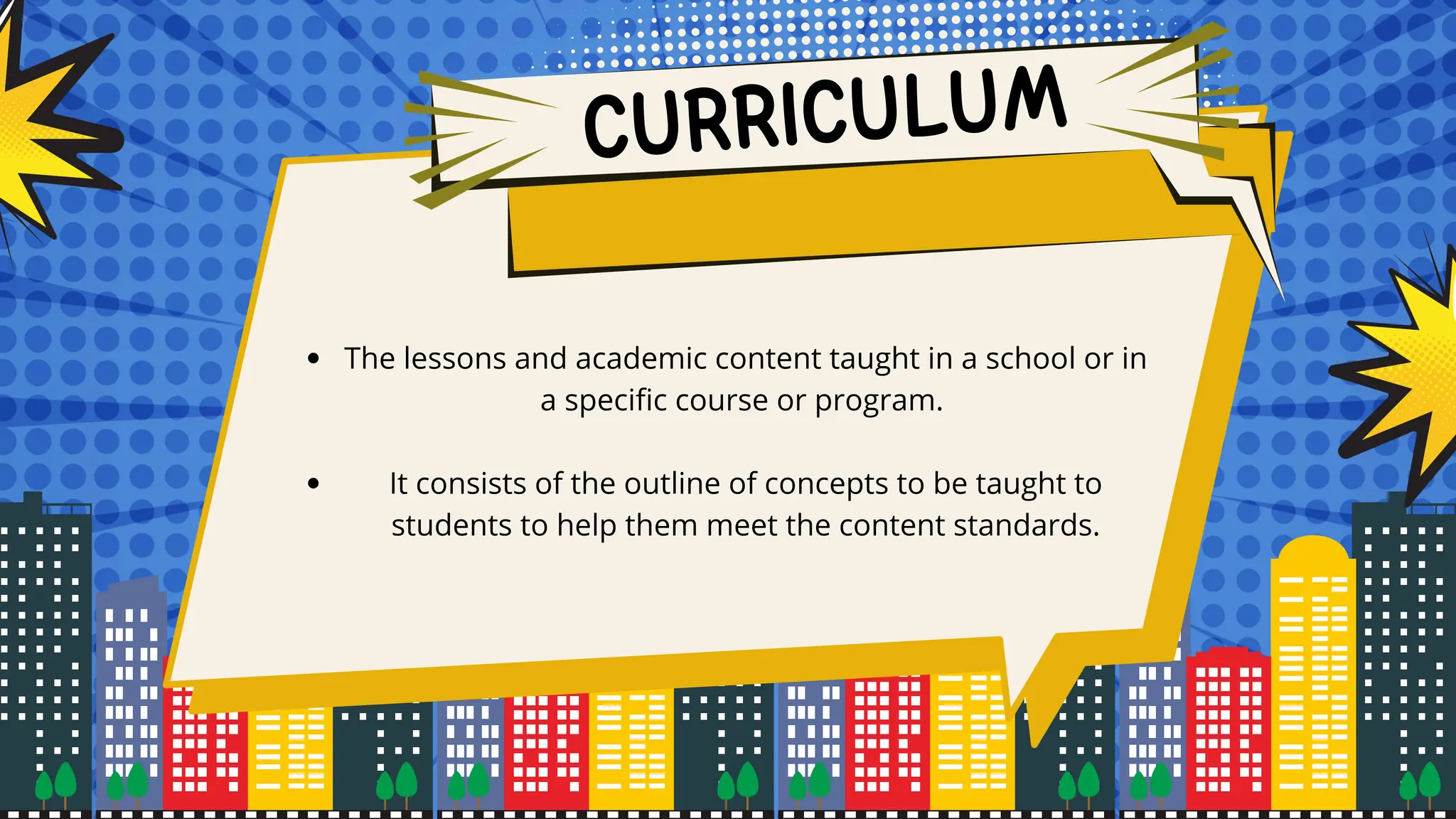
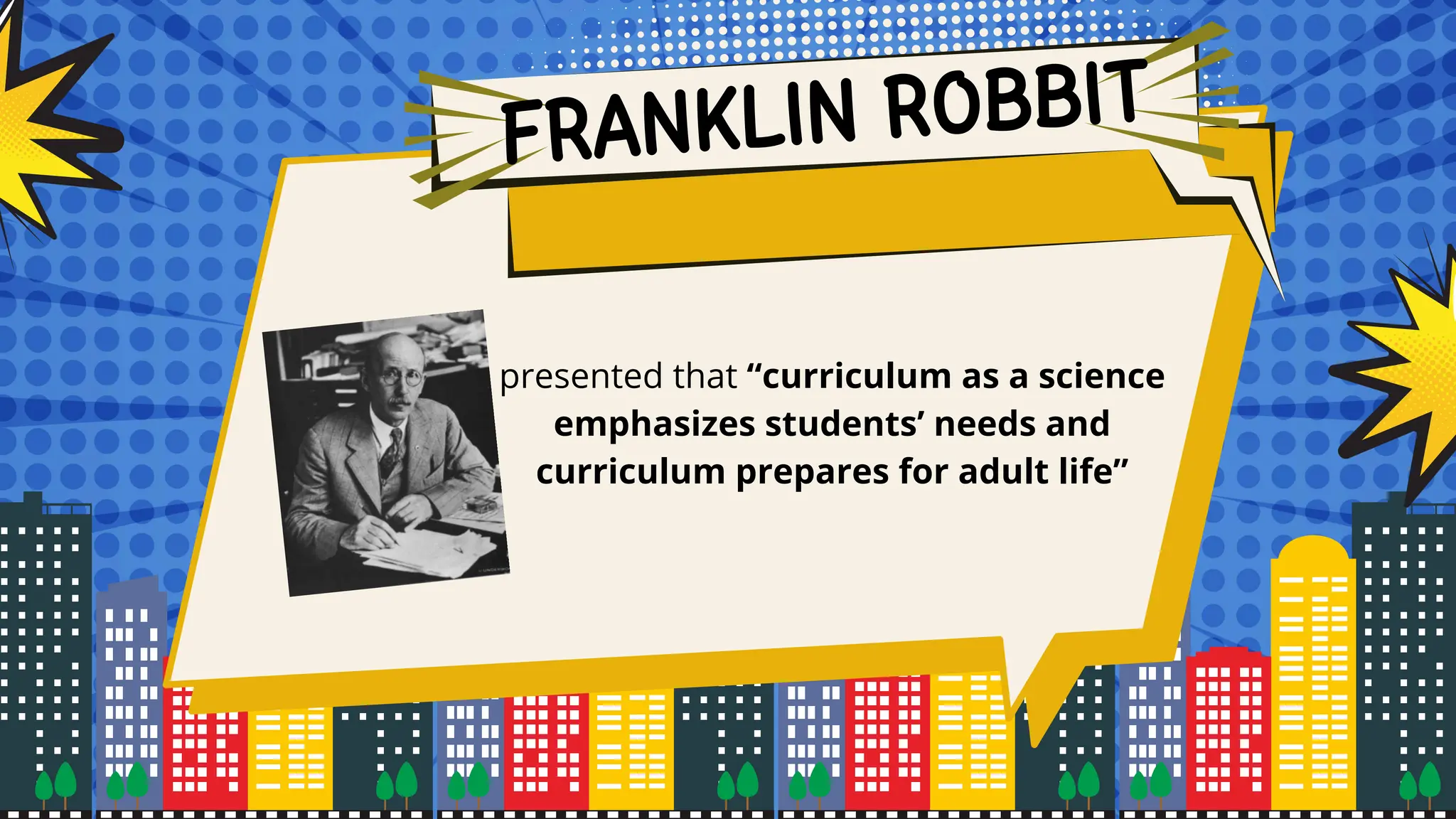
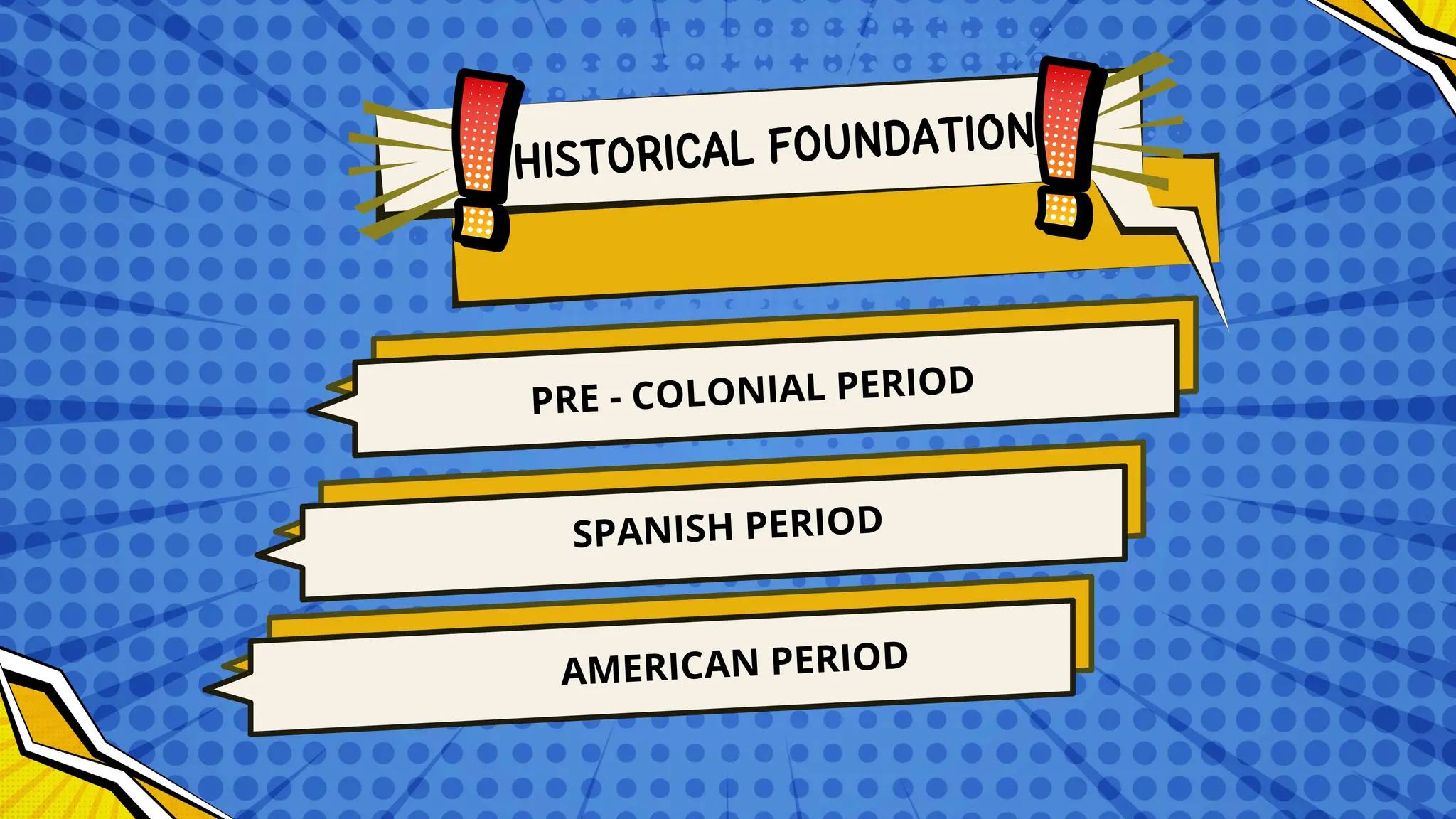
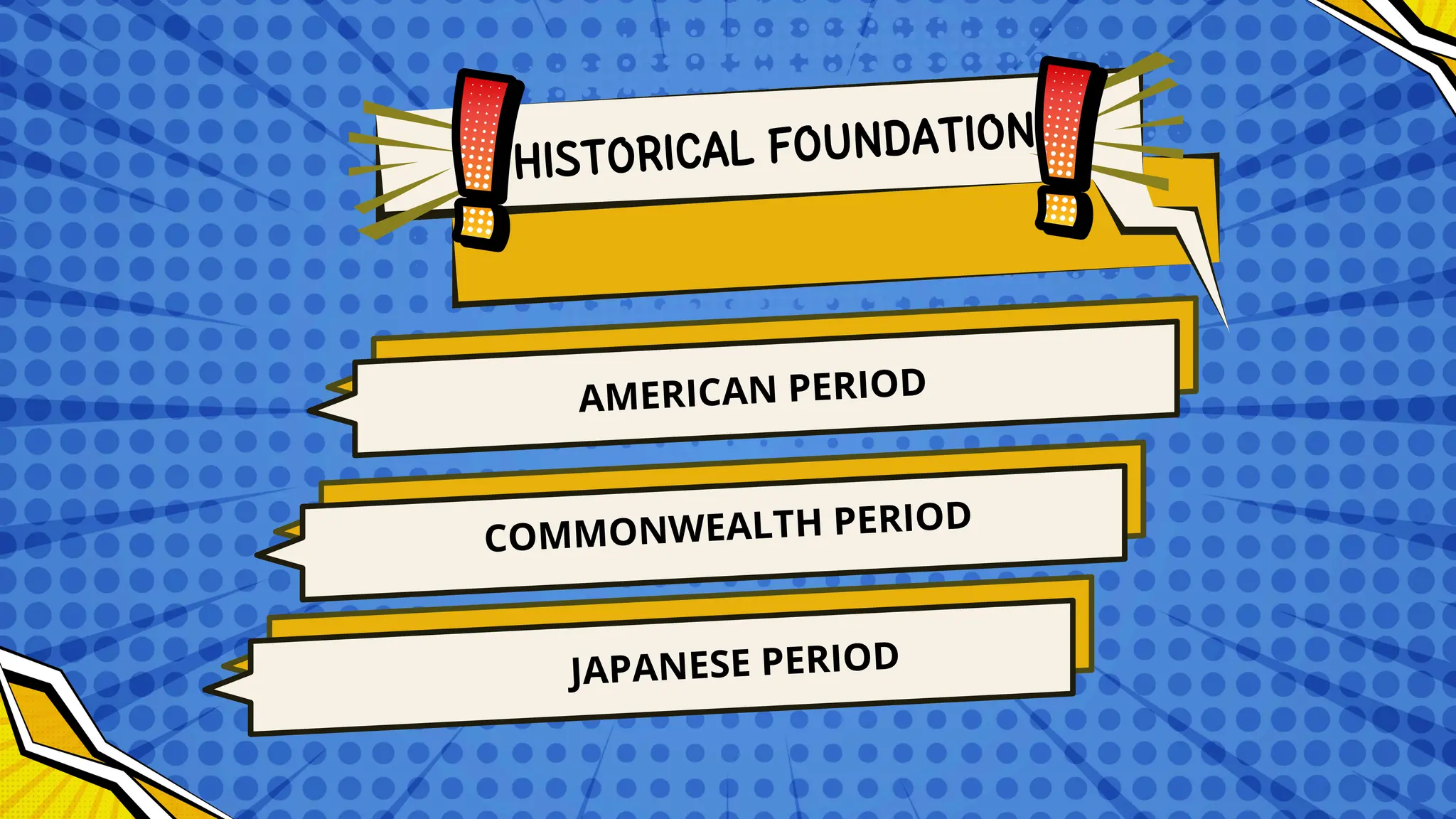
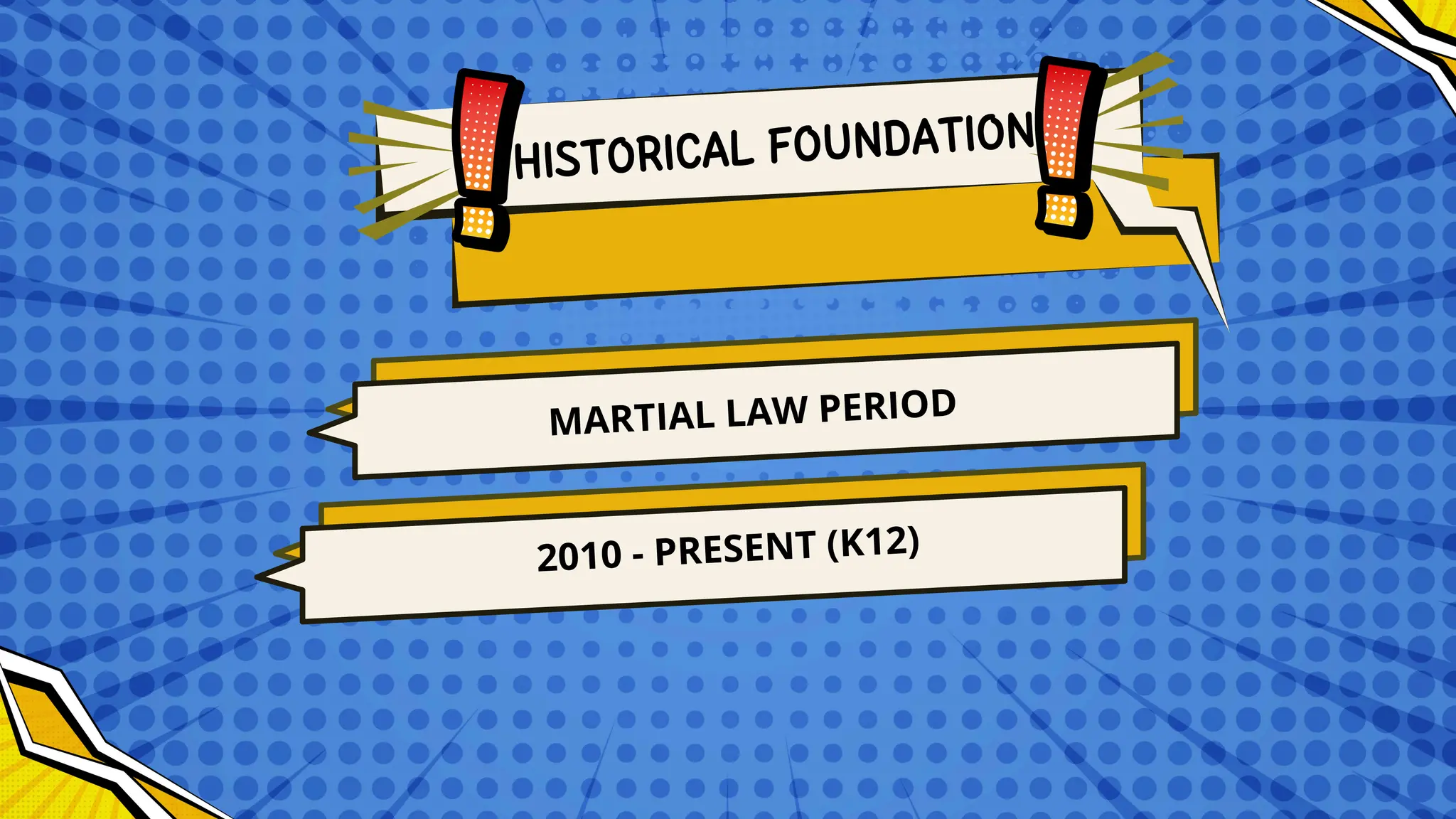
The document discusses the historical and sociological foundations of curriculum, emphasizing its role in education and societal context. It outlines various historical periods influencing curriculum development and asserts the need for curricula to reflect societal culture, respond to changes, and promote educational reform. Additionally, it highlights the importance of incorporating cultural diversity and the dynamic nature of curriculum to meet students' needs and societal demands.