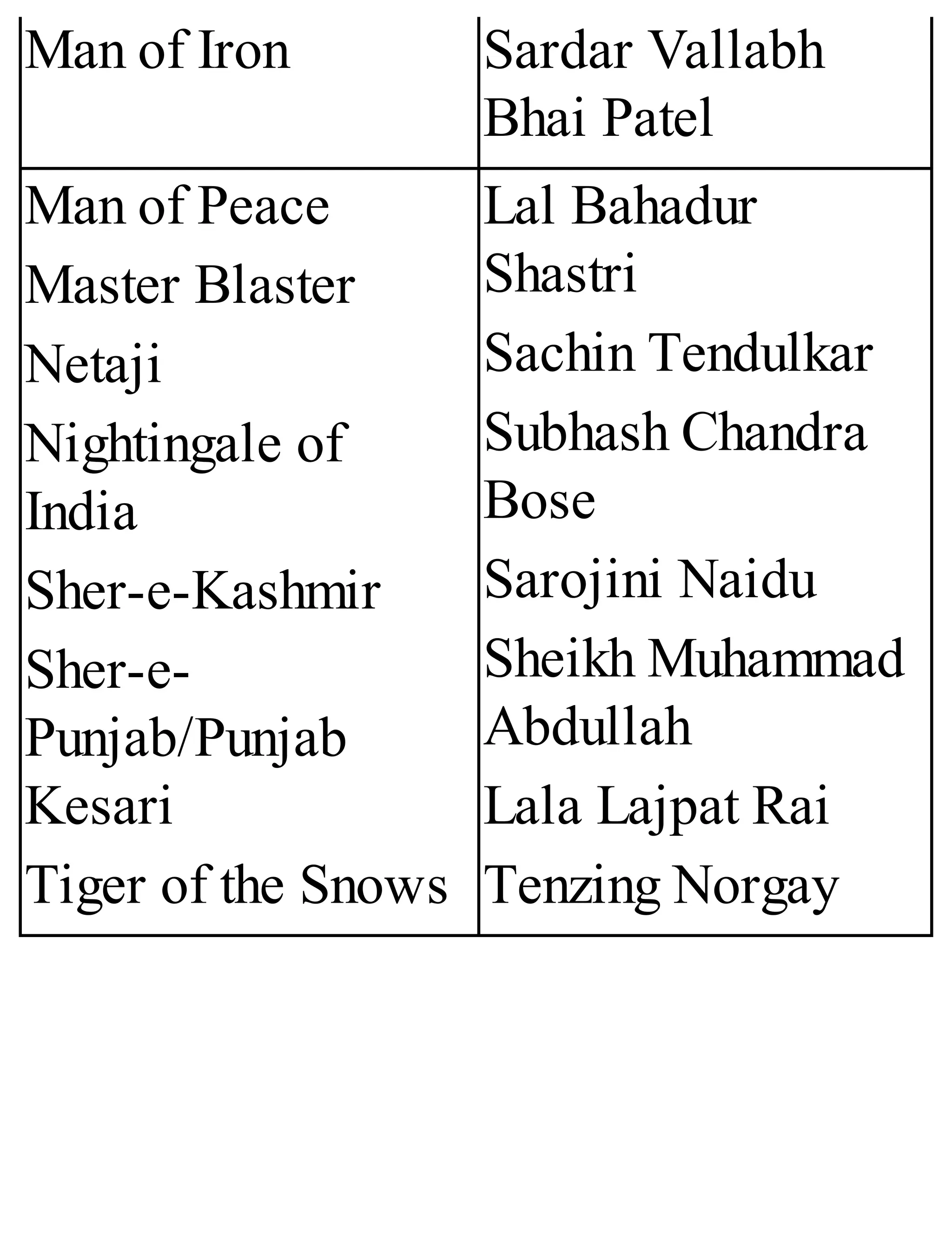
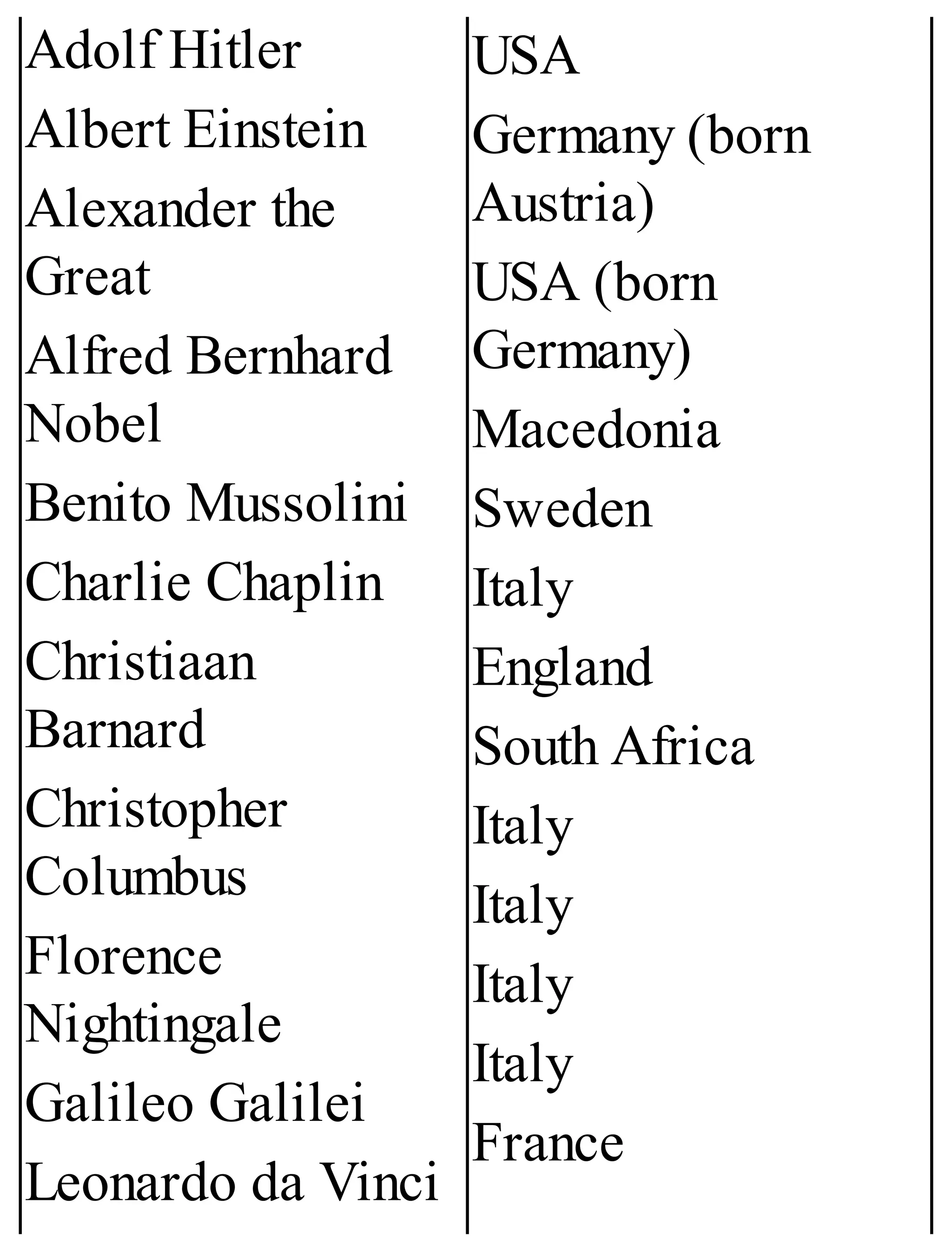
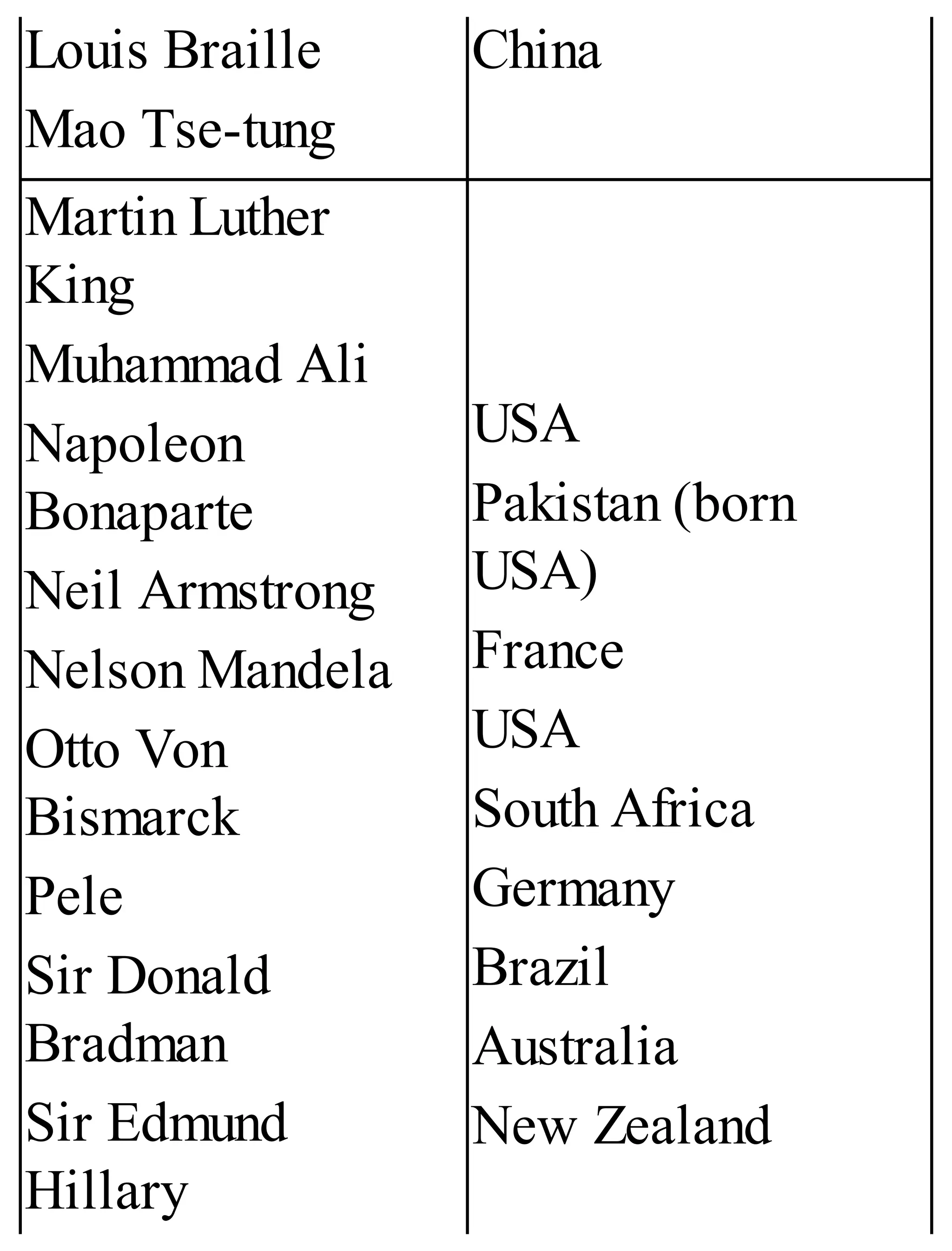
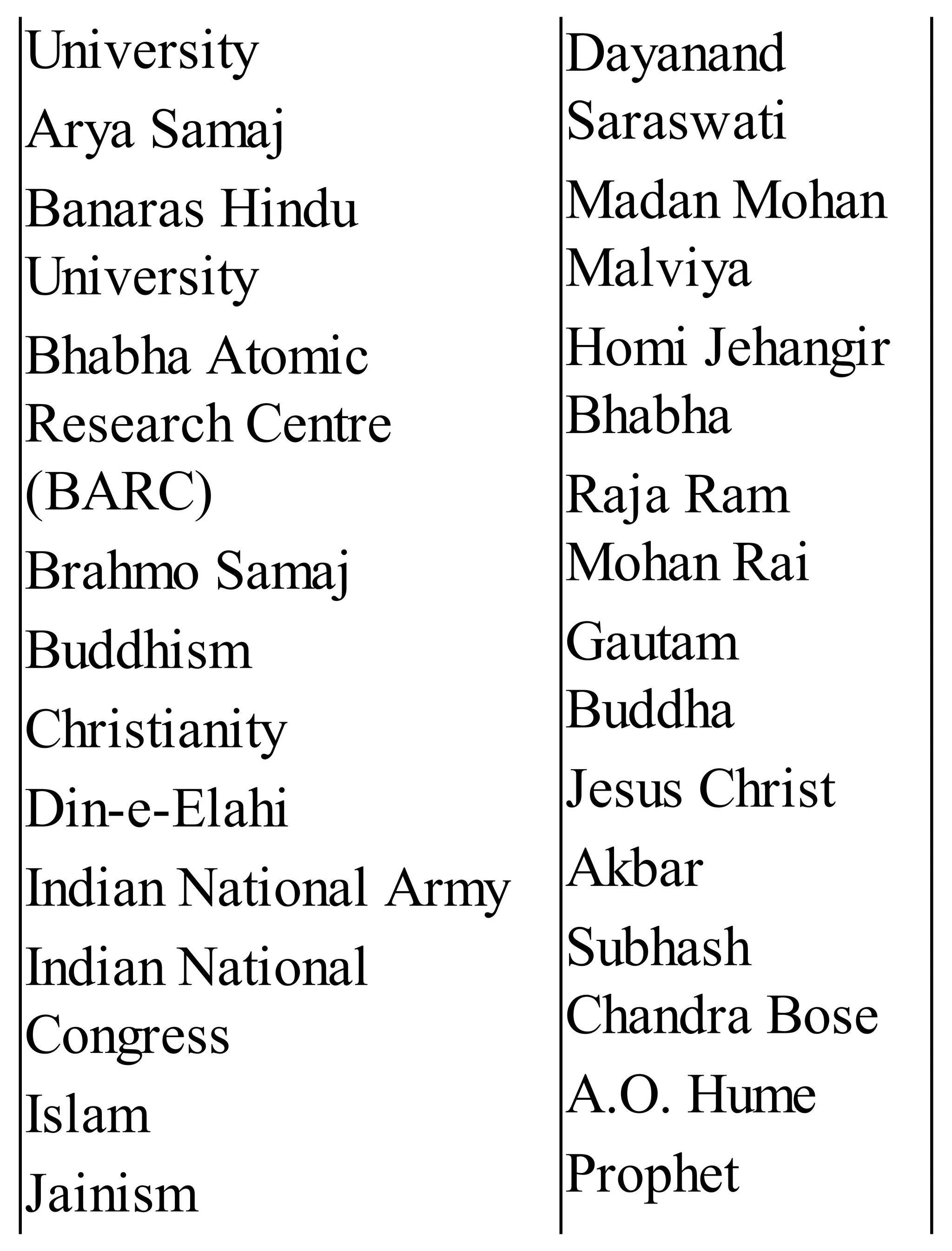
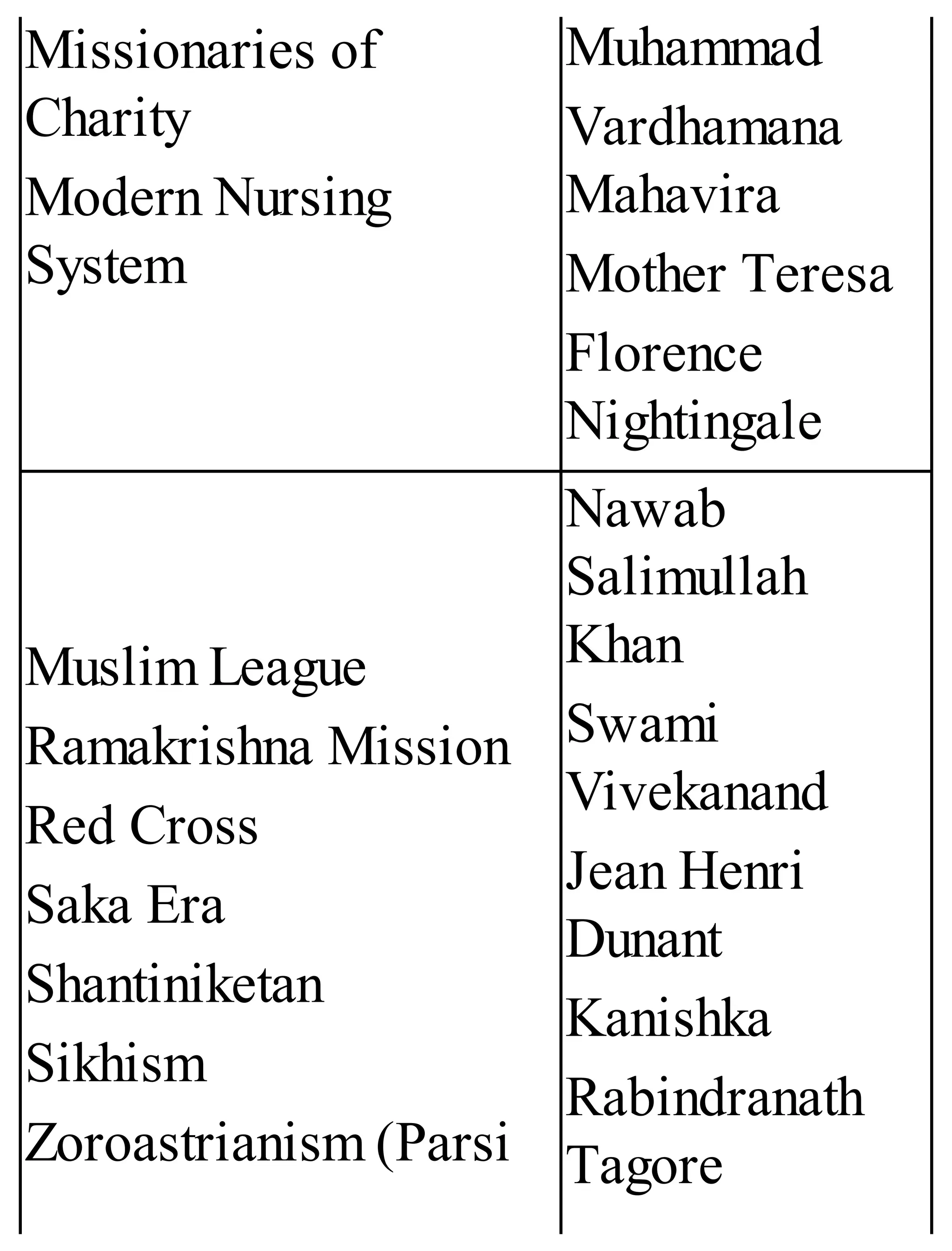
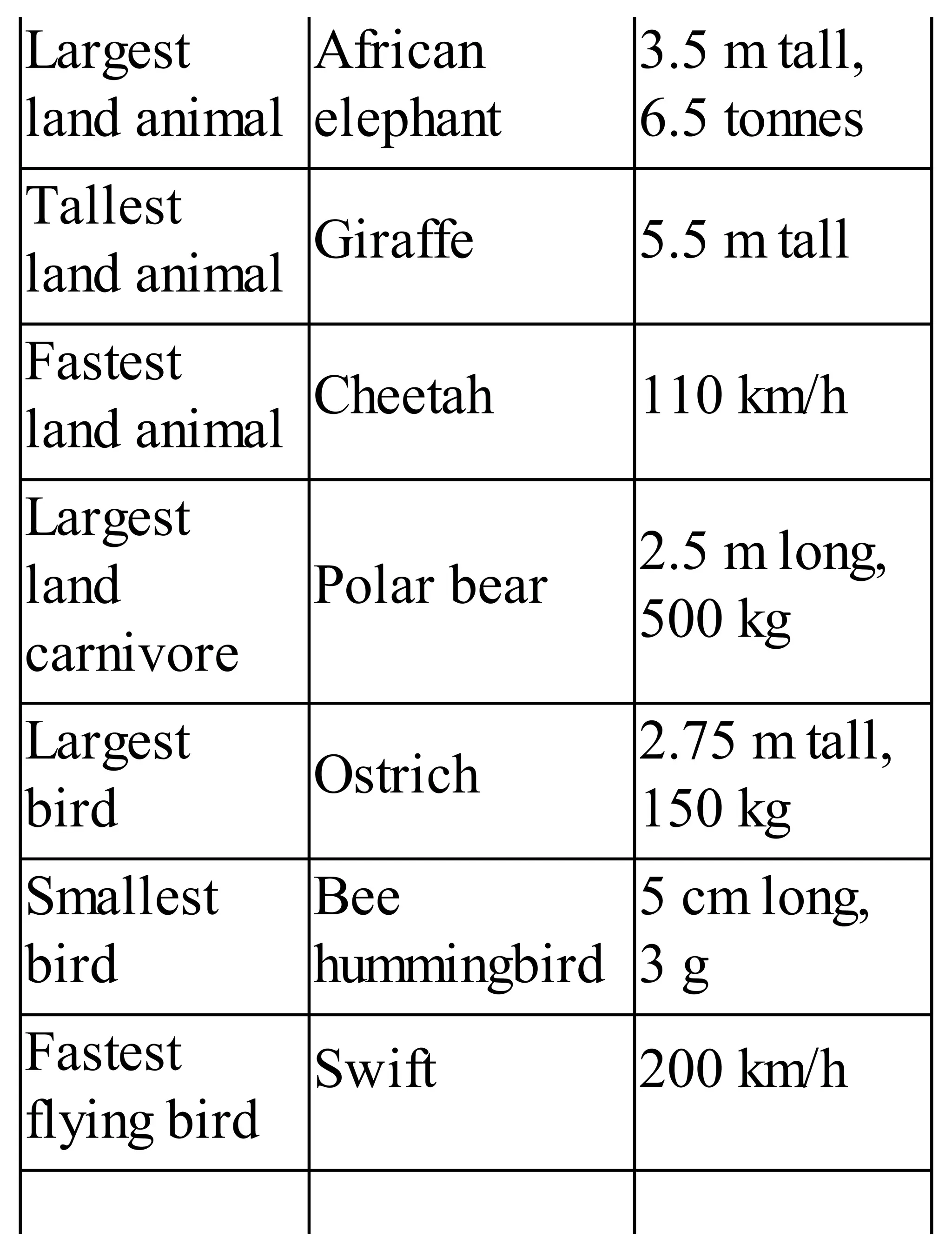
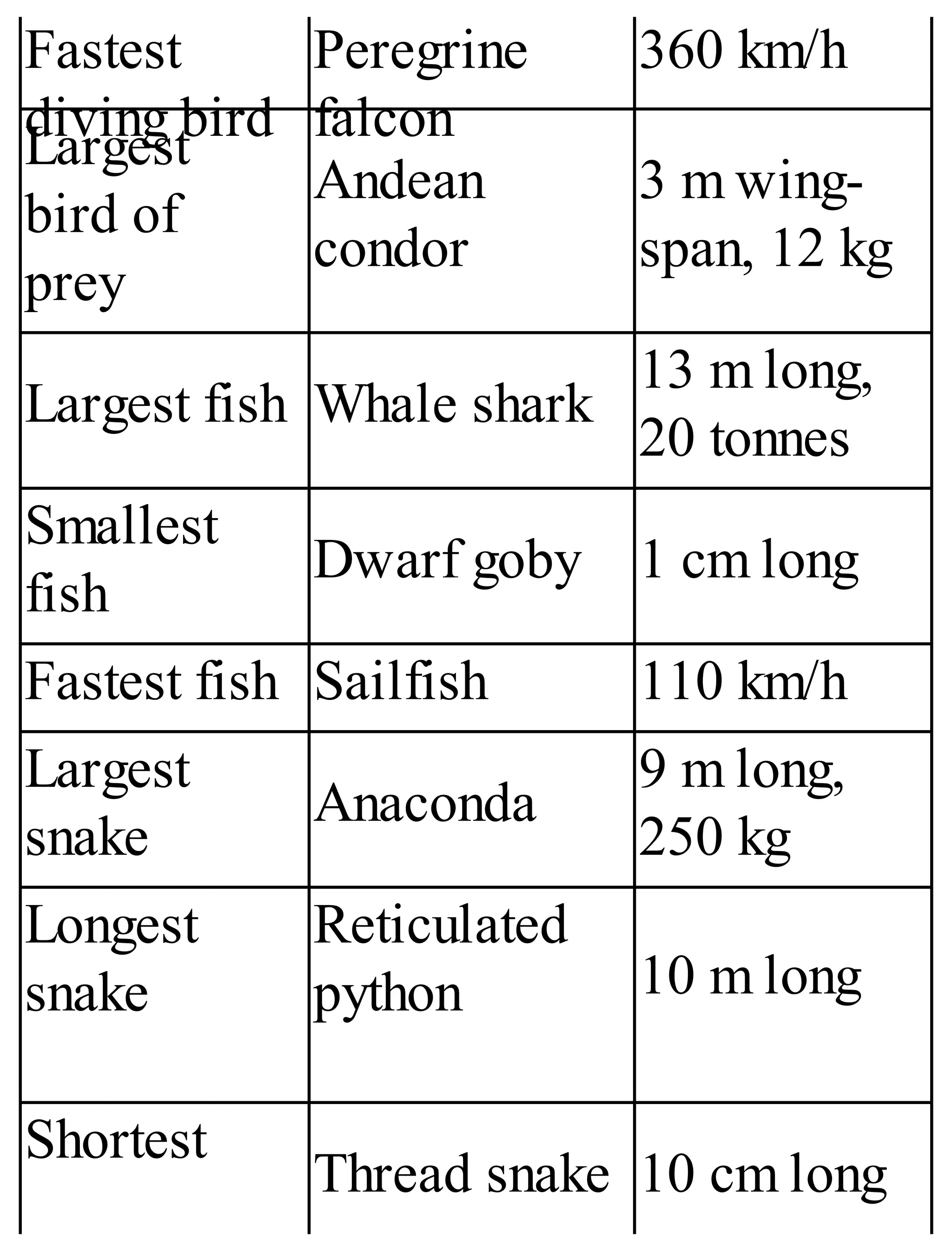
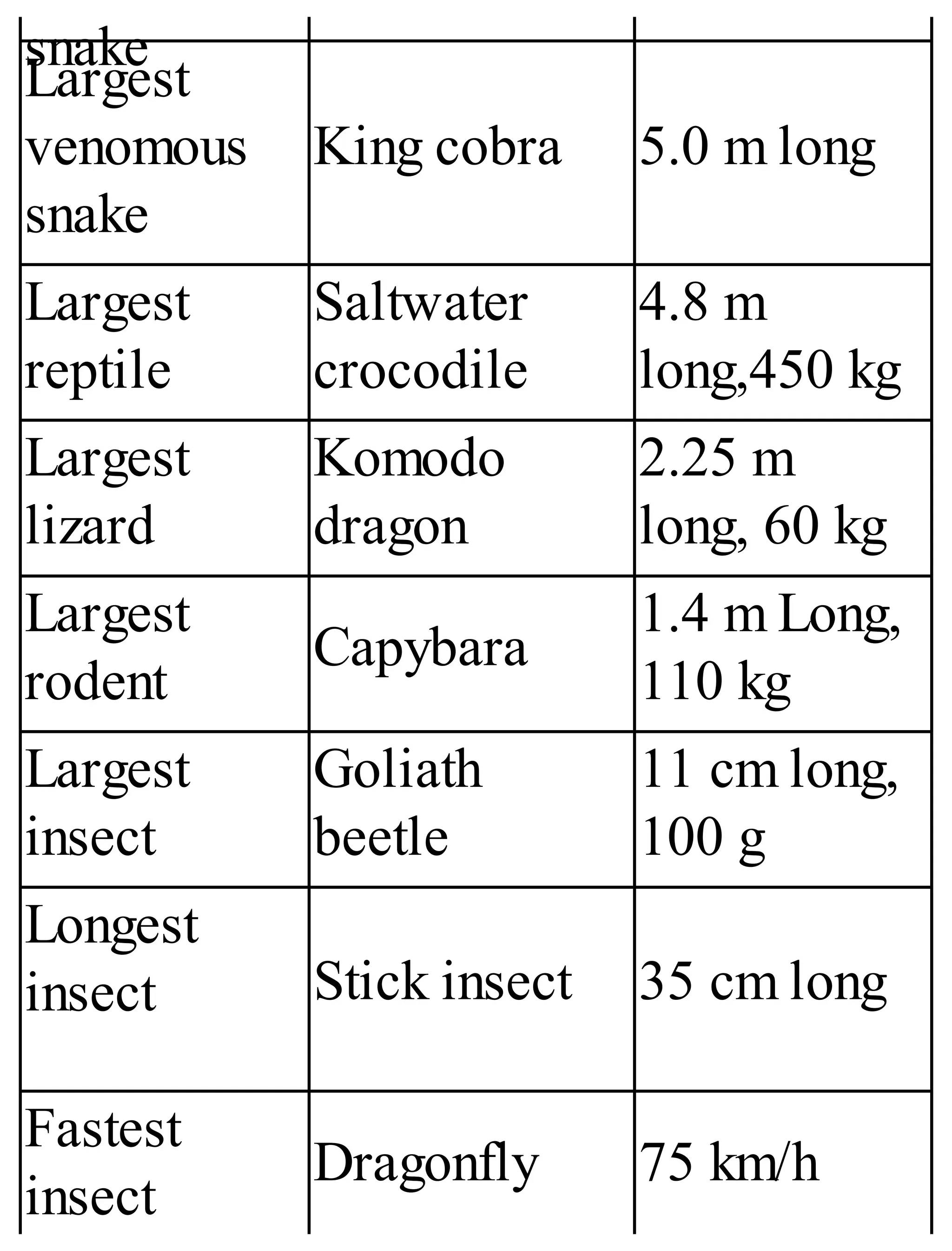
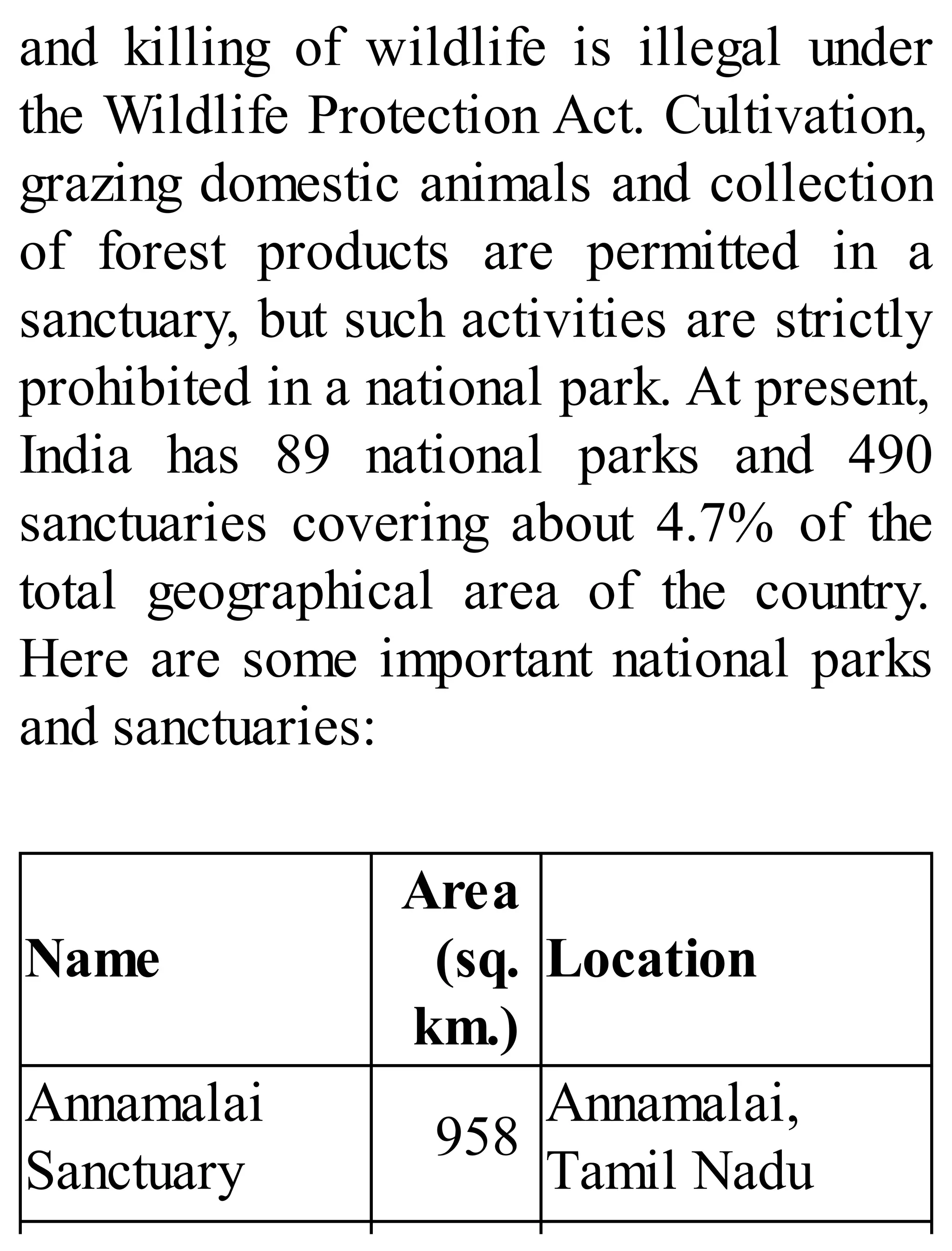
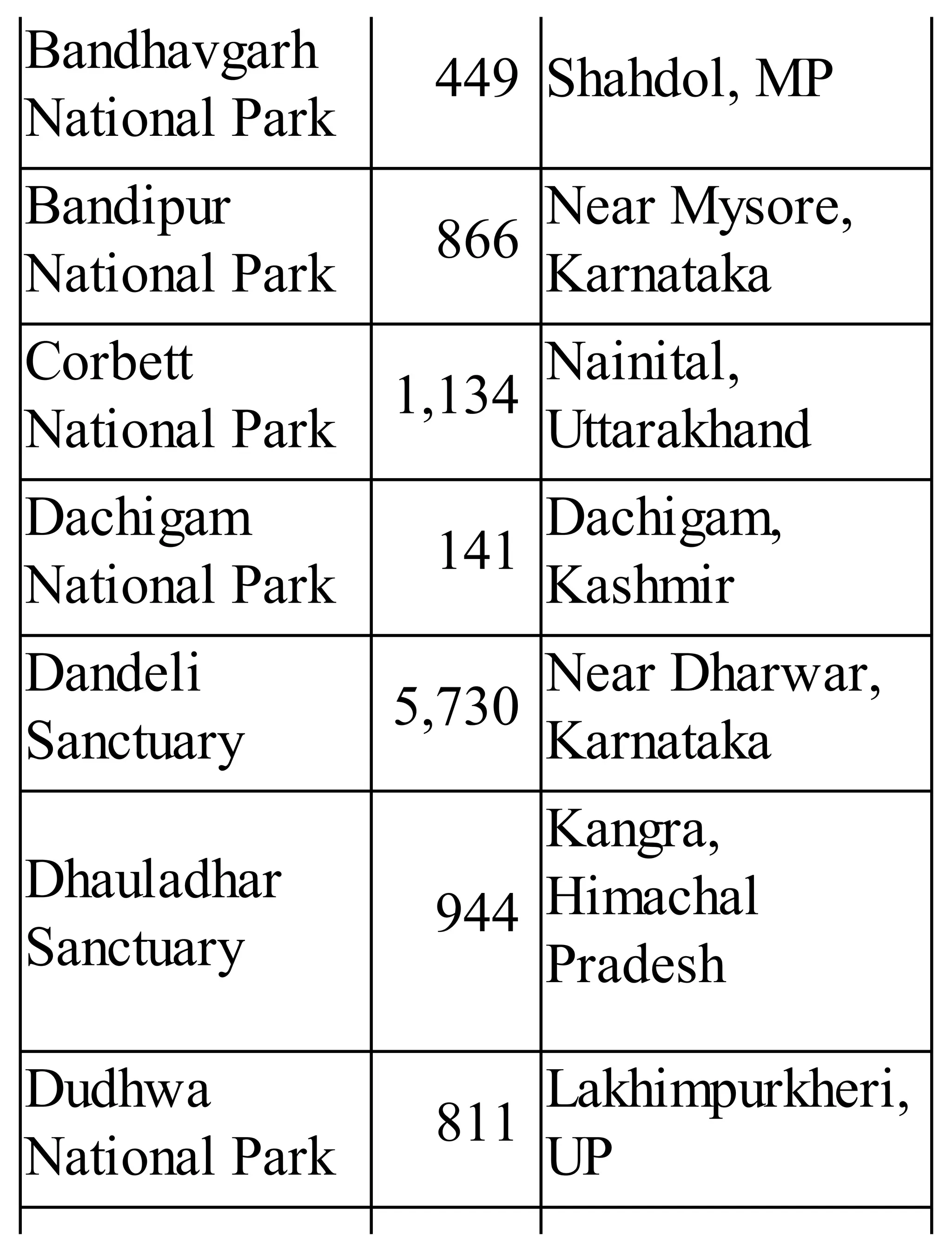
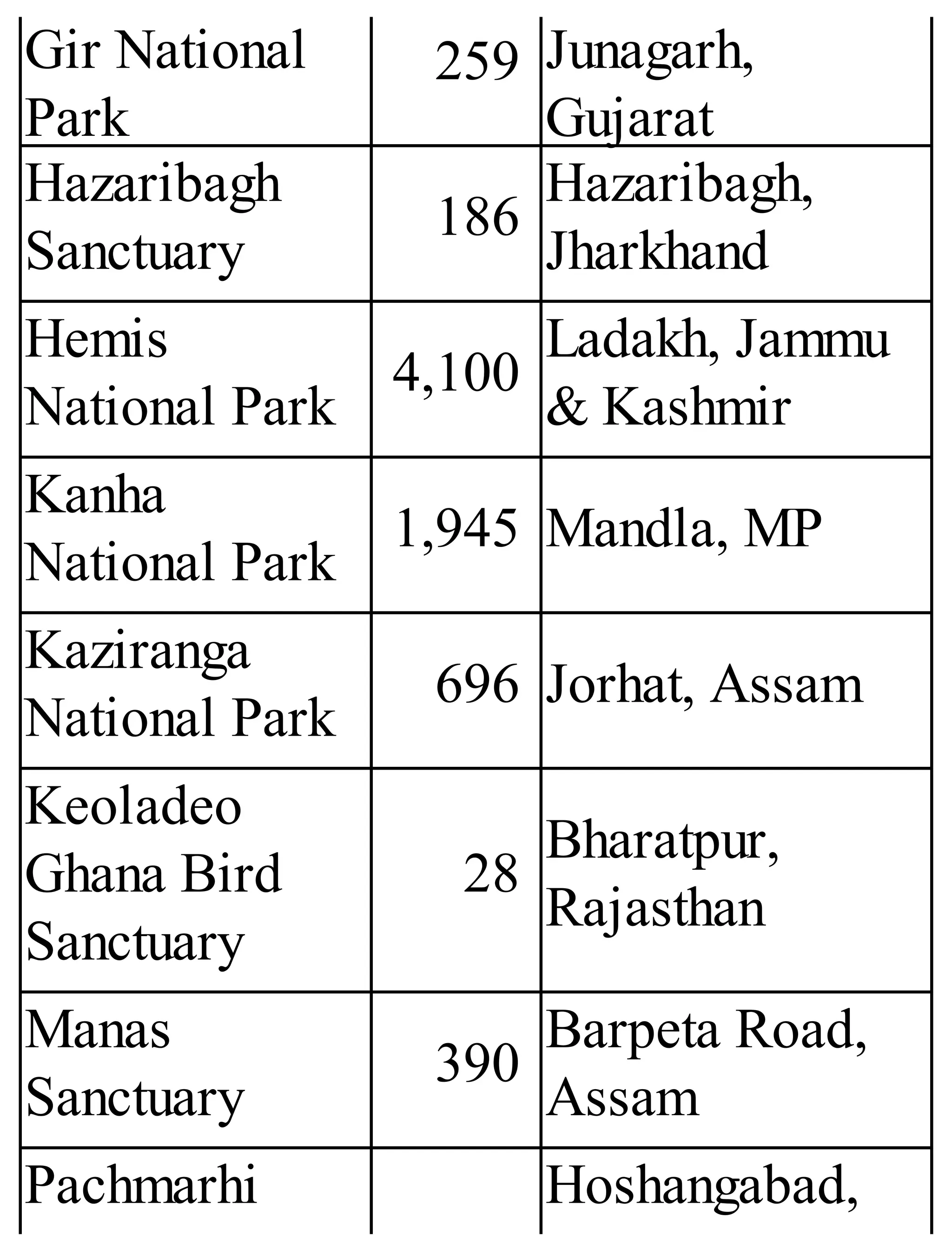
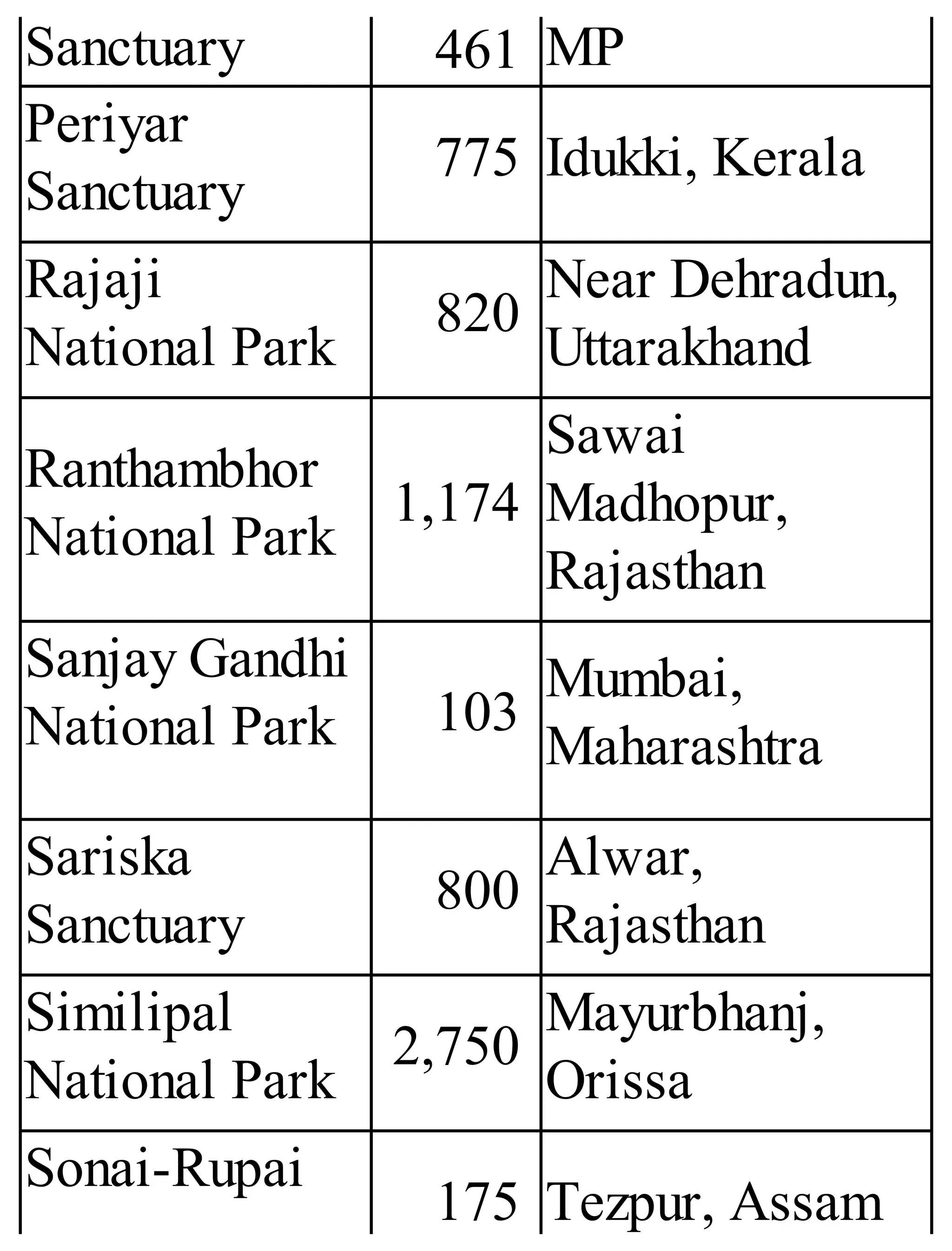
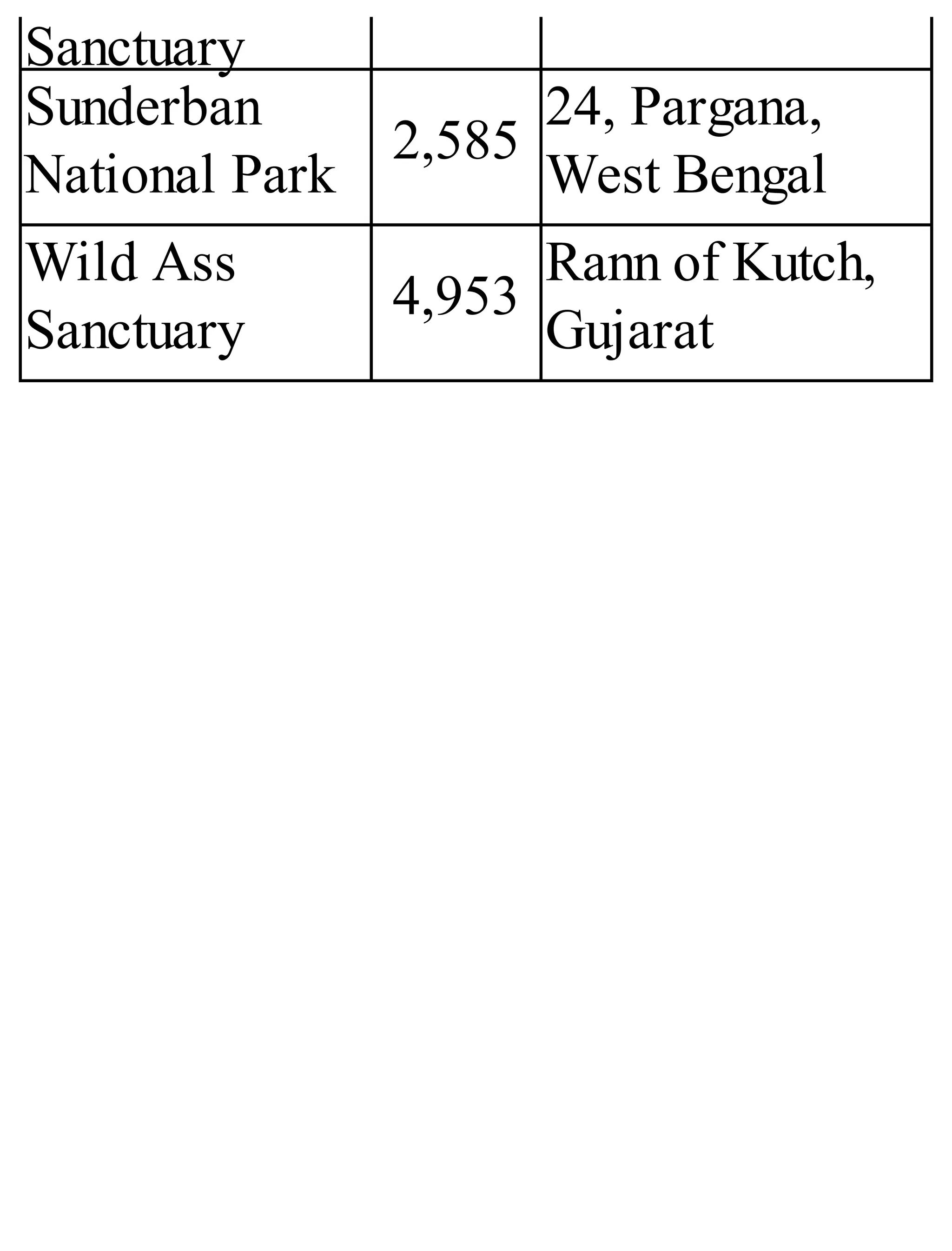
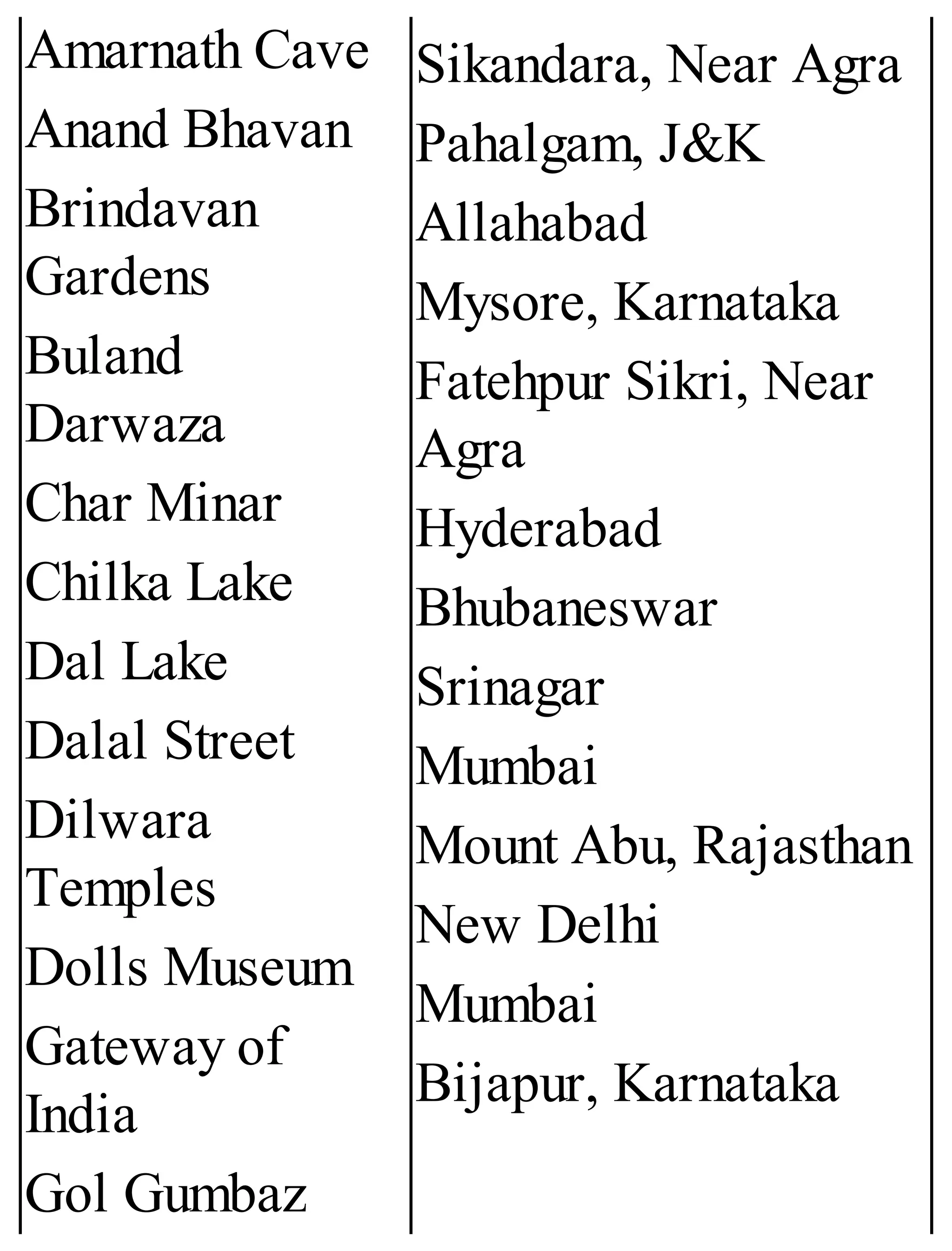
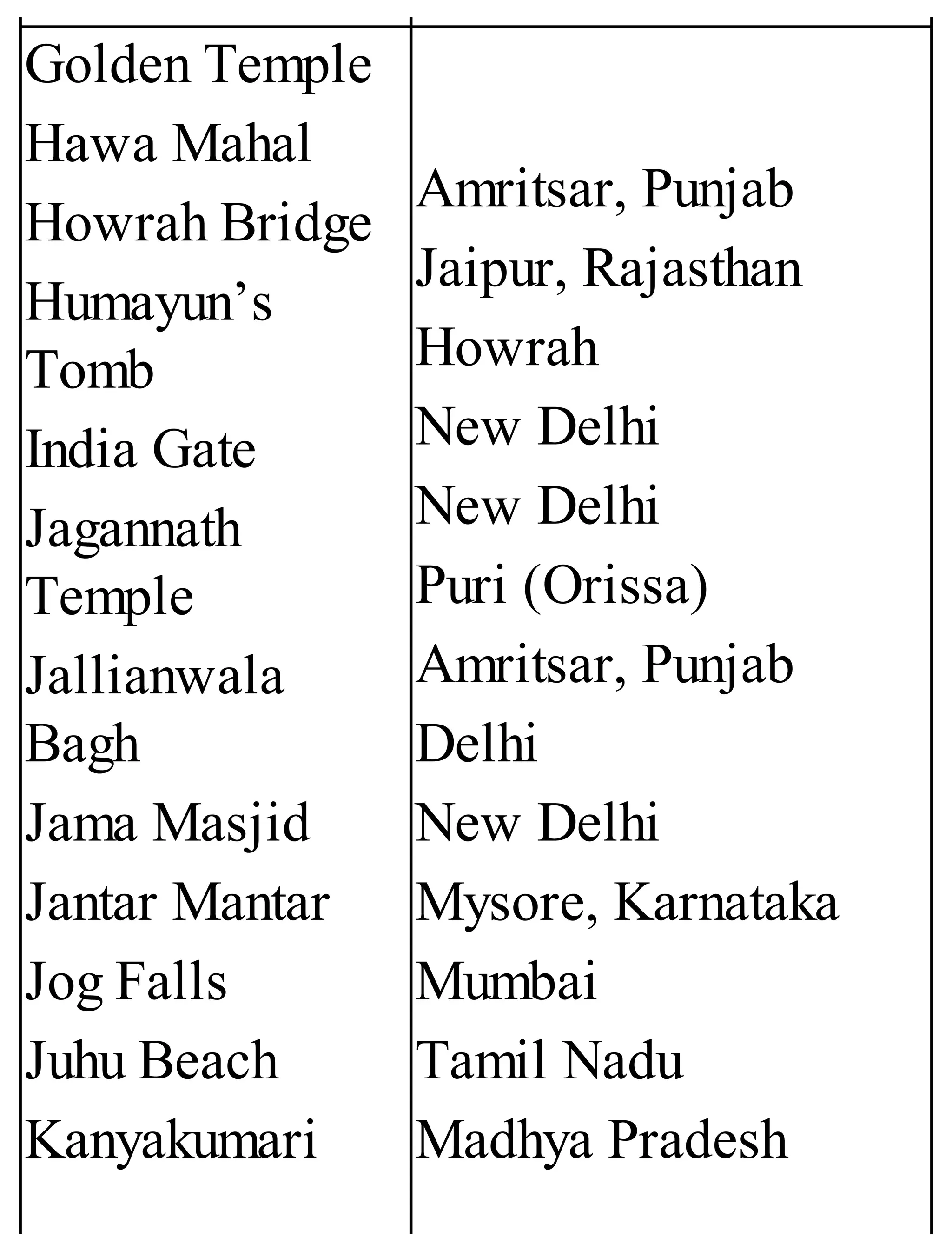
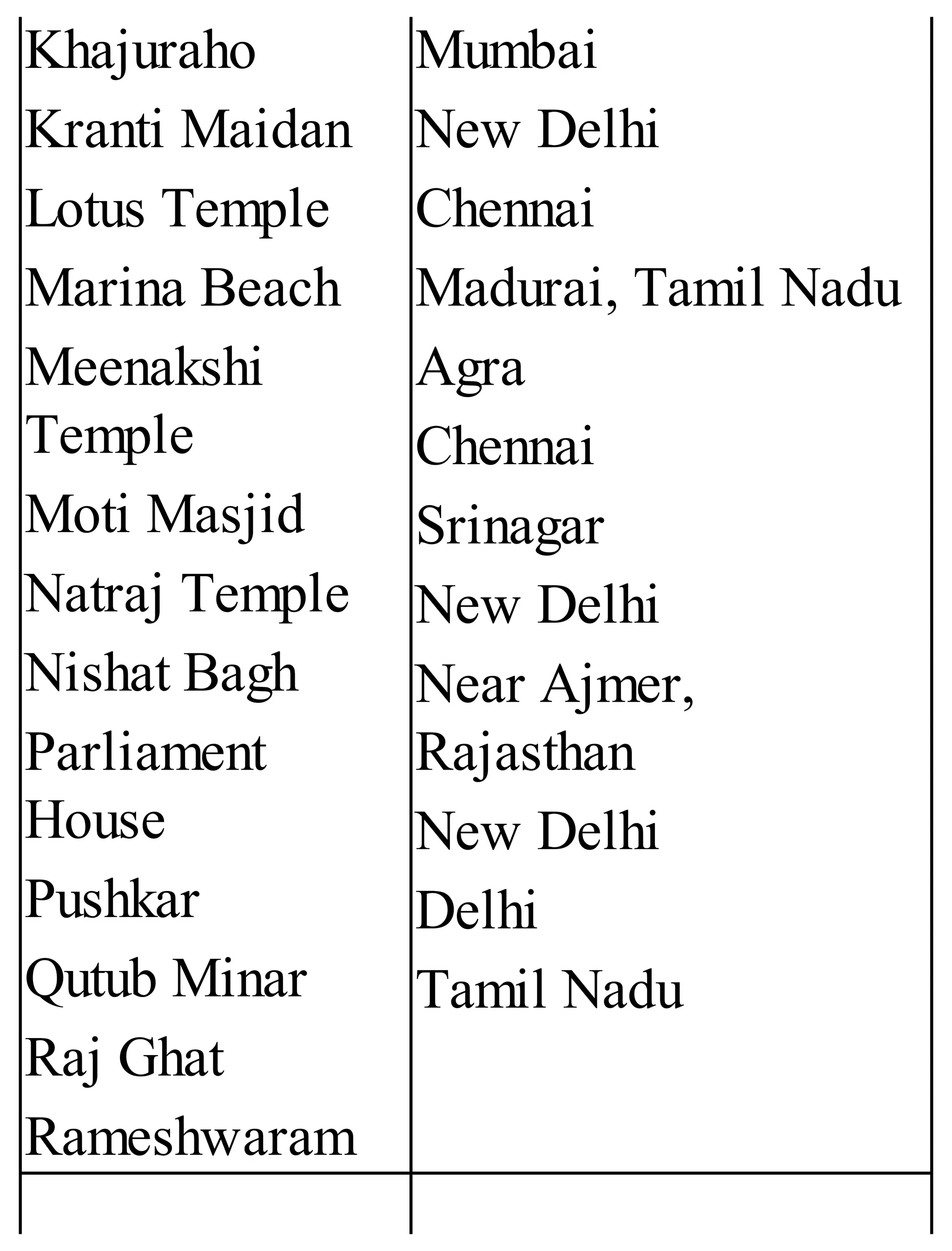
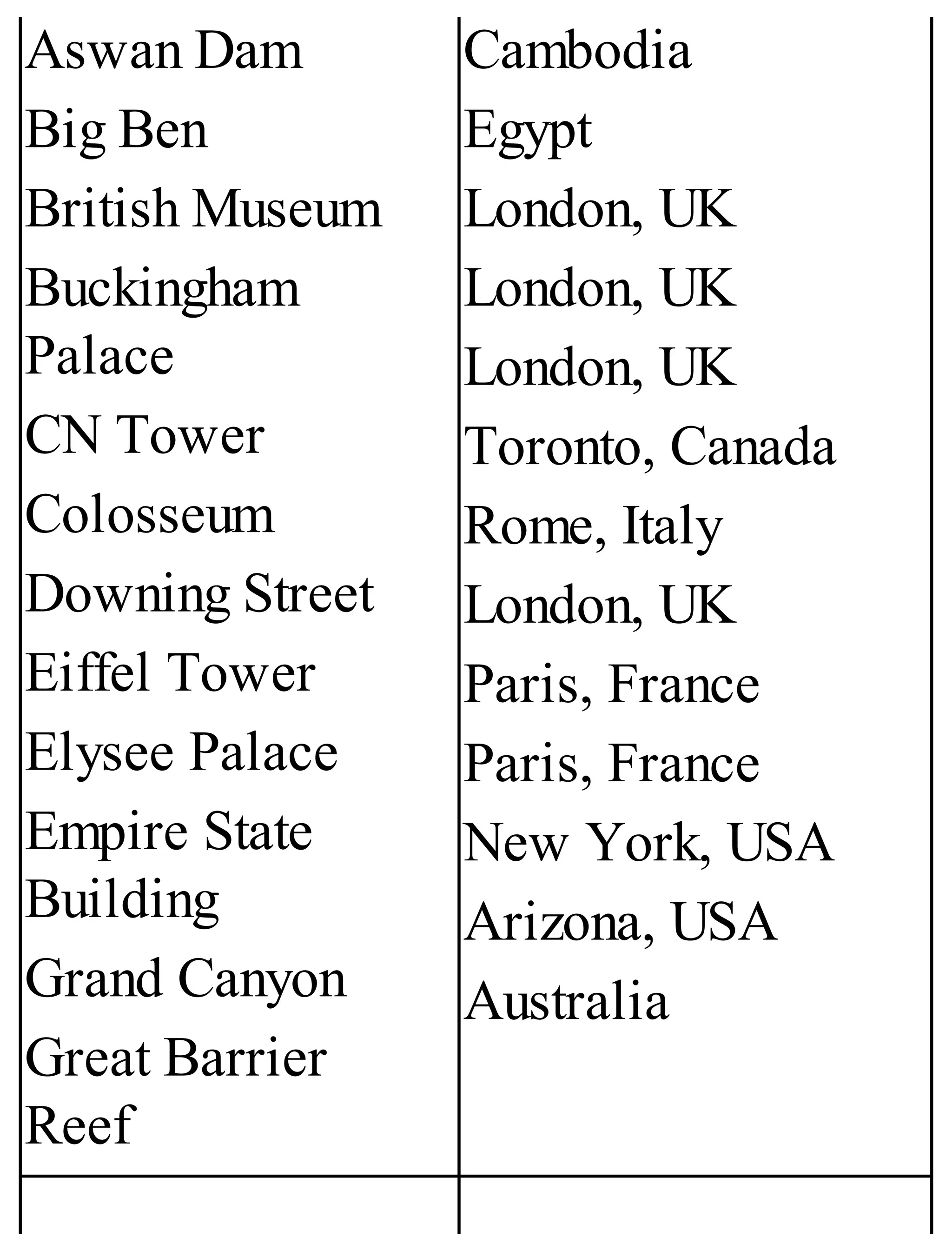
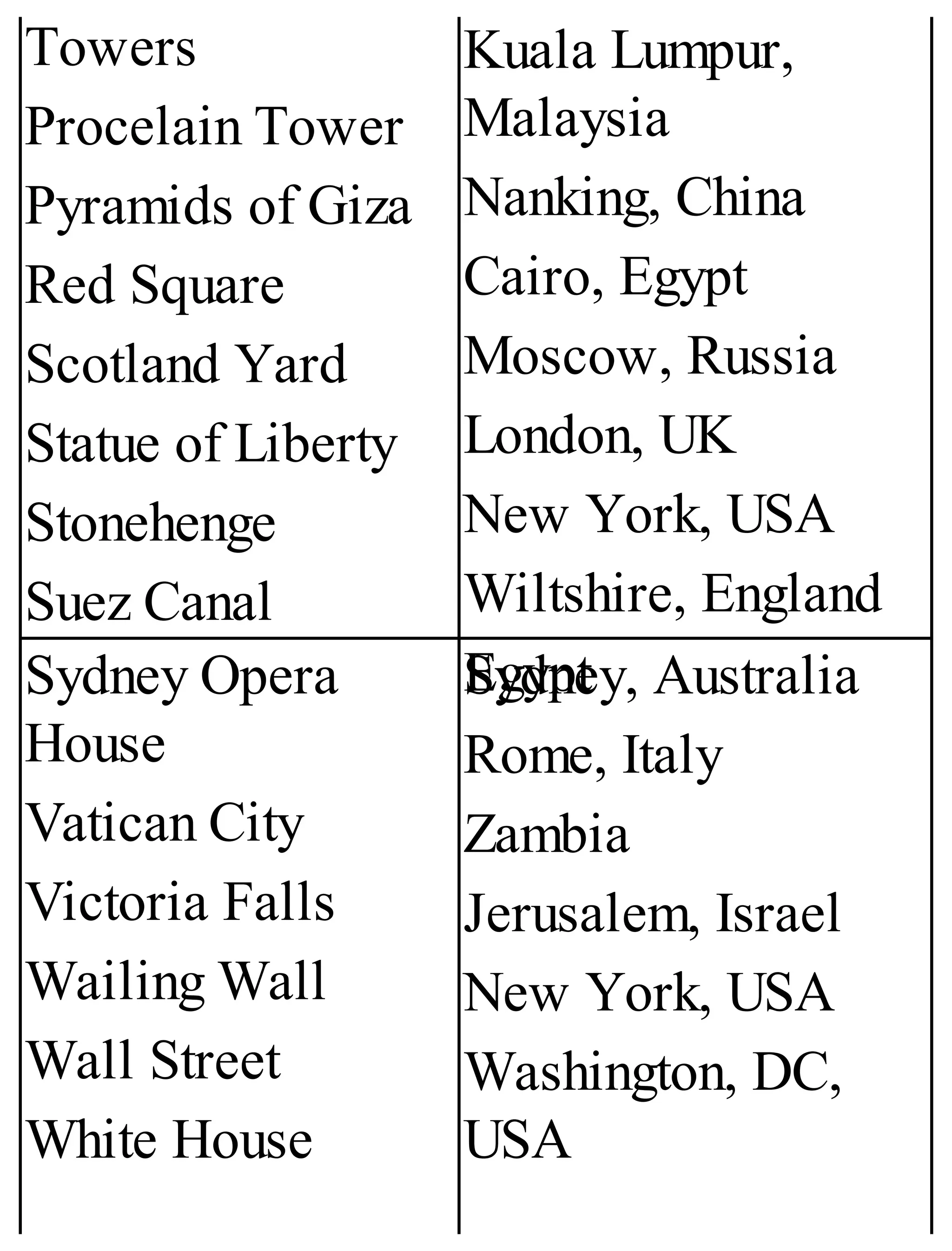
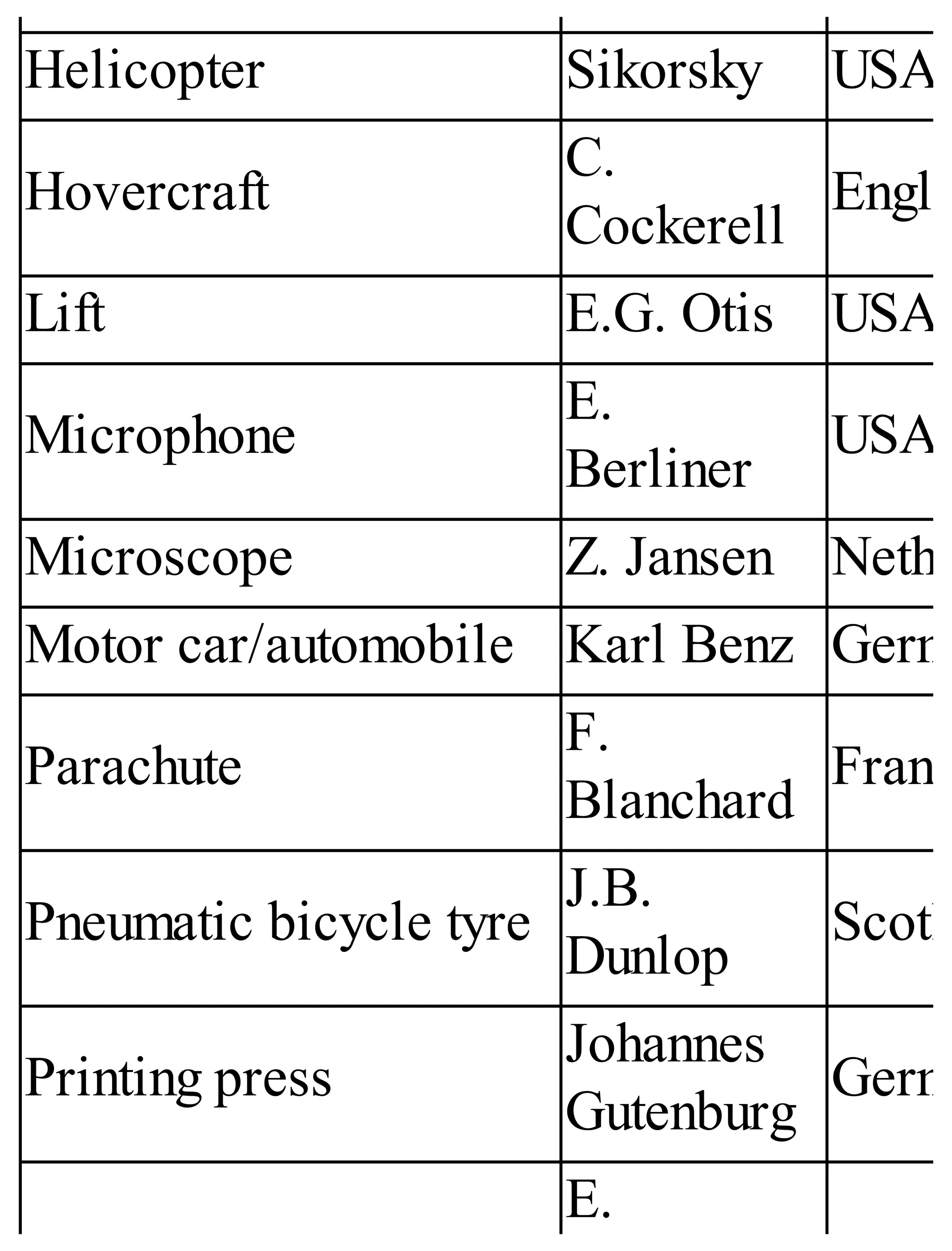
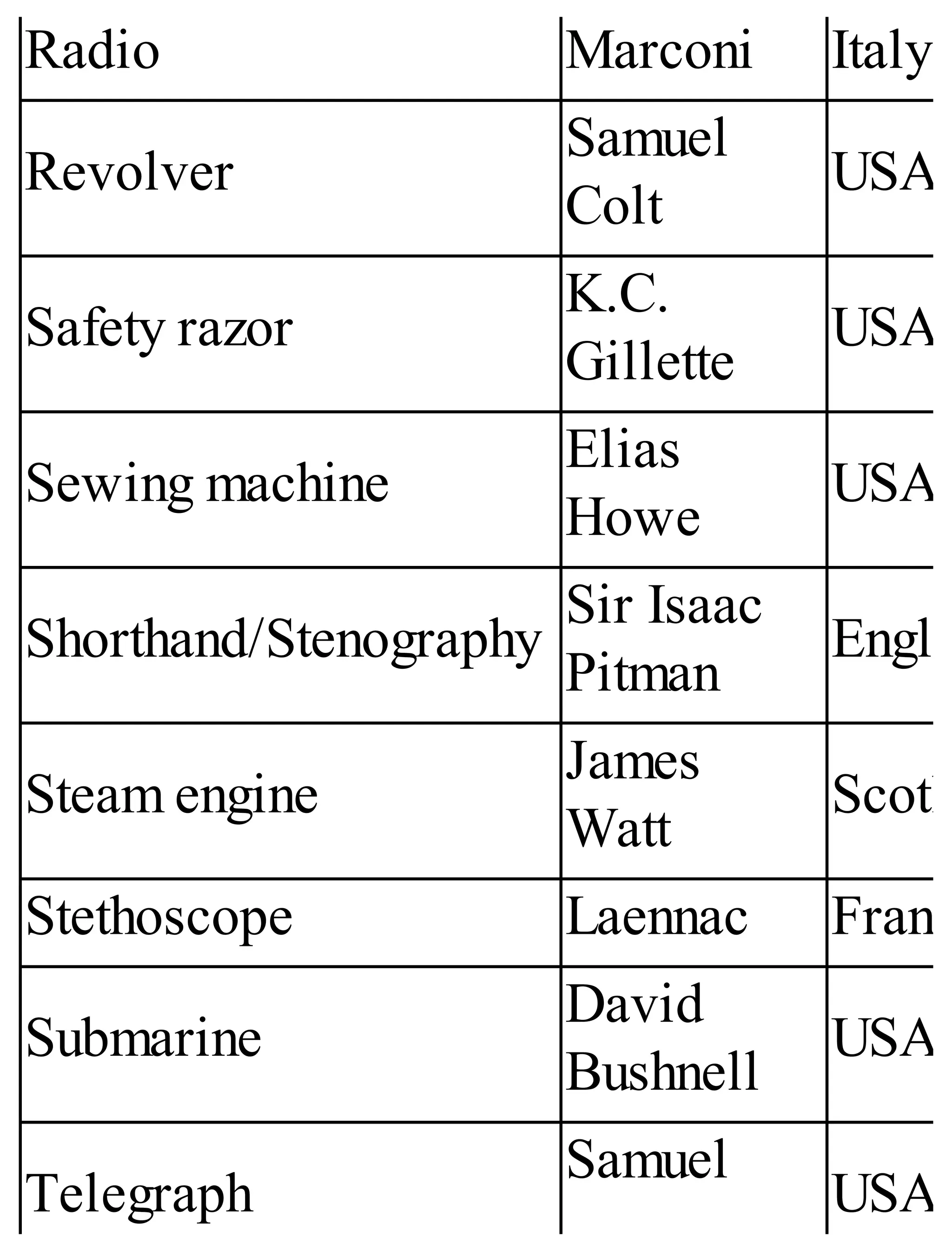
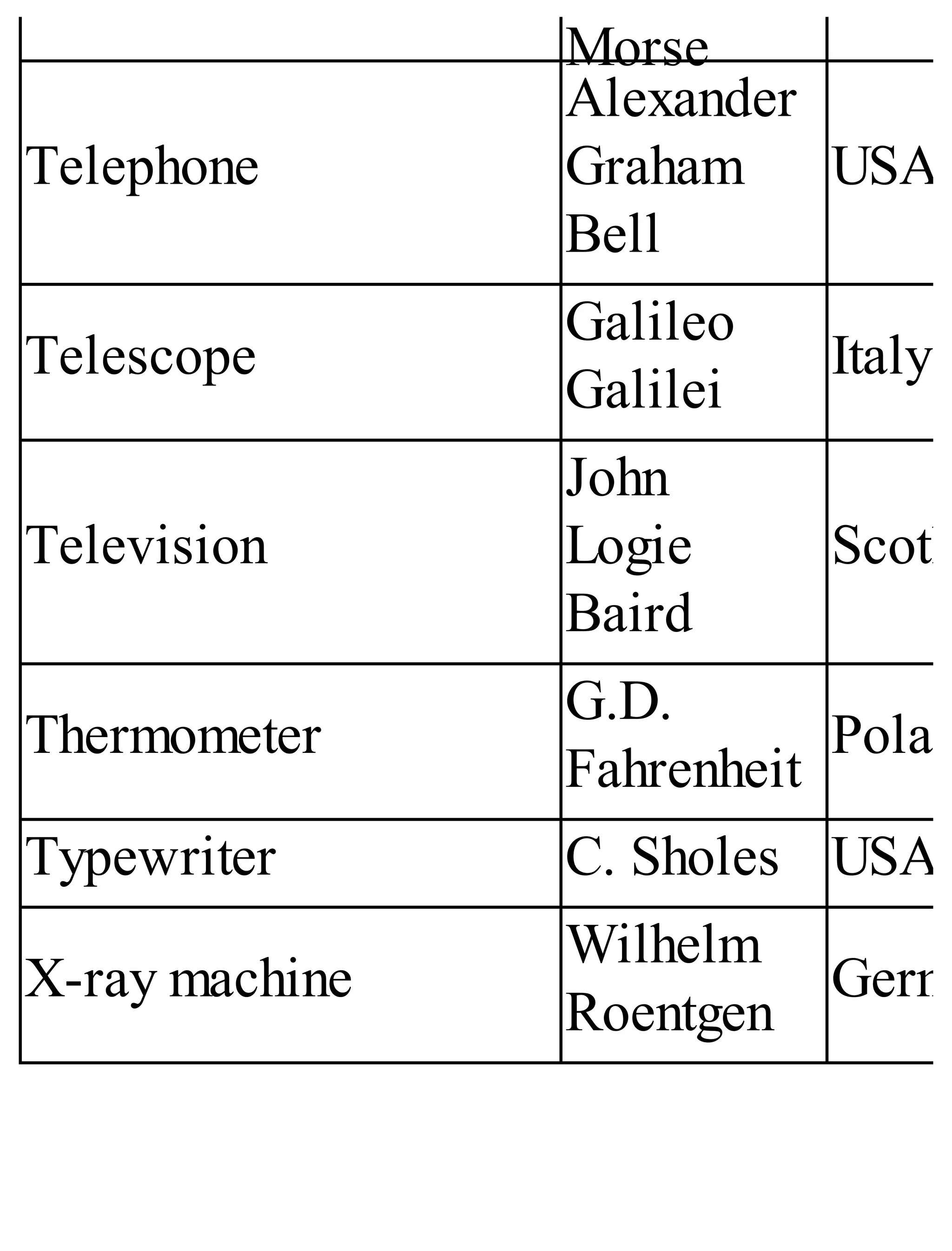
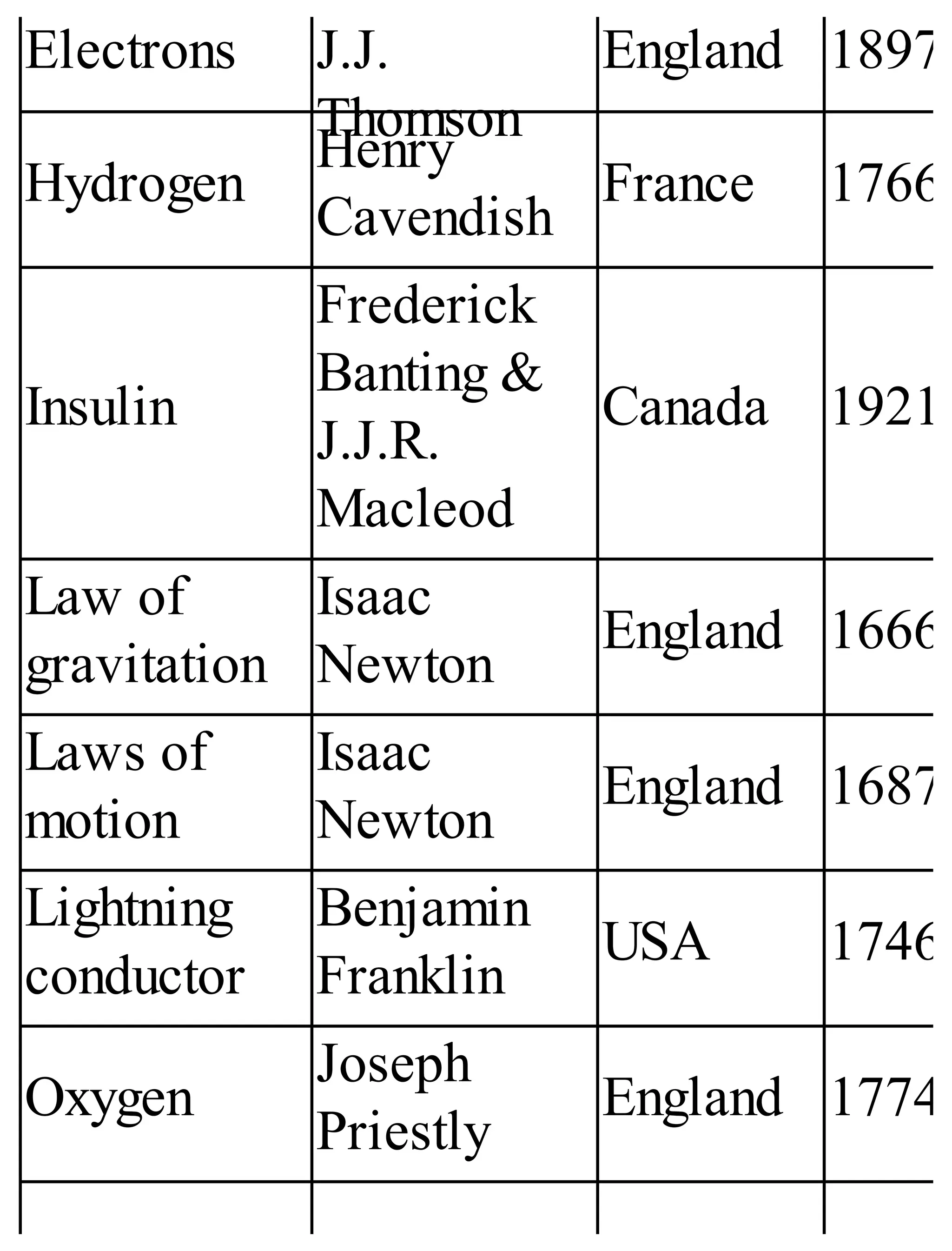
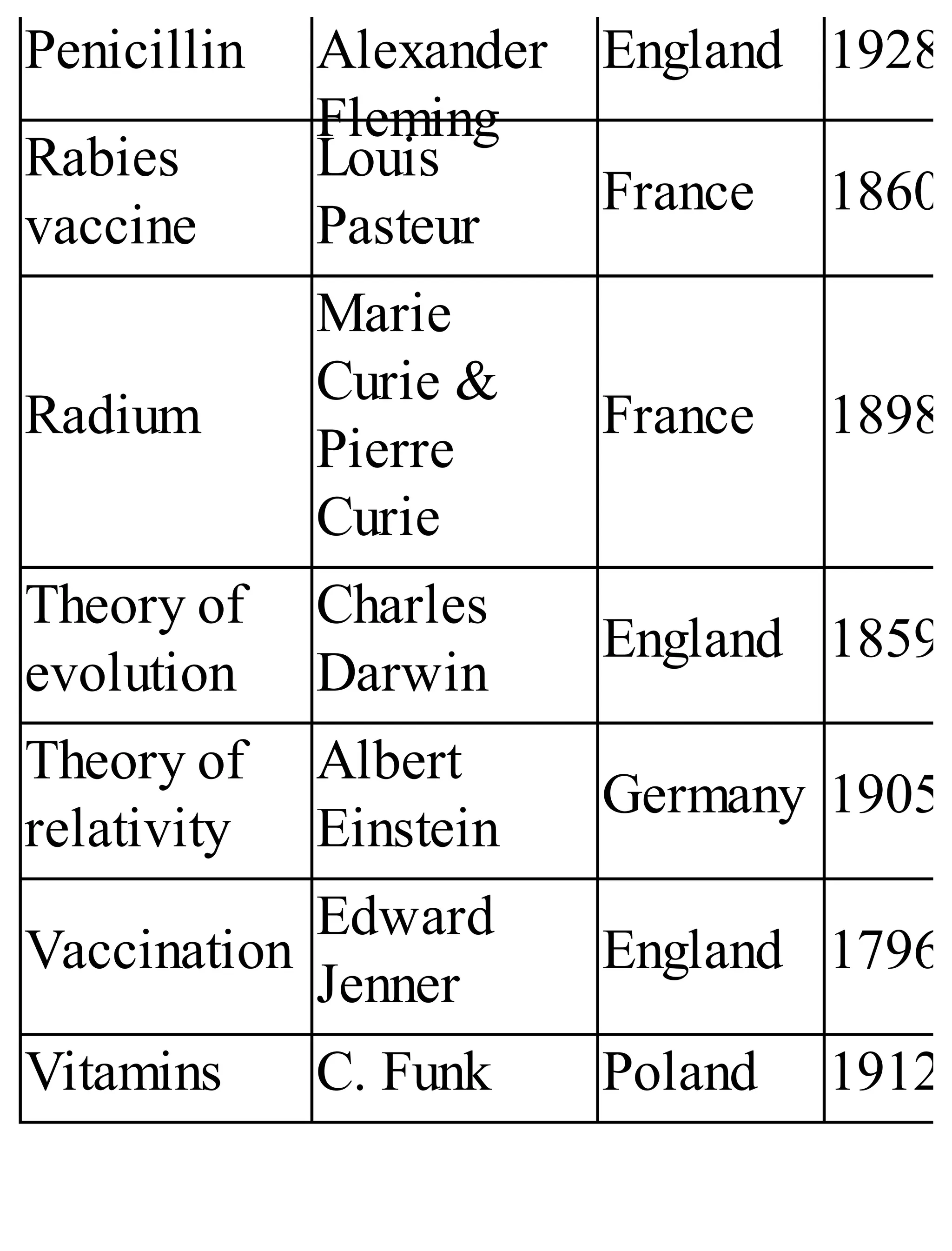
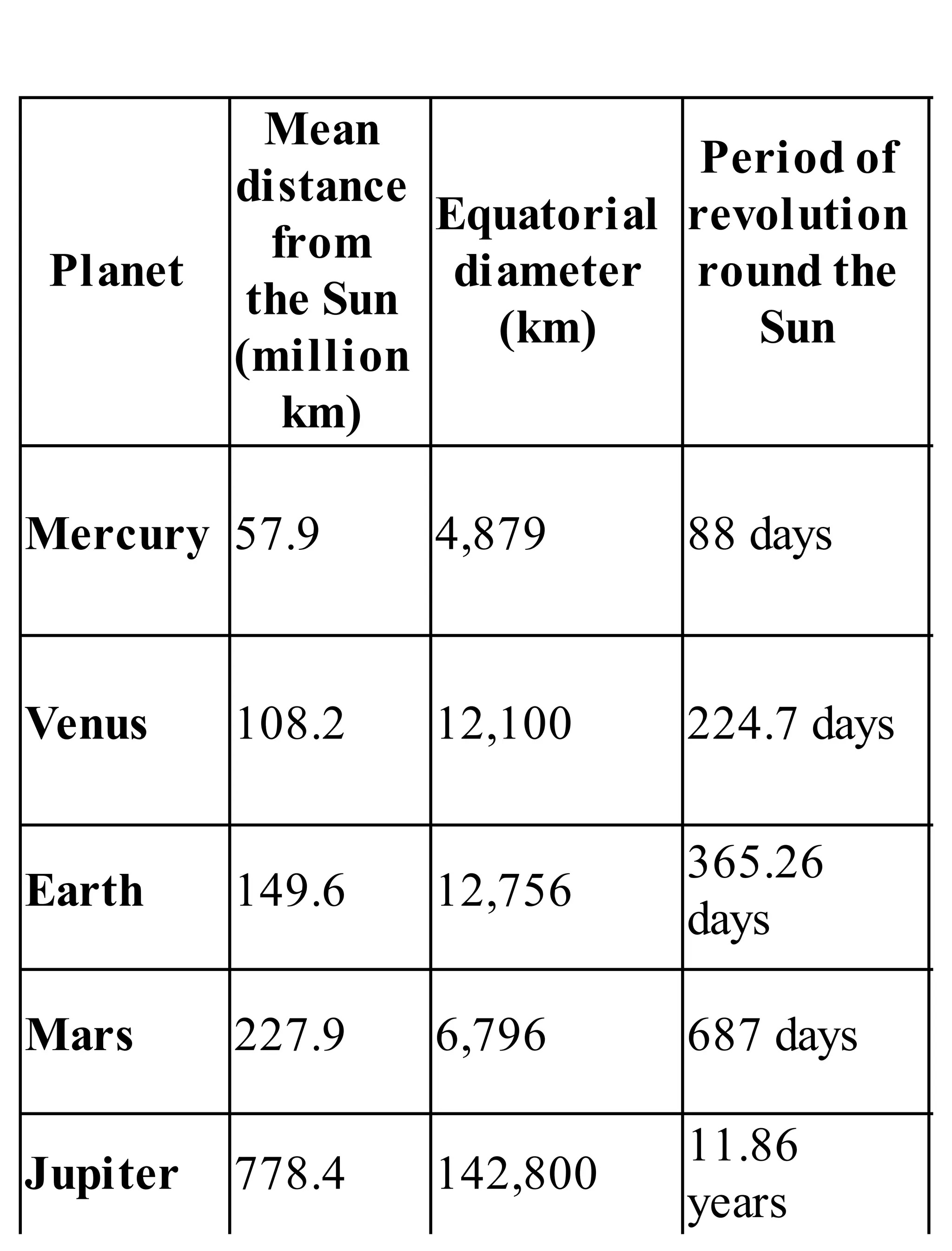
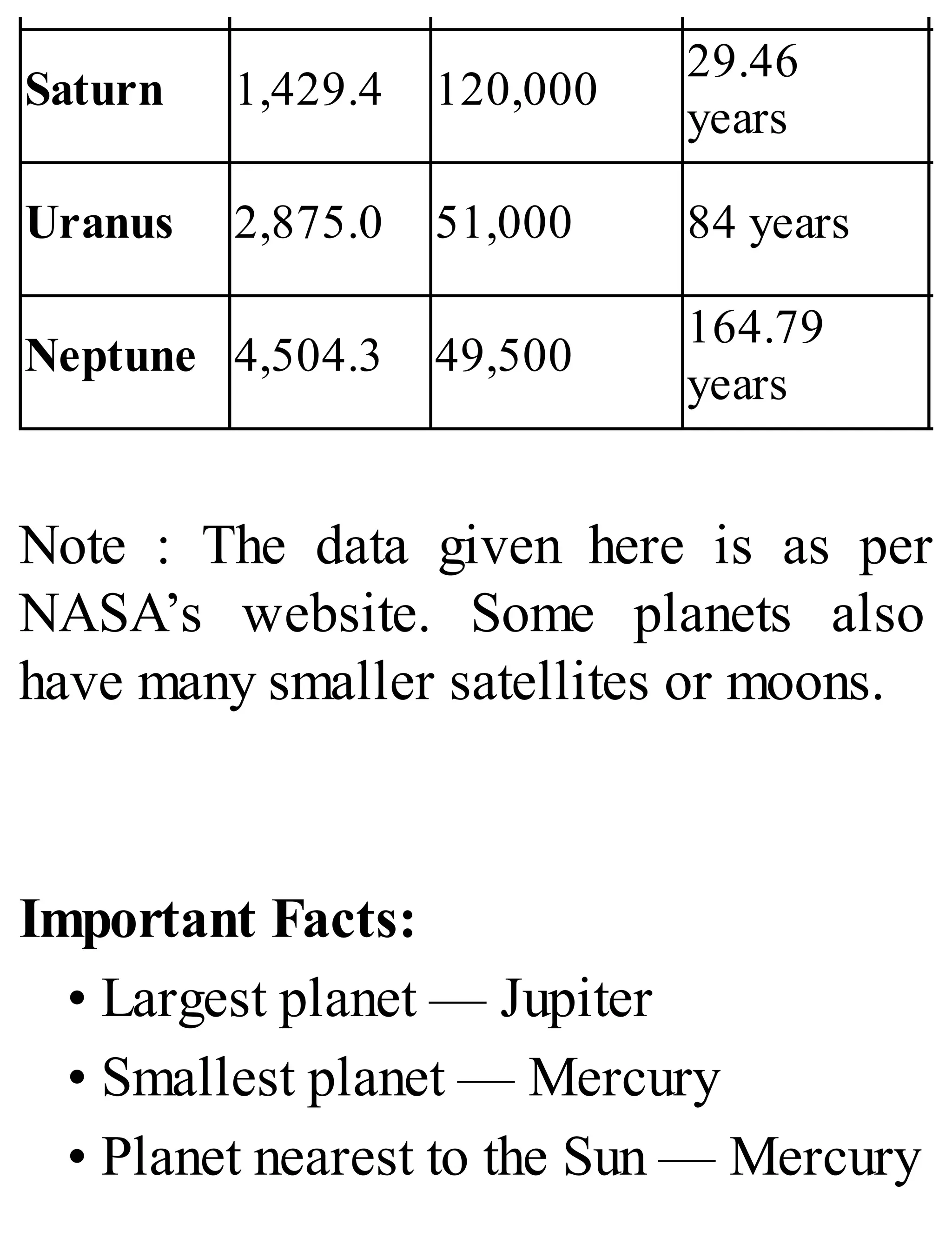
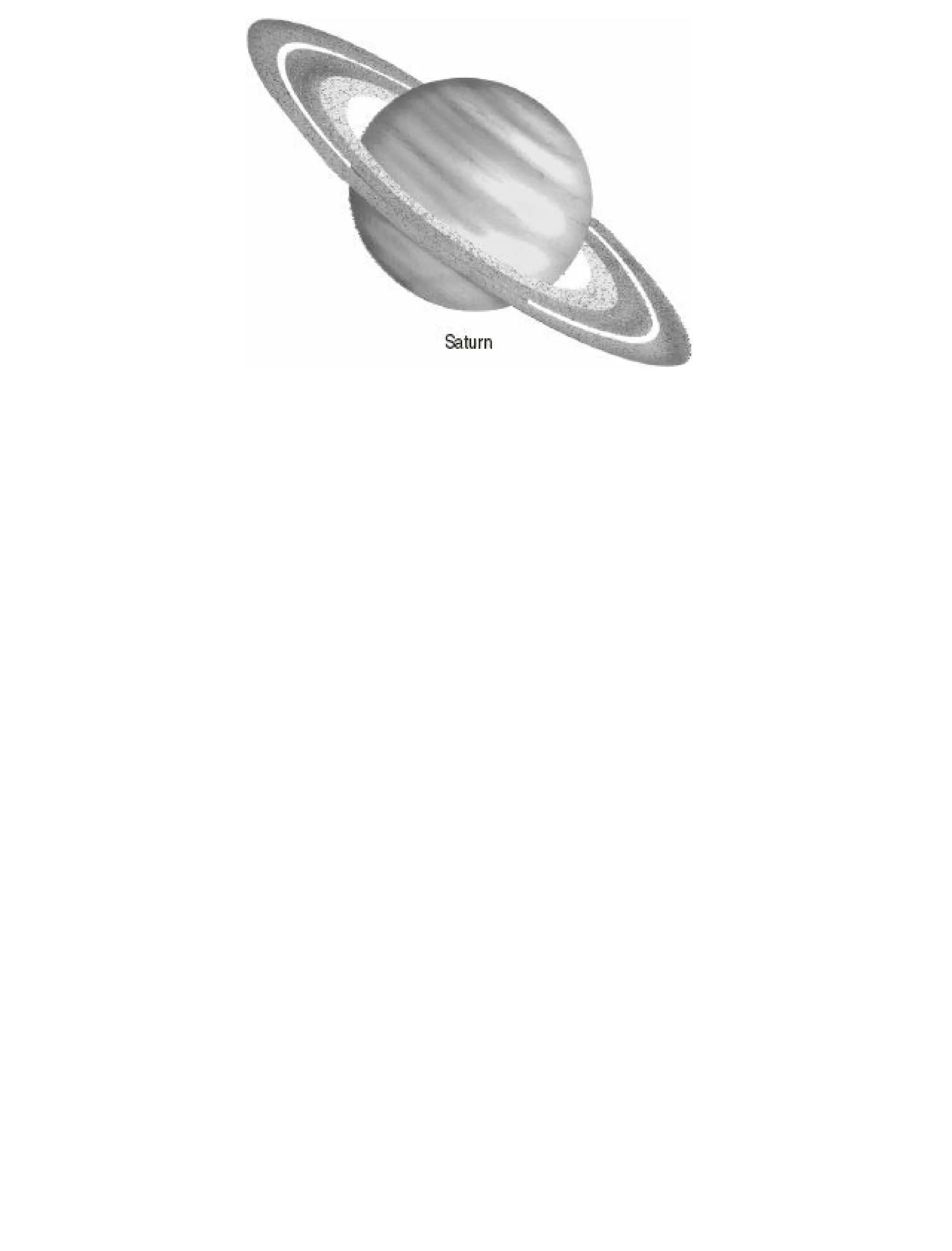
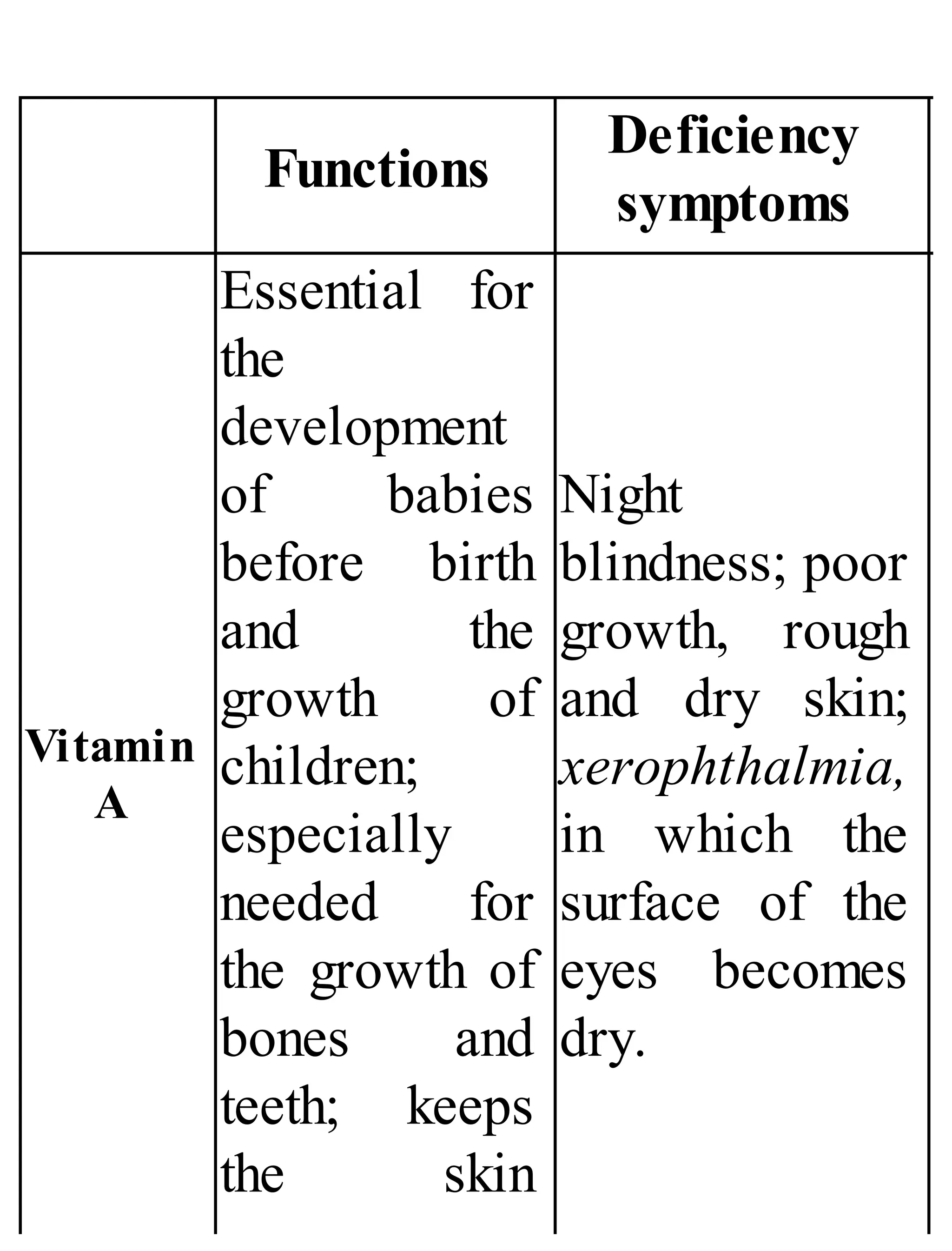
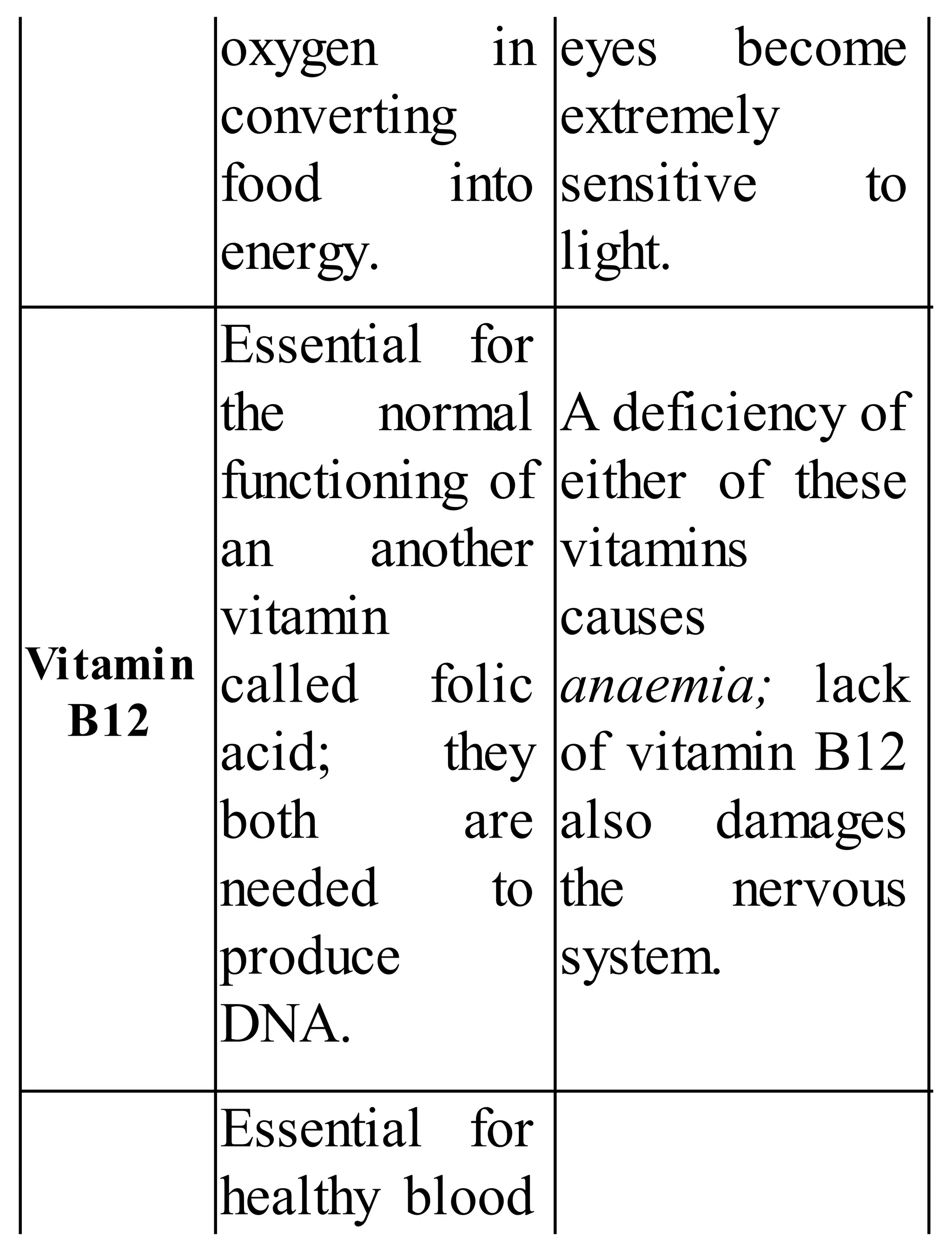
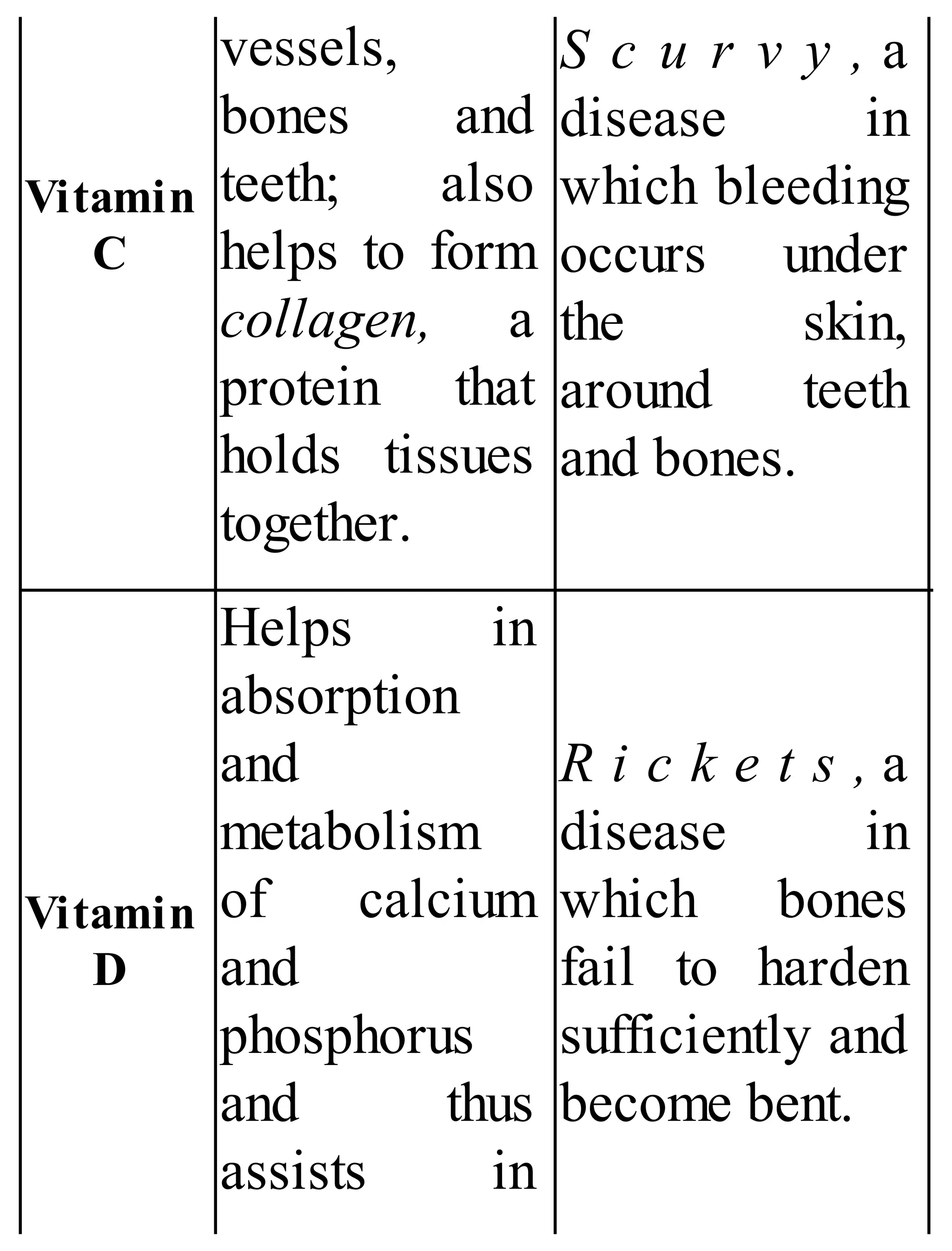
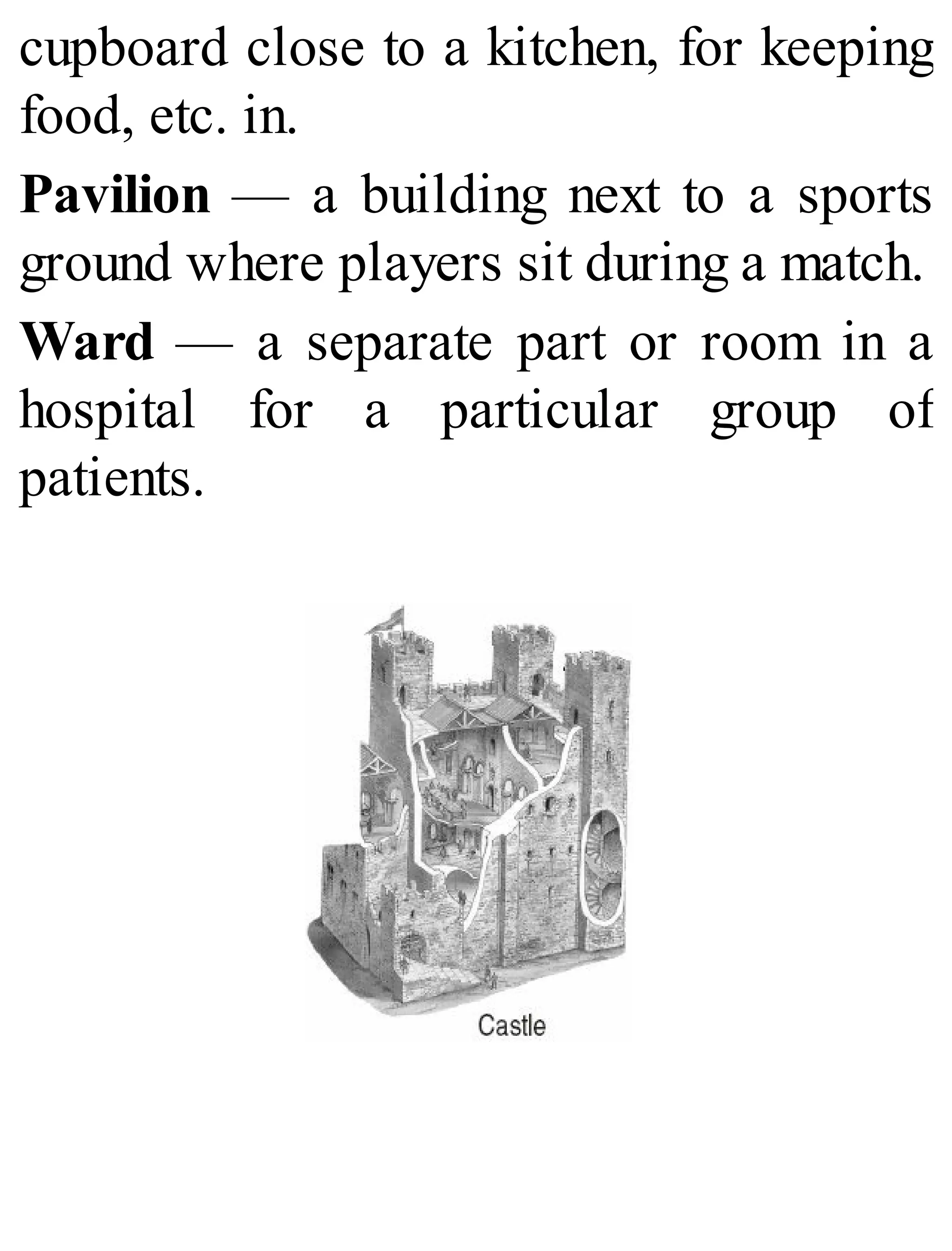
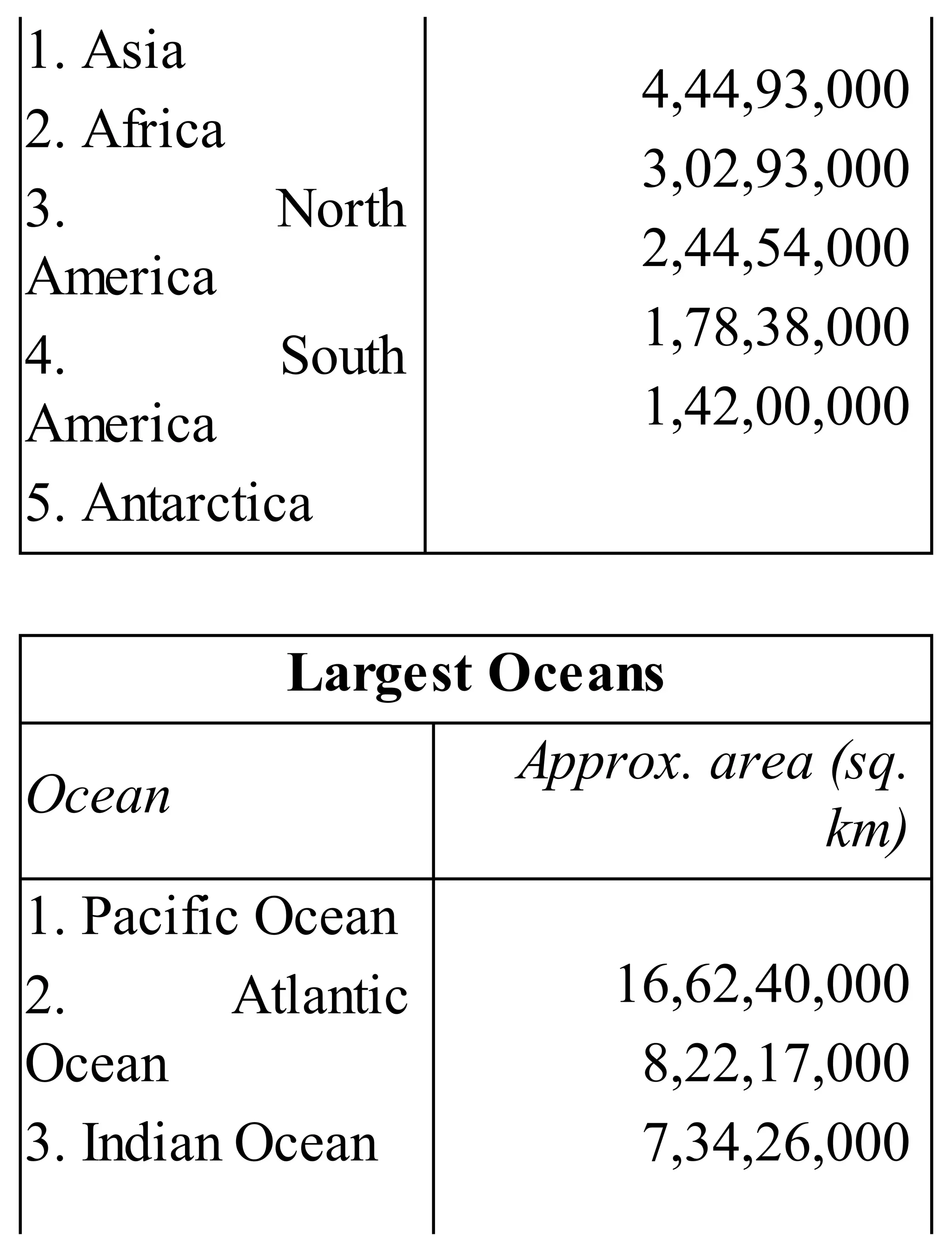
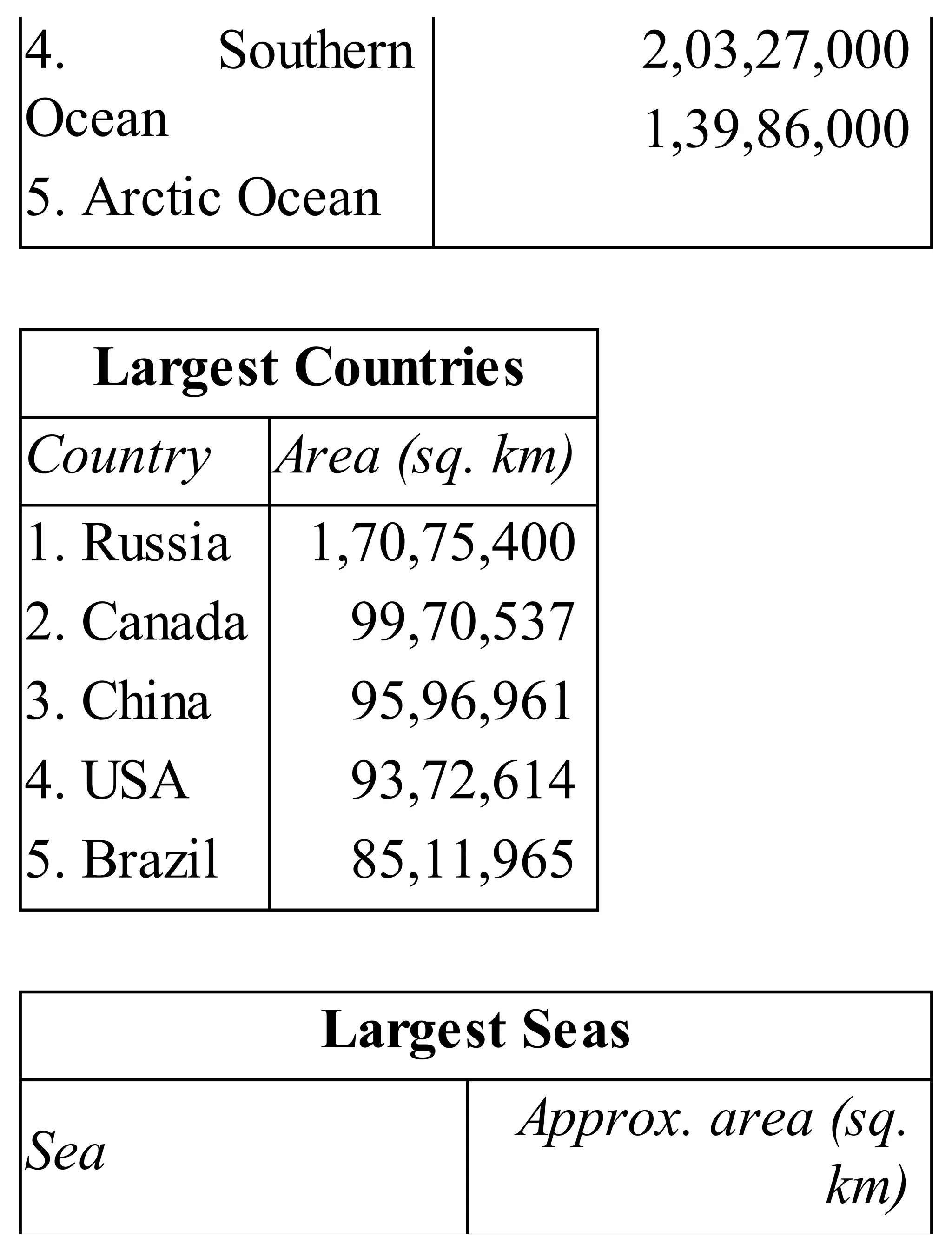
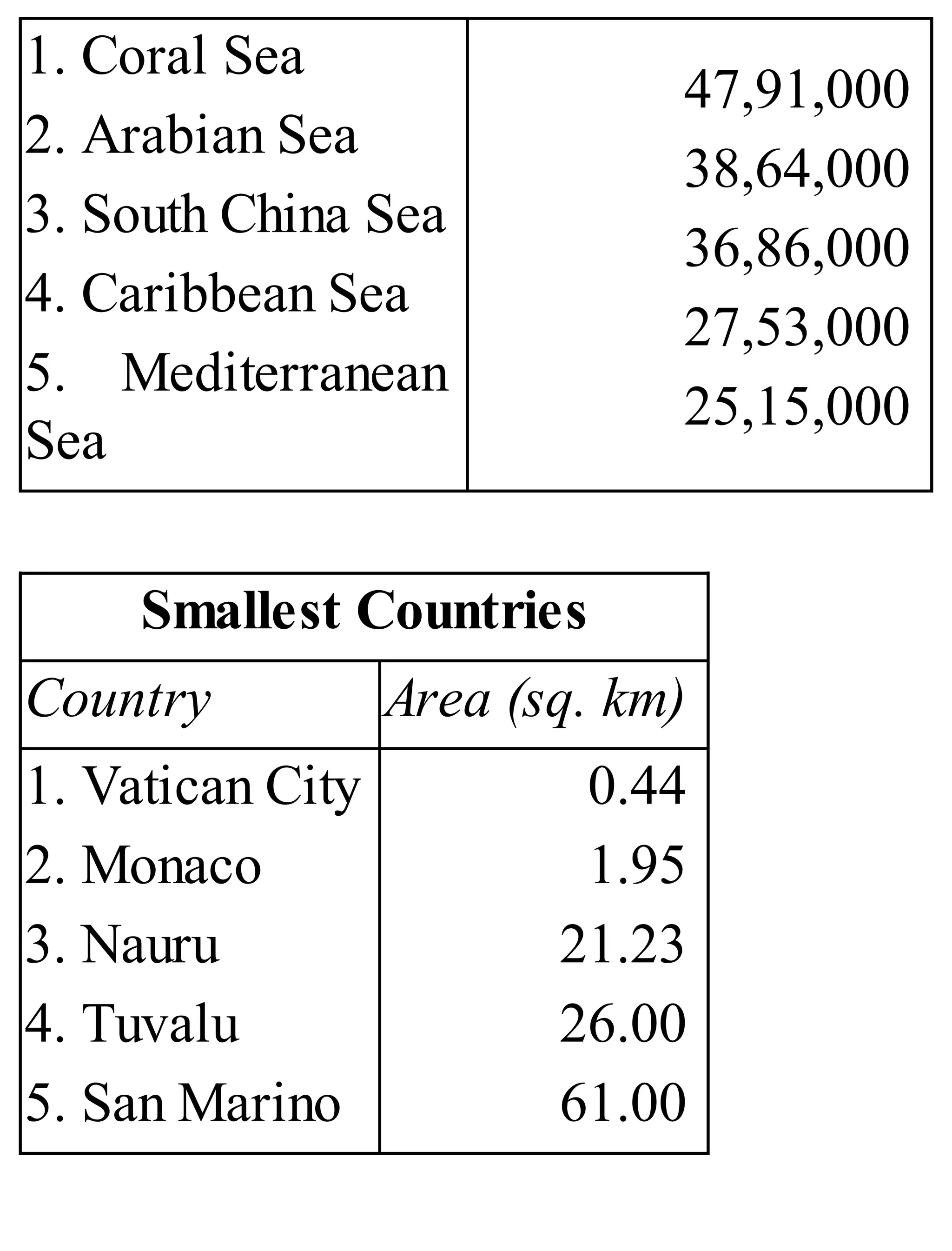
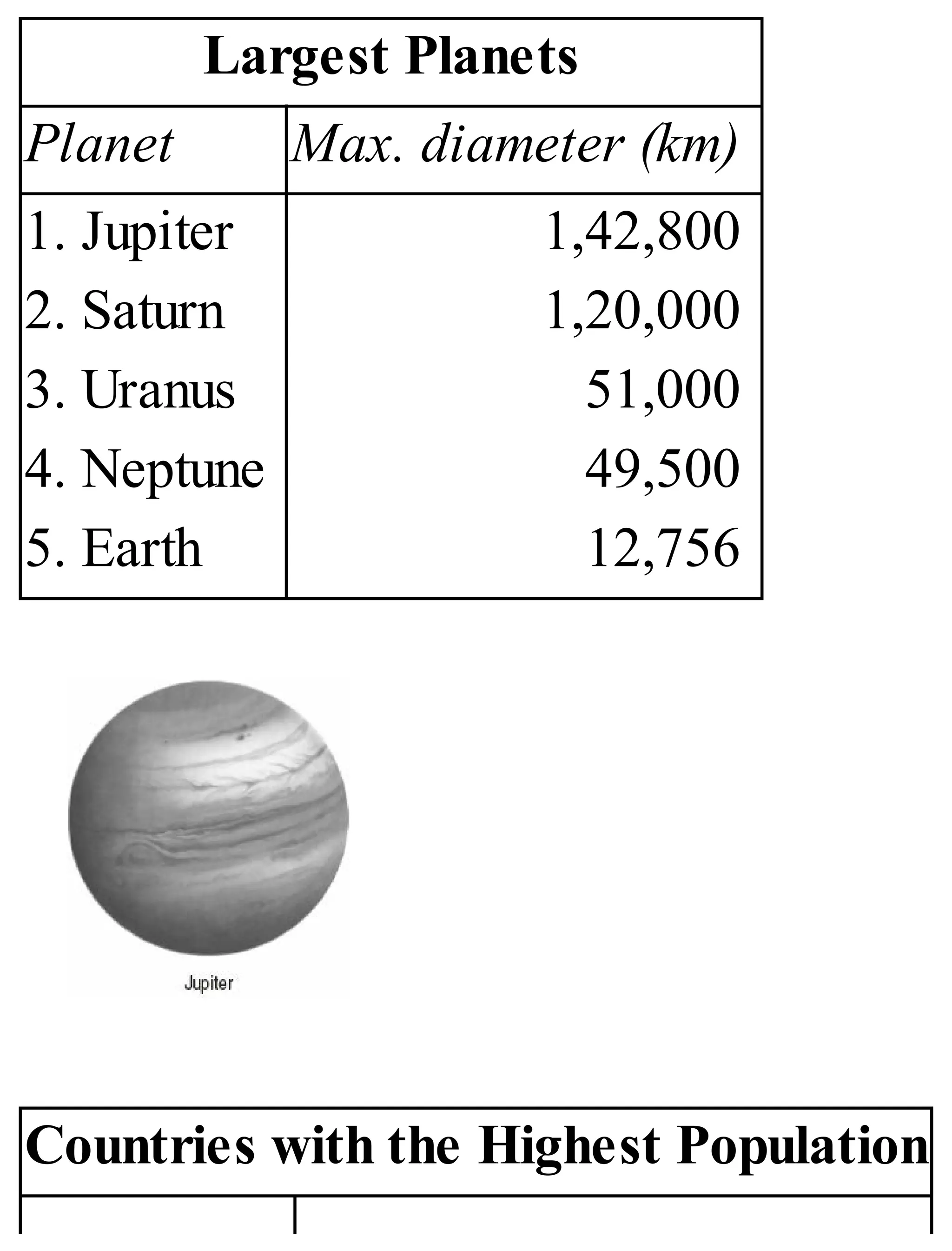
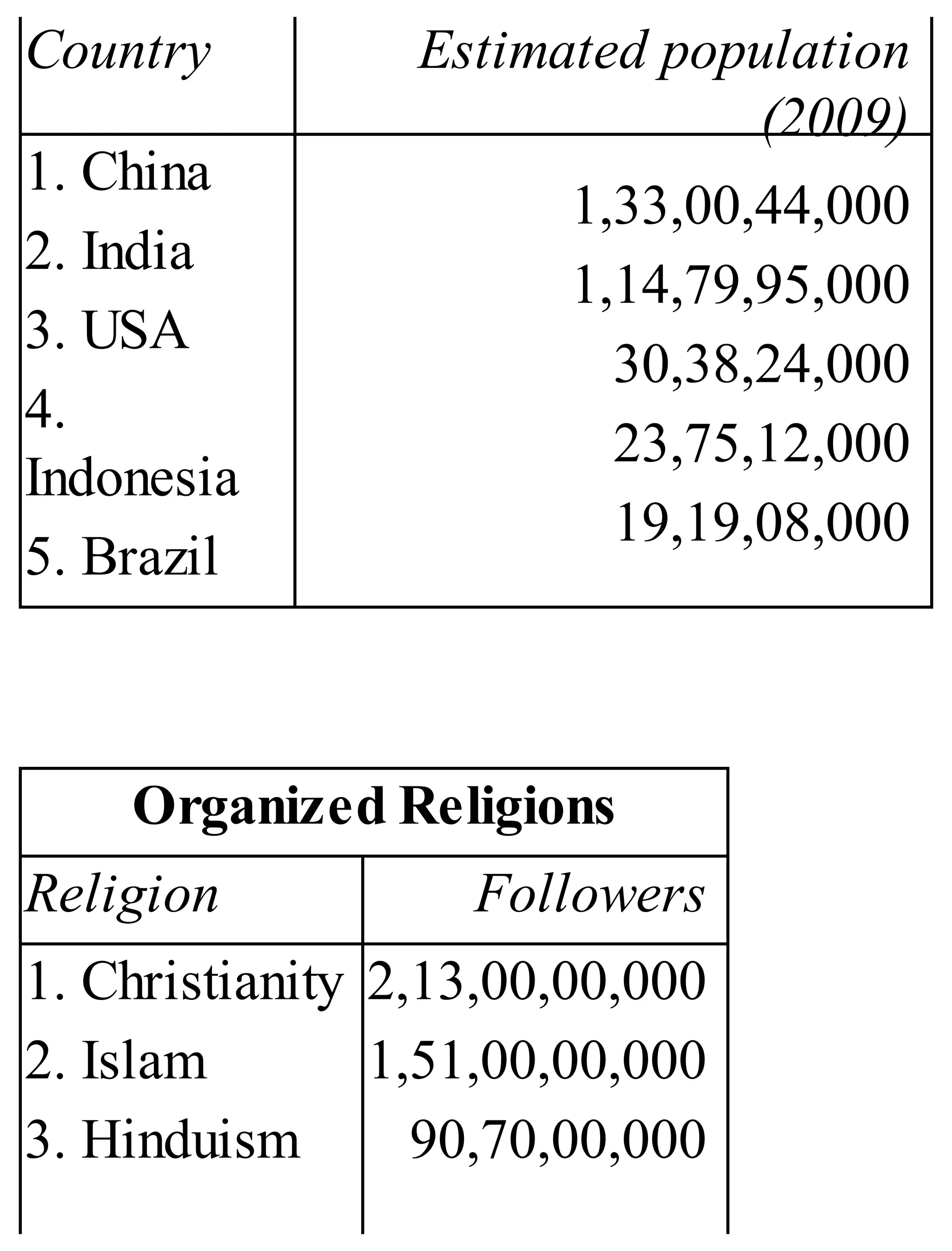
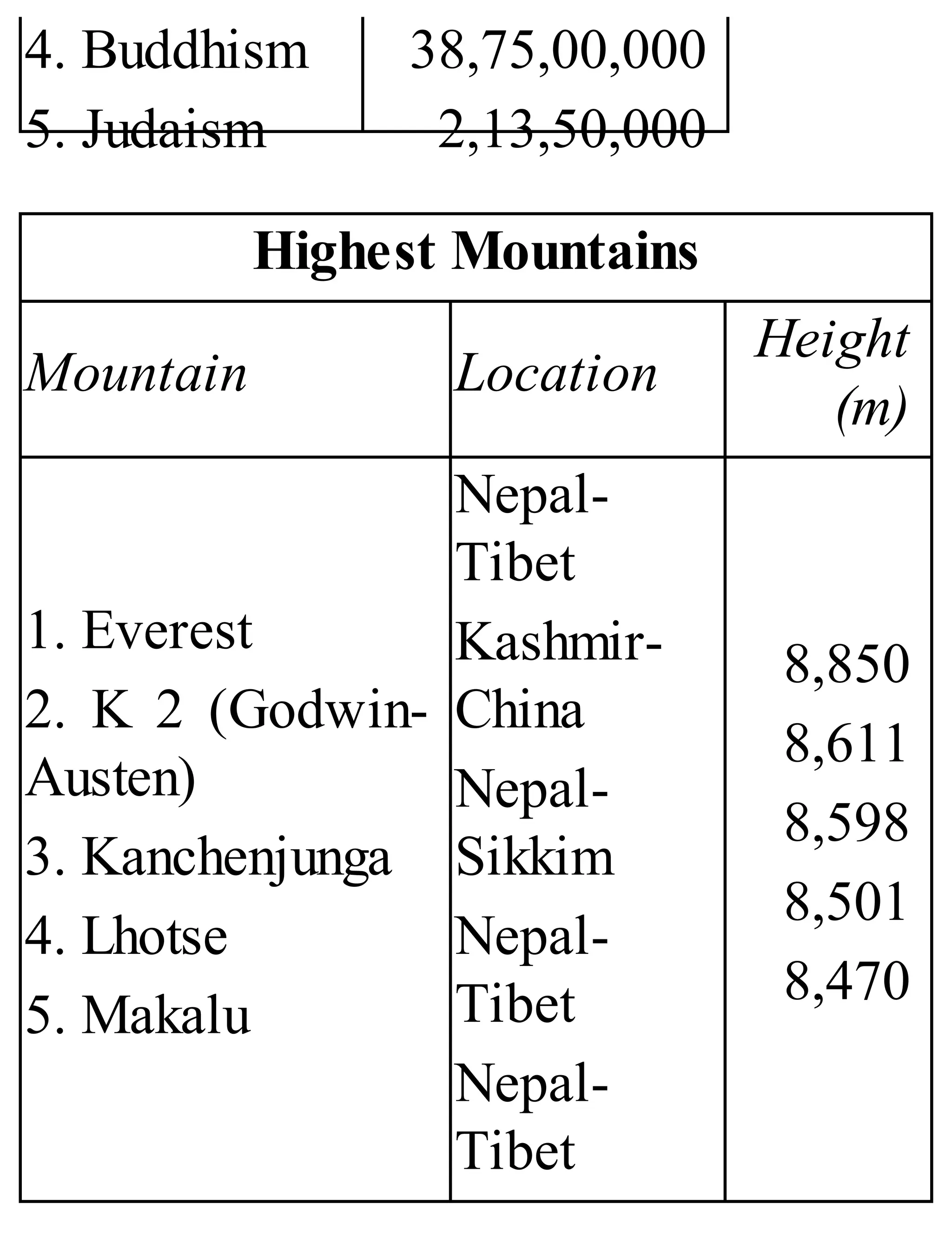
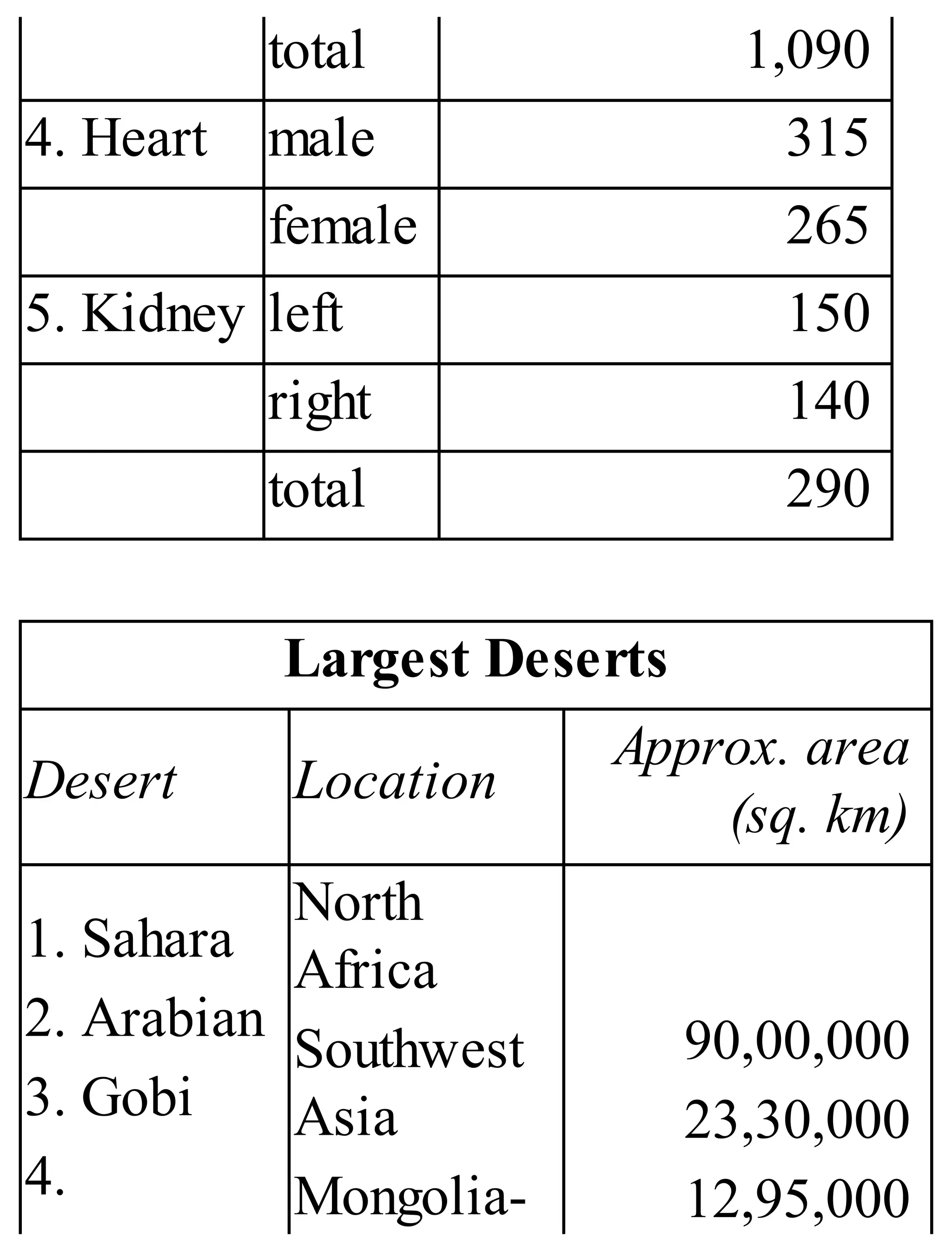
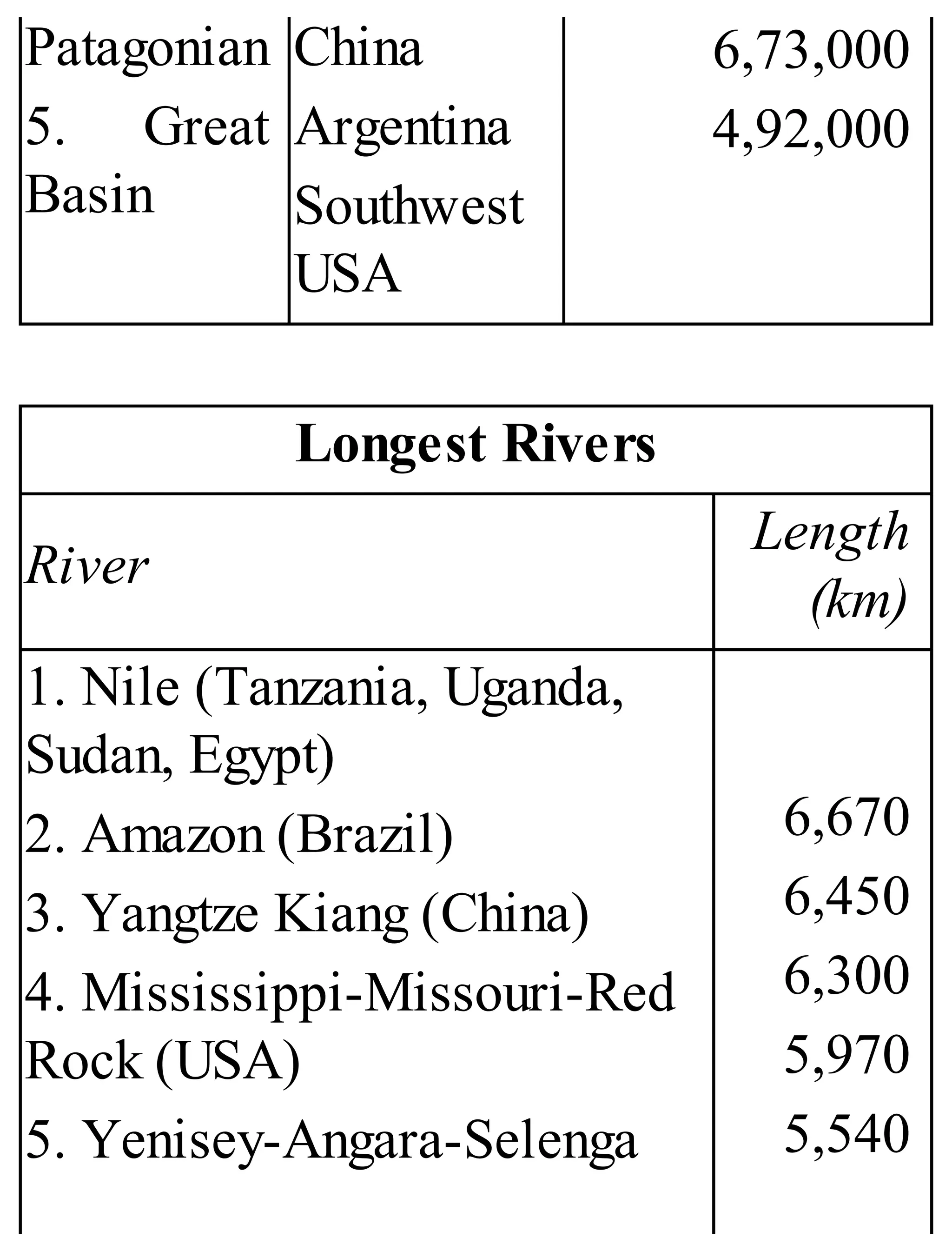
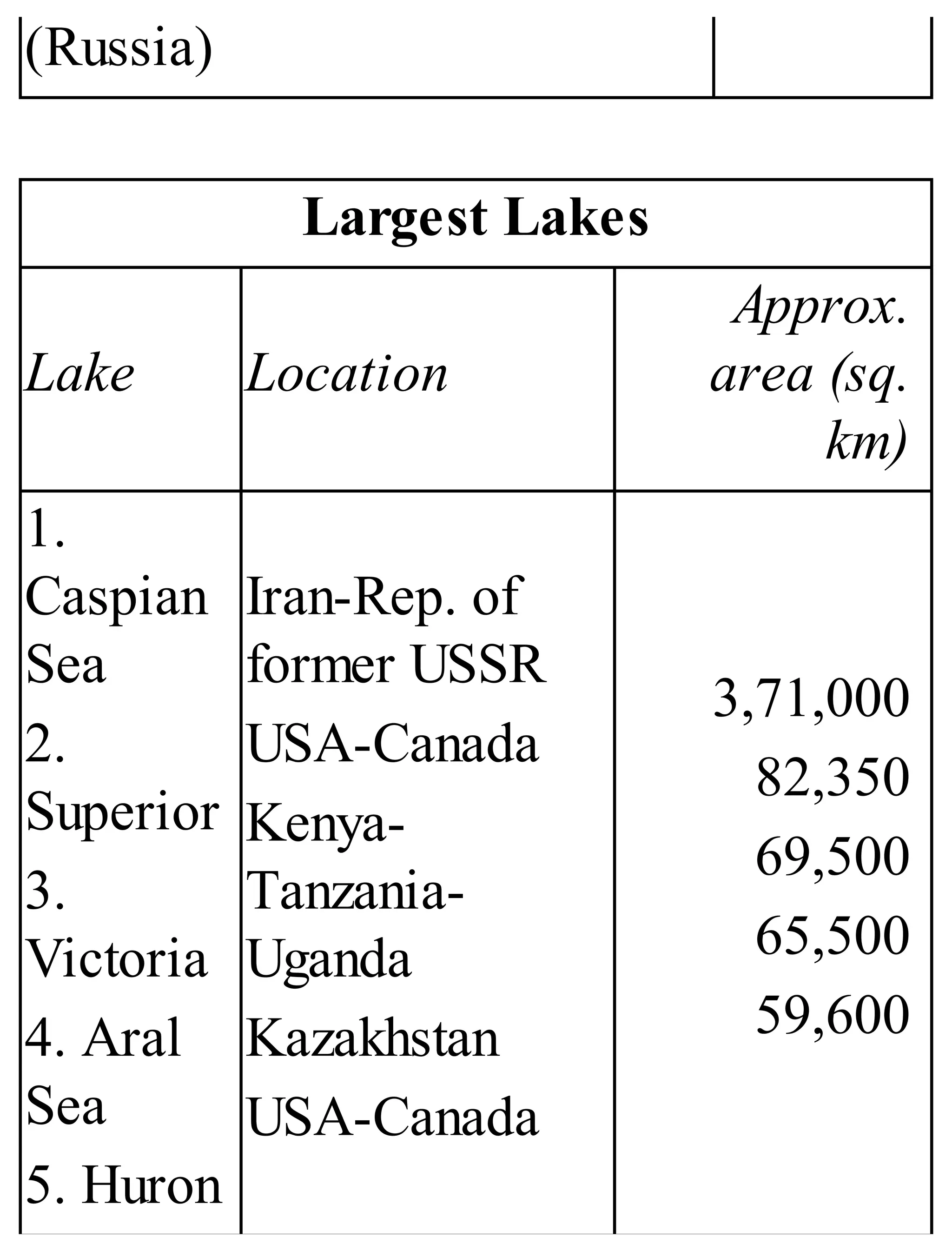
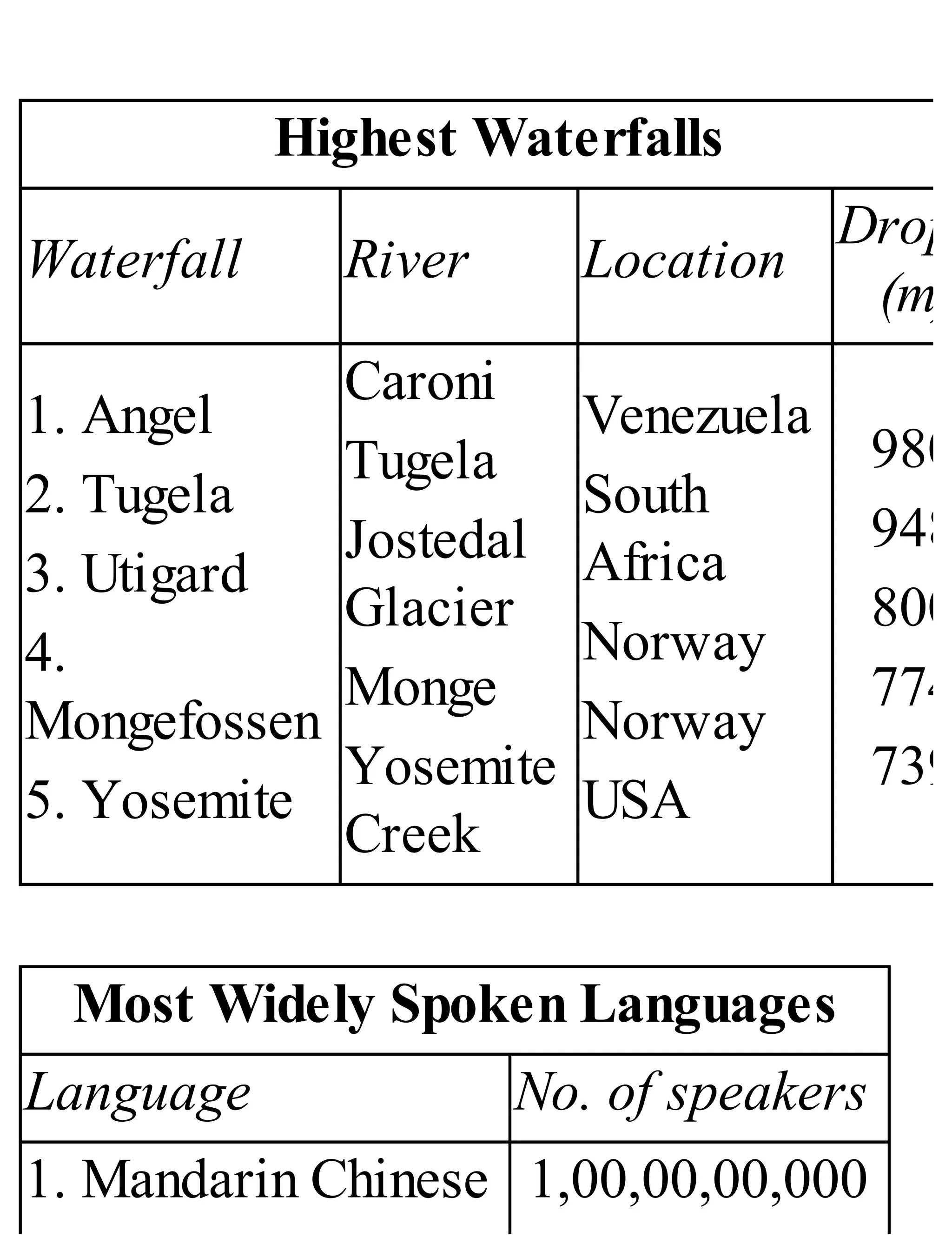
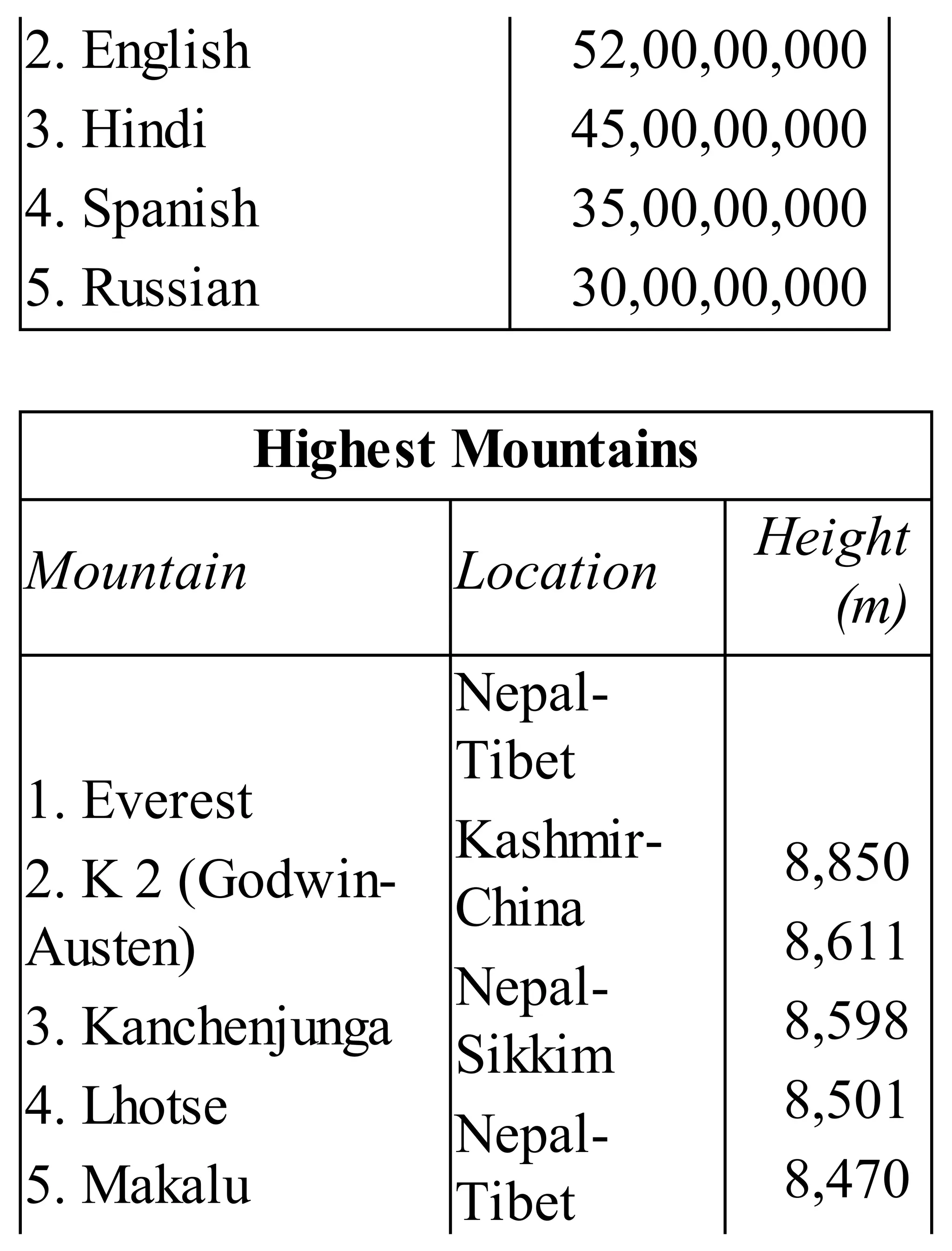
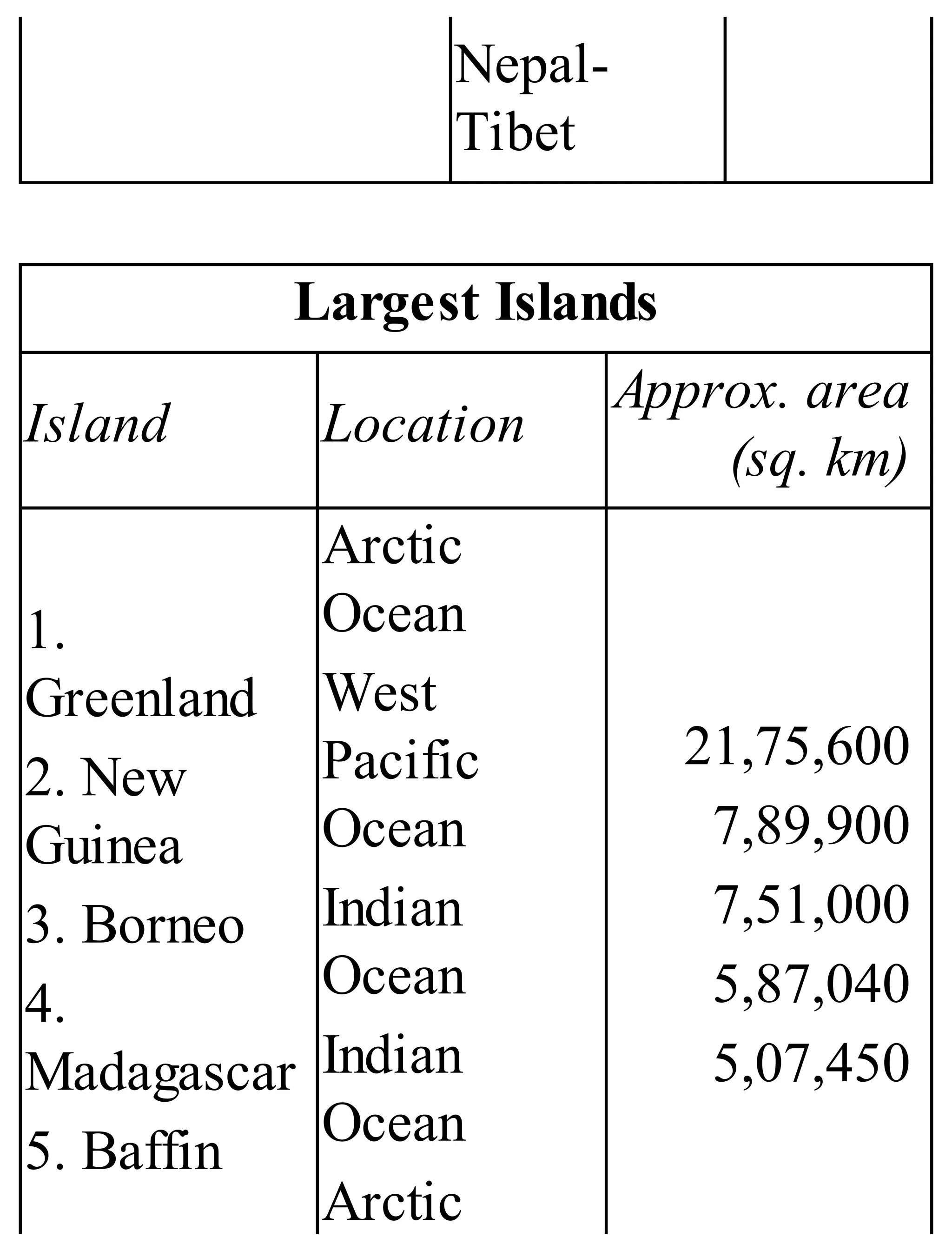
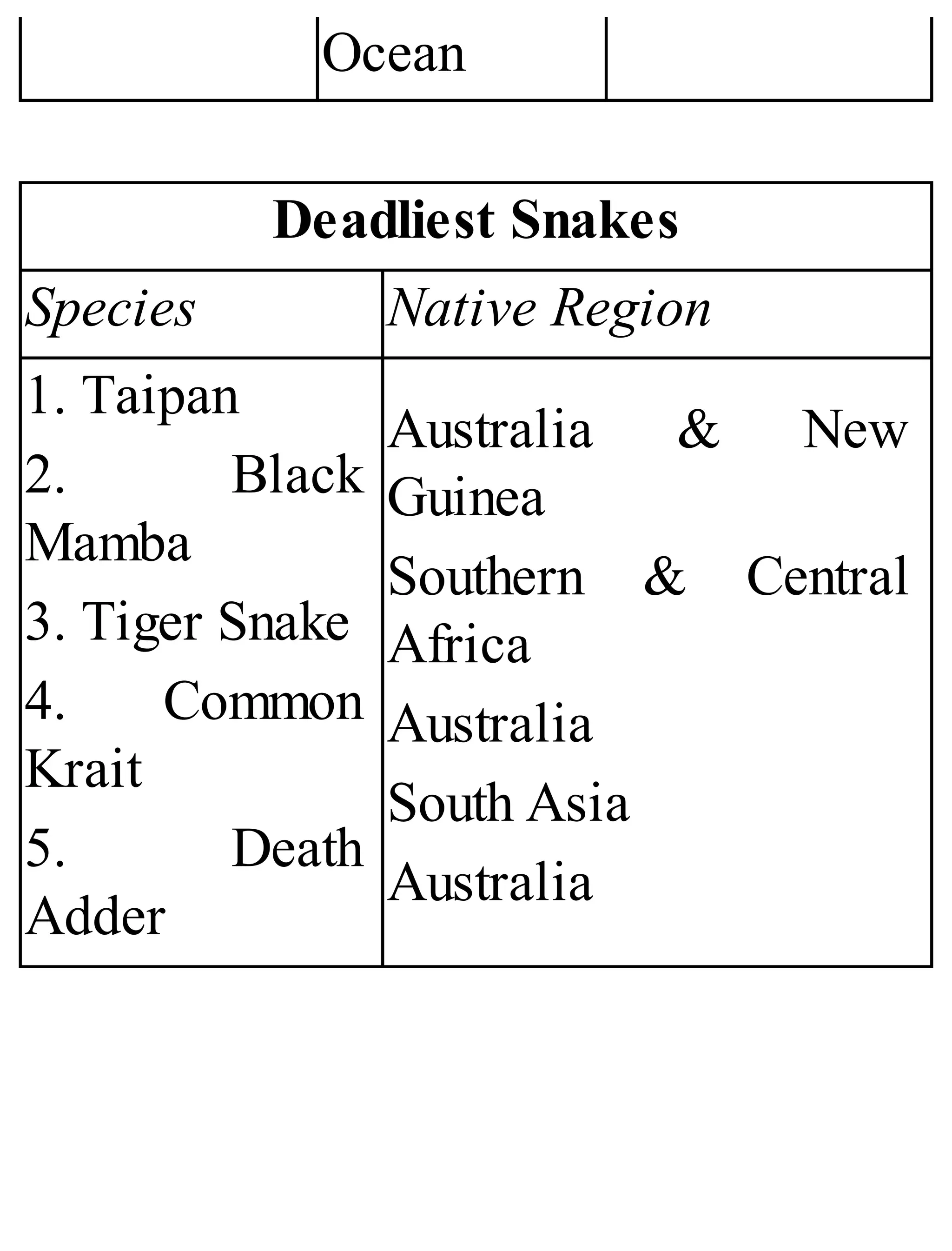
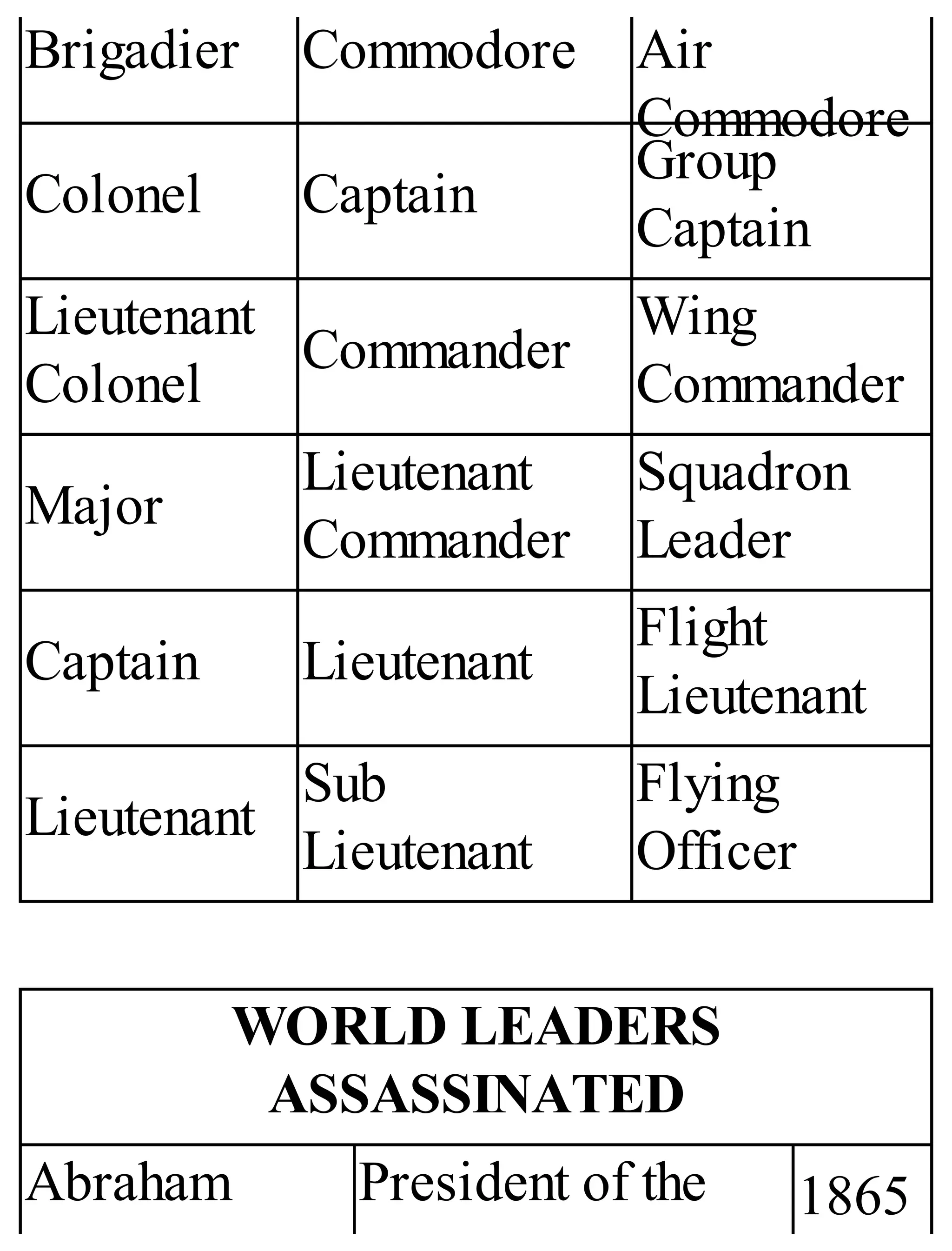
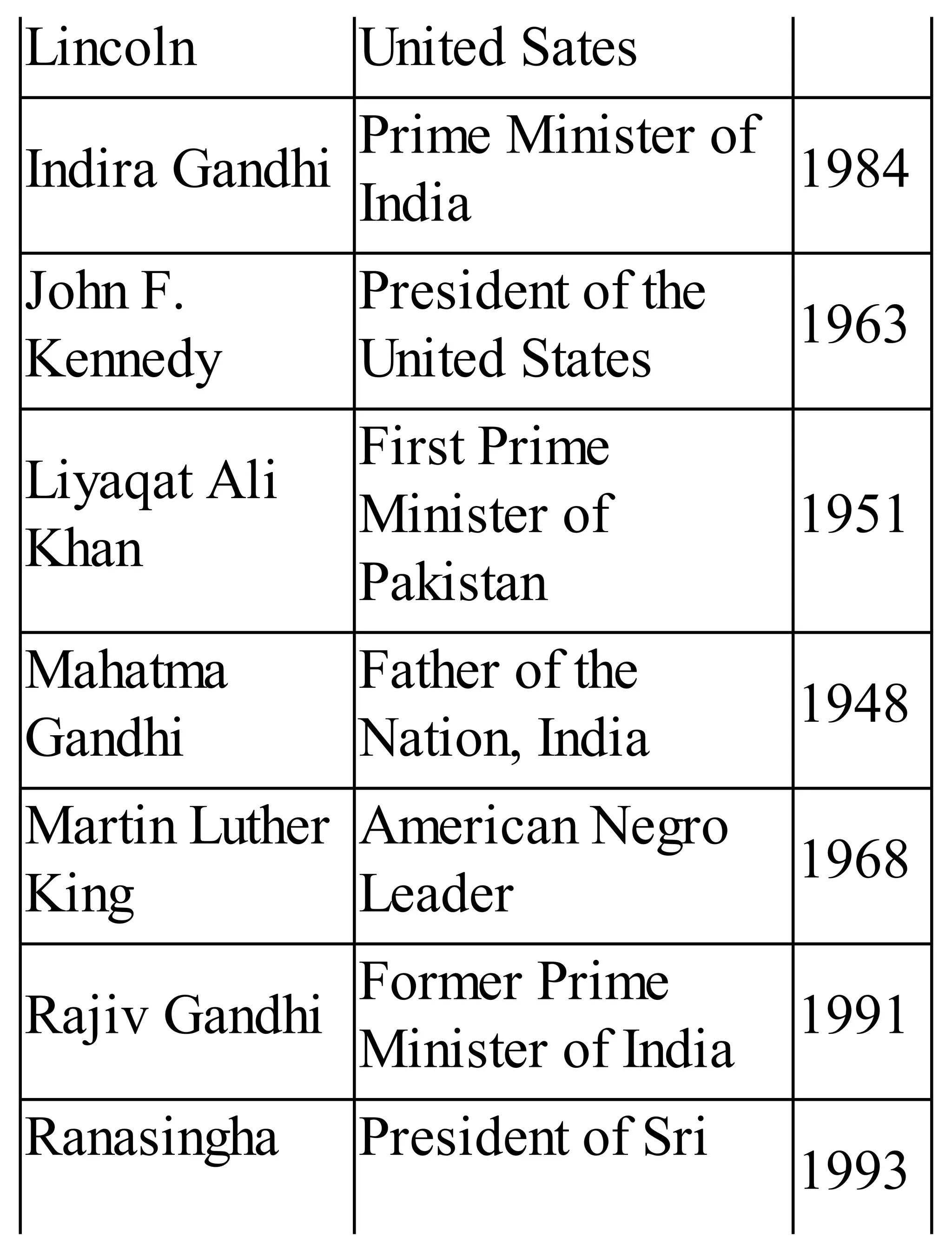
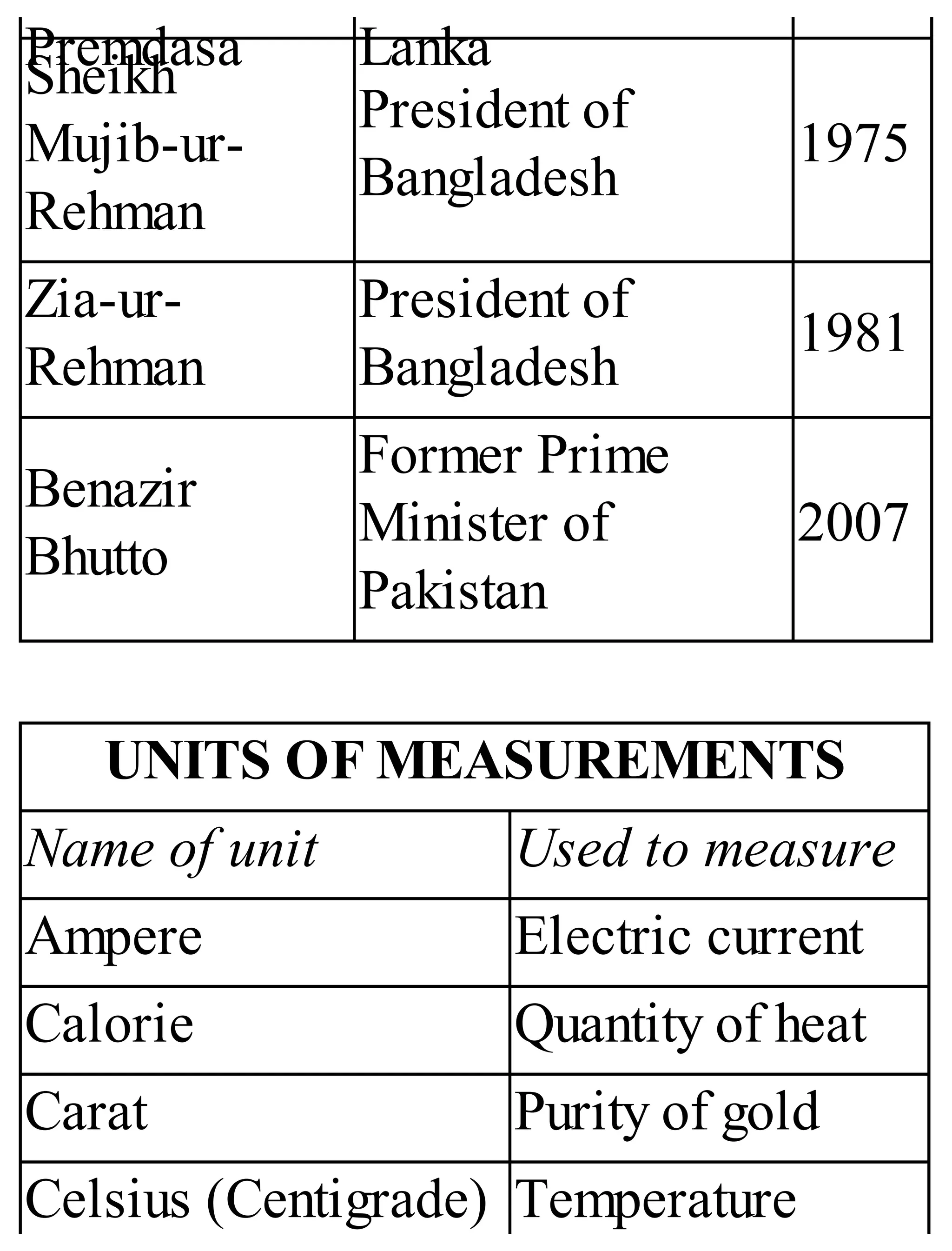
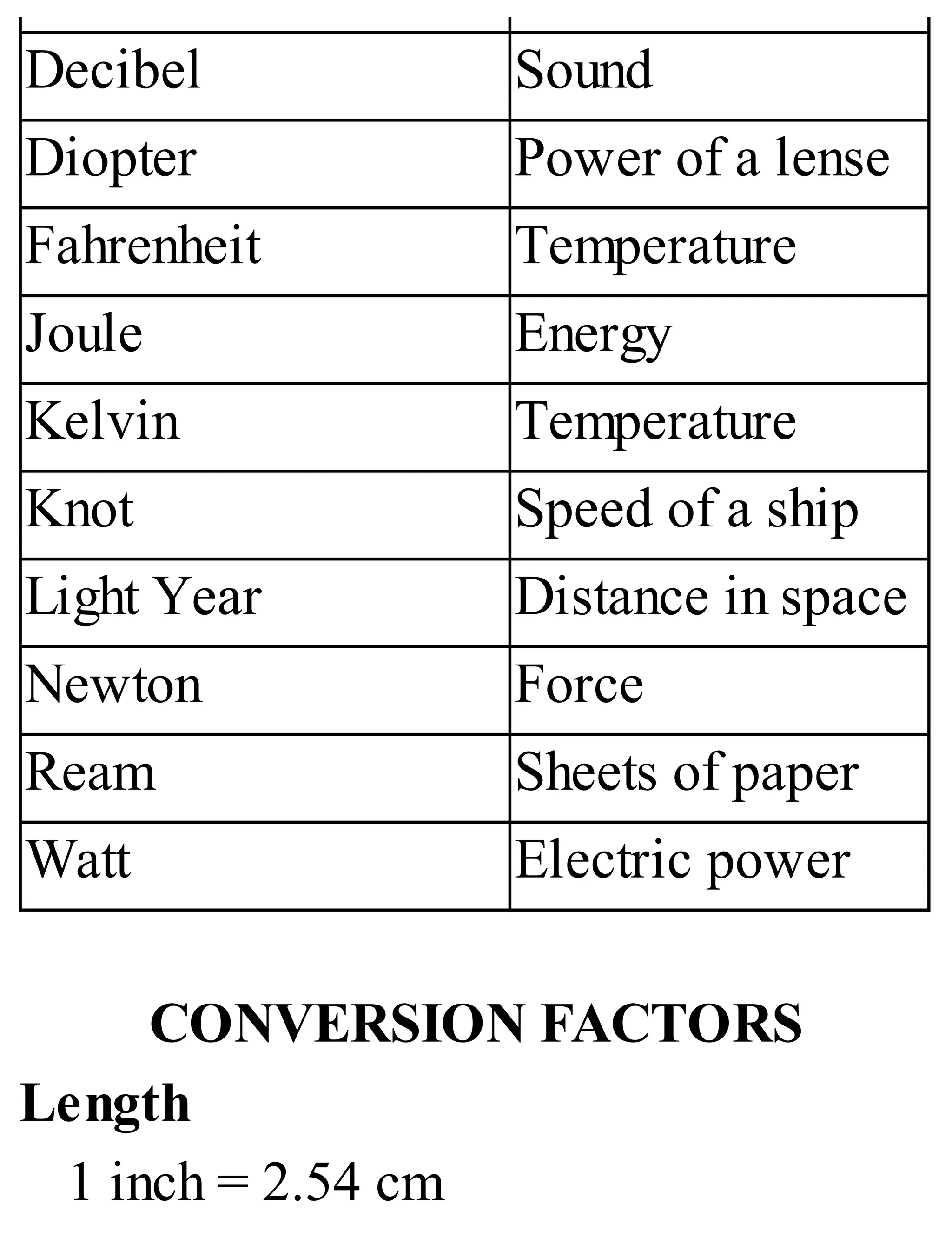
The 'Student’s Encyclopedia of General Knowledge' is a comprehensive reference book aimed at students from classes III to VIII, covering a wide array of topics including history, geography, science, and culture. It offers factual information presented in an engaging manner with illustrations, quizzes, and an alphabetical index for easy access. The book is updated annually to ensure accuracy and relevance, making it a valuable resource for students, teachers, and parents.